C/ Liquidity Risk
Liquidity risk involves the risk of not being able to sell an
instrument or close a position
when required without facing significant costs.
In other words it refers to the possible difficulties in
selling large amounts of assets quickly, in a situation where market conditions
are also unfavorable, resulting in adverse price movements. A highly liquid
portfolio is a necessary constraint in the investment strategy because reserves
need to maintain a high level of liquidity at all times in order to be able to
meet any unforeseen and emergency needs.
D/ Operational Risk
A range of different types of risks, arising from
inadequacies, failures, or nonobservance of internal controls and procedures
that threaten the integrity and operation of business systems[1]. This risk
includes: the risk of the collapse of the internal control systems, risk of
financial mistakes....
3. Evolution and Adequacy of foreign exchange reserves in
Algeria
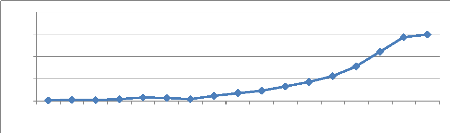
Algeria's foreign exchange reserves have grown (as Figure 1
indicates ) significantly since 1993. The reserves, which stood at US$ 1.5
billion at 1993 increased gradually to US$ 8 billion by 1997. Thereafter, the
reserves declined to US$ 4.4 billion by 1999.The growth continued in the first
half of the 2000s with the reserves touching the level of US$ 18 billion by
2001. Subsequently, the reserves increased to US $ 162.2 billion by 2010.
5
Figure1
Algeria Foreign Exchange Reserves1993-2010 (US $
billions)
200
150
100
50
0
1993 1994 1995 1996 1997 1998 1999 2000 2001 2002 2003 2004 2005
2006 2007 2008 2009
Source: Bank of Algeria.
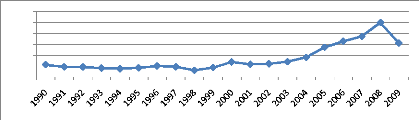
Algeria's foreign exchange reserves vigorous growth has been
driven by higher hydrocarbon production, and record-high oil prices, especially
since2000 (see figure2). The Algerian crude oil export unit value which was
22.6 US$/barrel in 1990, increased to 27.6 US$/barrel in2000, Thereafter the
oil price touching the level of100 US$/barrel in 2008.
Figure 2
Algerian crude oil export unit value (1990-2010)
(US$/barrel)
120
100
40
80
60
20
0
Source : International Financial statistics, IMF.
3.2. Adequacy of Reserves in Algeria
To make sure that the current levels of international reserves
are still comfortable and safe, there are four applicable measures for
assessing the adequacy of reserves [4] : - The traditional measure of import
covers of reserves. The optimal level is about three
months at least.
- The ratio of money supply to the foreign
exchange reserves. The optimal level is at least 20%.
- The ratio of short-term debt to the foreign exchange
reserves. The optimal level is at least 150%.
6
- Foreign exchange reserves should exceed at least the
non-resident deposits in foreign currencies, in the banking system.
This section provides a complete assessment of these measures in
the context of the Algerian economy.
3.2.1. Import Cover of Reserves
Table 1
Algeria's Import Cover of Reserves (1993-2009)
|
Years
|
Foreign Reserves (US $ billion)
|
Months of Imports
|
|
1993
|
1.5
|
1.9
|
|
1994
|
2.6
|
2.9
|
|
1995
|
2.1
|
2.1
|
|
1996
|
4.2
|
4.5
|
|
1997
|
8
|
9.4
|
|
1998
|
6.8
|
7.6
|
|
1999
|
4.4
|
4.6
|
|
2000
|
11.9
|
12
|
|
2001
|
18
|
14.9
|
|
2002
|
23.1
|
17
|
|
2003
|
32.9
|
18.1
|
|
2004
|
43.1
|
19
|
|
2005
|
56.2
|
26.5
|
|
2006
|
77.8
|
28
|
|
2007
|
110.2
|
27.4
|
|
2008
|
143.1
|
35.2
|
|
2009
|
148.9
|
36.4
|
Source: international Financial statistics, IMF.
The table 1 show that the import cover of reserves indicator,
which fell to a low of three months of imports at 1993, rose to 12 months of
imports at 2000, and increased further to 36.4 months of imports (or about
three years) at 2009.
