2.2 OPTICAL FIBER CABLE
To guide signals carrying information from a transmitter to a
receiver, the technique of telecommunications uses primarily two means such
as:
> Material support between the transmitter and the receiver;
> Transmission by radio waves.
Among the transmission material medium, best adapted for
significant traffics to high flow is the optical fiber; this is why, this
chapter is devoted to the meticulous treatment of this transmission
resource.
2.2.1 Definition
Fiber optics are long, thin strands of very pure glass about
the diameter of a human hair, They are arranged in bundles called optical
cables and used to transmit light signals over long distances that light
contains information which are being transmitted, the basic structure of an
optical fiber consists of three parts; the core, the cladding, and the coating
or buffer. The core is a cylindrical rod of dielectric material, Dielectric
material conducts no electricity, Light propagates mainly along the core of the
fiber, The core is generally made of glass, the core is described as having a
radius and an index of refraction. The core is surrounded by a layer of
material called the cladding, even though light will propagate along the fiber
core without the layer of cladding material, the cladding does perform some
necessary functions.[6]
The following picture shows the basic structure of the optic
fiber
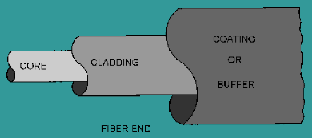
Figure 3 : Basic structure of an optical fiber
9
The cladding layer is made of a dielectric material with an
index of refraction; the index of refraction of the cladding material is less
than that of the core material. The cladding is generally made of glass or
plastic, the cladding performs the following functions it Reduces loss of light
from the core into the surrounding air, reduces scattering loss at the surface
of the core ,Protects the fiber from absorbing surface contaminants
For extra protection, the cladding is enclosed in an
additional layer called the coating or buffer. The coating or buffer is a layer
of material used to protect an optical fiber from physical damage, the material
used for a buffer is a type of plastic. [6]
2.2.2 Principle of optical transmission.
The fiber carries a signal encoded beam of light by virtue of
total internal reflection (TIR). TIR occurs at the interface of a transparent
medium with another medium, if the transparent medium has a higher index of
refraction than the surrounding medium, TIR occurs. This makes the optical
fiber a waveguide for frequencies in the range 1014 to
1015 Hz, covering the visible and part of the Infrared spectrum
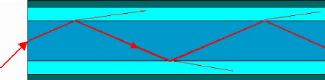
Figure 4 : Principle of optical transmission
The figure above illustrate the principle of total internal
reflection as used in fiber optical communications, Total internal reflection
is an optical phenomenon that happens when a ray of light strikes a medium
boundary at an angle larger than a particular critical angle with respect to
the normal to the surface. If the refractive index is lower on the other side
of the boundary, no light can pass through and all of the light is reflected.
The critical angle is the angle of incidence above which the total internal
reflection occurs.
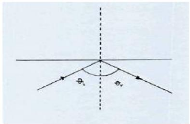
Figure 5: Total internal reflection
So the critical angle is defined as the angle of incidence that
provides an angle of refraction of 90-degrees.
Let's consider two different media creatively named medium i
(incident medium) and medium r (refractive medium). The critical angle is the
èi that gives a èr value of 90-degrees. If this
information is substituted into Snell's Law equation, a generic equation for
predicting the critical angle can be derived. The derivation is shown
below.[7]
ni
· sine(èi) = nr
· sine
(èr) (2.2)
when èr=900
ni
· sine(ècrit) = nr
· sine
(90 degrees) (2.3)
ni
· sine(ècrit) = nr
sine(ècrit) = nr/ni
ècrit = sine-1 (nr /ni) = arcsin
(nr/ni) (2.4)
Two stages transducers thus should be added (the equipment
intended to convert the signals), one at the beginning, to ensure conversion
electricity/light; the other on arrival for opposite conversion. In the first
case, it is about a laser diode or LED diode ; in the second a photo diode.
By convention, an impulse of light indicates a bit to 1 and
the absence of light to 0, But as any ray whose incidence reaches the critical
angle undergoes an internal reflection, many rays are propagated under various
angles in optical fiber. it is said that each one has a different mode a fiber
presenting this property is thus called fiber multimode.[8]
However, if the diameter of fiber is tiny in proportions such
as only one luminous ray can there be propagated, then the fiber acts like a
guide of waves and the light can be propagated only in straight line without
reflection is called a monomode fiber, it is more expensive than fiber
multimode but is largely used at longer distances because it transmit data to
50 Gbit/s out of 100 km without amplification.
| 


