IV.2.2 Qualification of respondent Table2:
qualification of respondent
|
Responses
|
Frequencies
|
Percentage
|
|
No level
|
64
|
22
|
|
With p3
|
58
|
20
|
|
With p6
|
156
|
54
|
|
With s3
|
9
|
3
|
|
With s6
|
3
|
1
|
|
Total
|
290
|
100
|
Source: primary data
In the table2 above, it is clearly evident that the majority
of the respondent, about 54% have a minimum of 6 years in primary school, 22%
have no reached the school, 20% have 3 years in primary, 3% have 3years of
secondary school and 1% have 6years of secondary school. The level of education
assisted to assess the relevancy and reliability of the respondents to
questions. The qualification of respondent in education helped to know which
the group of women likely vulnerable depend on their qualification background
in education.
IV.2.3 Socio-cultural factors that influence HIV
transmission among women.
Regarding on cultural norms there are many social cultural
practices and factors that
can influence in HIV/AIDS transmission among
women. This question was asked to
find out whether there are social cultural
factors or practices that affect women and girls
and the maximum of respondent were agreeing that there are those
social cultural factors.
With giving their attitudes, girls and women are facing with the
responsibilities of being the household and family keeper.
Table2. The social and cultural practices that influence
HIV/AIDS transmission.
|
Responses
|
Frequencies
|
percentage
|
1. marriage
|
200
|
69
|
2. polygamy
|
|
290
|
100
|
|
|
3 .early marriage
|
120
|
41
|
4. multiple sexual partners
|
290
|
100
|
5. female genital cutting
|
160
|
55
|
6. Gender based violence
|
290
|
100
|
7. stigma and taboos
|
290
|
100
|
8. religion
|
180
|
62
|
9. poverty
|
|
290
|
100
|
|
|
10.lack of education and training
|
290
|
100
|
The above table presents the data from different respondents
on what they consider to be the social cultural factors that influence HIV
transmission among women in RWANDA, especially in RUGALIKA sector. What is
clear is that about 100% of the respondents know that polygamy, multiple sexual
partners, Gender based violence, stigma and taboos, poverty and lack of
education and training are the major social cultural practices and norms that
affect women and girls in general. About 69% of
respondent were agreeing that marriage is one of factors that
influence HIV transmission among women, about 41% were agreeing that early
marriage contribute indirectly in HIV transmission, about 55% were agreeing
that female genital cutting (gukuna) is a cultural practice which facilitates
HIV infection among women and about 62% said that religion is also a factor in
HIV transmission among women in RUGALIKA sector.
a) Marriage
After the findings, marriage is not seen by
all respondents as a factor of HIV transmission among women while a great
number is the young women infected with HIV and a number of young women
infected is different from a number of girls infected. And a simple question
can be asked «why the young women are more vulnerable to HIV
infection?». In Rugalika sector about 99 young women are infected in total
of 2990 women aged between 21-35 years old, it means that 3.3% is infected with
HIV; the causes of that HIV infection among young women are various like:
violence against women, stigma, to have multiple sexual partners, unfaithful
for married couple and biologically status (vagina) which facilitate the HIV
transmission to the women than to the men. After the findings found on the
field and with secondary data used in this research, the marriage is taken as a
factor of HIV transmission among women because many of women are more likely
infected by their husband who more cheating their partner (women) and then the
fact that more women have the ability to sell their body in exchange of money
so that they had the ability to feed their family,
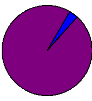
3,3
96,7
women with HIV women without HIV

Fig. 2. Number of women infected with HIV
Source: labo kigese
b) Polygamy
For along time, a Rwandan society has known polygamy as a
cultural value ad until today the polygamy is very practicable even if it is
illegal. Looking at a census done in 2005, shows that 52% are the girls and
women against 48% of the men. And in RUGALIKA sector the girls and women count
about 16349 in total of 24728 of all population, it means that 66.11% is the
girls and women.57
|
70 60 50 40 30
|
|
|
|
|
boys and men
girls and women
|
|
20 10 0
|
|
|
57 .source : labo KIGESE
Fig.3 Percentage of men and women in Rugarika Sector
Source: lab KIGESE
This chart shows us that the polygamy is practicable even if
it is illegal so that 33.8% boys and men satisfy the sexual needs of 66.1% of
the girls and women. Polygamy is indirectly known in RUGALIKA sector, because
of the great number of girls and women who wished to be married and they prefer
to satisfy their sexual needs by having sex with different husband (men), and
this causes that many women are facing with HIV infection than men.