7
It is clear that record-high oil prices have translated into huge
foreign reserves especially since 2000 .So , Algeria foreign exchange reserves
are in a very comfortable level in comparison to the optimal limit (three
months at least).
3.2.2. The Ratio of Money Supply to the Foreign Exchange
Reserves Table 2
The Ratio of Money Supply to the Foreign Exchange Reserves
(1993-2009)
|
Years
|
Foreign Reserves
(US $ billion) (1)
|
M2
(DZD billion) (2)
|
The exchange rate
(DZD/USD)
(3)
|
M2
(US $ billion)
(4)
|
The ratio
(1/4)
|
|
1993
|
1.5
|
625.2
|
23.36
|
26.76
|
0.05
|
|
1994
|
2.6
|
723.5
|
35.09
|
20.61
|
0.12
|
|
1995
|
2.1
|
799.5
|
47.68
|
16.76
|
0.12
|
|
1996
|
4.2
|
915.1
|
54.77
|
16.76
|
0.25
|
|
1997
|
8
|
1081.5
|
57.73
|
18.73
|
0.42
|
|
1998
|
6.8
|
1287.9
|
58.74
|
21.92
|
0.31
|
|
1999
|
4.4
|
1789.4
|
66.5
|
26.9
|
0.16
|
|
2000
|
11.9
|
2025.1
|
75.3
|
26.89
|
0.44
|
|
2001
|
18
|
2475.2
|
77.2
|
32.06
|
0.56
|
|
2002
|
23.1
|
2905.8
|
79.7
|
36.45
|
0.63
|
|
2003
|
32.9
|
3357.9
|
77.4
|
43.38
|
0.75
|
|
2004
|
43.1
|
3742.5
|
72.1
|
51.9
|
0.83
|
|
2005
|
56.2
|
4142.4
|
73.4
|
56.43
|
0.99
|
|
2006
|
77.8
|
4933.7
|
73.7
|
66.94
|
1.16
|
|
2007
|
110.2
|
5994.6
|
69.2
|
86.62
|
1.27
|
|
2008
|
143.1
|
6955.9
|
64.6
|
107.67
|
1.32
|
|
2009
|
148.9
|
7173.1
|
72.5
|
98.93
|
1.50
|
Source: author's calculations using data available from
bank of Algeria statistics.
The Data from the table above Indicate that the ratio of money
supply to the foreign exchange reserves increased slightly from 5 per cent at
1993 to 99 per cent as at 2005, the
8
ratio further increased to 150 per cent at the end of
2009.This results show clearly that the current foreign reserves level exceed
the international standards for this indicator (at least 20%).
3.2..3. The Ratio of Short-Term Debt to the Foreign
Exchange Reserves Table 3
The Ratio of Short-Term Debt to the Foreign Exchange Reserves
(1996-2009)
|
Years
|
Foreign Reserves
(US $ billion) (1)
|
Short-Term Debt
(US $ billion) (2)
|
The Ratio
(1/2)
|
|
1996
|
4.2
|
0.328
|
12.8
|
|
1997
|
8
|
0.162
|
49.38
|
|
1998
|
6.8
|
0.186
|
36.55
|
|
1999
|
4.4
|
0.195
|
22.56
|
|
2000
|
11.9
|
0.222
|
53.60
|
|
2001
|
18
|
0.199
|
90.45
|
|
2002
|
23.1
|
0.108
|
213.88
|
|
2003
|
32.9
|
0.146
|
225.34
|
|
2004
|
43.1
|
0.410
|
105.12
|
|
2005
|
56.2
|
0.707
|
79.49
|
|
2006
|
77.8
|
0.550
|
141.45
|
|
2007
|
110.2
|
0.717
|
153.7
|
|
2008
|
143.1
|
1.304
|
109.73
|
|
2009
|
148.9
|
1.492
|
99.8
|
Source: author's calculations using data available from
bank of Algeria statistics.
The table 3 show that t the ratio of short-term debt to the
foreign exchange reserves increased from 1280 per cent at 1996 to 22534 per
cent at 2003.later, the ratio decline to 9980 per cent as at 2009.
The table above indicates that this indicator has exceeded the
optimal level in accordance with international standards which is 150%.This
means that foreign exchange reserves in Algeria allow enough cover to its short
external debt and insure its safety and financial solvency.
9
| 