c) Early marriage
It is much known in Rwandan society and in many regions of
Africa to marry a young girl at age of 16 or under. This factor it is not very
known by many respondents as one factor which influences the HIV transmission
among women and girls. Some of them have mentioned it as a latest factor of HIV
infection. And as it has been shown by many researchers, the vulnerability of
girls and young women is due to the immaturity of the vagina and their vagina
liquid which can contain a virus for along time and the contamination of men to
women is 2.4 times to the opposite.58 Early marriage increases the
girls and young women's vulnerability to HIV as they are likely forced to have
sex with their partners sometimes much older than them. In RUGALIKA sector, by
using an interview as one method to collect data, it was discovered that many
young women aged between 21-35 years old have more than 3 children, which means
that they were prematurely pregnant. The act of being married earlier caused to
the girl to be infected with HIV due to the immaturity of vagina.
d) Multiple sexual partners
Logically, multiple sexual partners are a main factor which
increases the spread of HIV infection. Respondents indicated that many young
girls have more than 2 children from different husband (men). This means that
those young girls are more exposed to HIV infection because they have sex with
different partners and without using condom. It is
58 . Le sida au feminin.2001.P14
known that the unfaithful of a couple married is more likely
to be a cause of HIV transmission among the family, which increases the
frequencies of infection among the people.
e) Female genital cutting
It was a cultural value and tradition, after the findings of
this study, some respondent has mention that those cultural practices are not
yet practicable in Rwandan society particularly in RUGALIKA sector but they
added that if it is still practicable in other some parts of the country it can
increase the vulnerability of girls and young women to HIV infection due to
useful of unsterilize instruments.
Those useful of unsterilise materials which easily transmit
the HIV infection to the women. So this cultural factor is known as a factor of
transmission of HIV infection to the girls and young women.
f) Gender based violence
Almost in all societies, they are gender based violence even
if it is done in indirect ways and manners for the married couple. In RUGALIKA
sector, the violence is very common in many families, where the women have no
control over the timing of sexual intercourse. In sexual violence the
vulnerability to HIV infection depends upon the degree of immaturity of vagina
which tears easily during sexual intercourse. In that sector many women are
beaten due to the fact that they refuse to have sex with their husband while it
is known in Rwandan culture that it is a wife's duty to have sex with their
husband because that is the main reason she come together. This shows that the
violence is a key factor of HIV infection to the women.
g) Stigma and taboos
In that sector, a 100% of the respondents were agreeing that
the young women and girls have the low capacity to negotiate the use of condom
with their partners which increase the vulnerability of HIV/AIDS to the women.
The young girls fear that their friends (partners) will end hate them if they
refuse to have sex with them. In Rwandan culture it
is a taboo to tell to the young children about their body,
something related to their sex; those cultural values which are taken as a
taboo influence the HIV infection among young girls because they can not
negotiate and say about the good manner to prevent themselves.
As it is said in a Rwandan proverb «isoni zirisha
uburozi» which means «with stigma a people can eat the poison»
and this proverb show us that a stigma can influence HIV infection to the girls
and women. The fear of being hated by their partners or their boy friends, lack
of access to information, lack of access to productive resources make the girls
and young women to be much vulnerable for HIV infection.
h) Religion
About 62% of all respondents were agreed that some religions
are been considered as a factor of HIV infection; among those religions, there
is Islam like a religion which allows the polygamy but indirectly, and the
protestant which can not allow their Christian to use a condom as one way of
preventing to HIV infection; the religions which are against the condom use
make a serious challenge to preventing the spread of HIV infection. As it has
said by Rwembeho, «every time as a Christian, I hear the church hesitant
to apply all means that would help people from catching the HIV virus,
including use of condoms, I shudder59.
i) Poverty
100% of all respondent put poverty at the first point as a
main factor of HIV infection to the girls and women. Many countries of
sub-Saharan Africa are developing country and poverty is a key factor leading
to expose girls and women of RUGALIKA sector to the risk of HIV infection, the
fact that many girls are orphaned, they are usually exposed to sexual
activities for more surviving and many rich husband known at the nick name of
«sugar daddies» they are often offer money and some materials to the
girls and young women in exchange of having sex; and many girls have preferred
to be at the street and selling their body as their only way of surviving.
59 . the new times .no 1538 .9july2008
j) Lack of education and training
About a 100% of respondents, show that the girls and young
women are more vulnerable to HIV infection because of lack to education and
training and lack of access to productive resources.
Many girls and young women in RUGALIKA sector they are not
aware about the prevention of HIV infection and lack of training to productive
projects and productive activities influence the girls and young women to
prostitution for surviving.
4.3 SUMMARY
This chapter was mainly to report on the findings from the
field on social cultural factors that influence HIV transmission among women in
RWANDA. What emerged from both qualitative and quantitative data gathered shows
that culture, poverty issues, polygamy, lack of access to productive resources,
lack of education and training, and religious beliefs are more influencing all
other factors like political factors, economic factors and physiological
factors in HIV transmission among women in RUGALIKA sector. It was also found
out that a number of measures have been put in place by government and
institutional levels to address the issues of social cultural factors.
CHAPTERV: GENERAL CONCLUSION V.1 GENERAL
CONCLUSION
In most sub-Saharan African countries women and young girls
are more vulnerable to HIV infection because of economic and social
inequalities that diminish women's ability to make choices that promote health
status.
In many instances, girls are forced to drop out of school and
are deprived of their right to basic education; women and young girls are also
subject to pressure to provide for their families.
Girls and Young women are more facing with HIV infection in
sector of RUGALIKA in KAMONYI district where about 2990 women aged between
21-35 years old ;99 women among them have been infected with HIV that means
that 3.3% have HIV infection.60 And that number is at high level in that
sector.
All social cultural factors said in chapter II, are mainly
responsible factors in transmission of HIV infection among women in that sector
and in a whole country in general. As it has shown by all respondent, gender
based violence and poverty are increasingly the most significant risk for HIV
transmission among women, it means that violent sex, poverty are the main cause
in HIV transmission among women, in that sector. Women are biologically facing
with HIV infection, but young women and girls are especially more vulnerable
because their immature genital track are not yet fully developed that is why a
researcher has interested for the group aged between 21-35 years old.
For a long time ago the society has taken the girls as useless
in terms of decision making. Looking at the answers given by the respondents
for all different ages, they argued that the poverty is a key element of HIV
infection for the girls even for the young women, means that poverty and lack
of access to productive resources put them at great risk of sexual
exploitation. After genocide of 1994, Rwanda has known many
60 .source : labo of KIGESE
orphans and in RUGALIKA sector young women and girls who are
orphaned are often to be sexually exploited in order to survive. The church
(religion) has been found on the wrong history during colonialism, recently
during the genocide and so can not afford once again to be on the wrong foot in
the HIV/aids debate. A church is influential and can play a decisive role in
stopping the spread of the HIV infection without it being part of the problem;
the war against the spread of HIV infection can only be won bye the church and
our government working together.
Religion as a social determinant of vulnerability has great
potential for prevention HIV and reducing HIV and AIDS related stigma. Because
of the influence religious leaders have on the community, they can play a
significant role in behaviour change interventions, including the promotion of
condom use, to reduce HIV transmission and de-stigmatized HIV and AIDS.
| 


