4.1.2.6 Gendered Perceptions of Foreign aid and
dependency
Figure 4.3:
The study findings reveal that a majority of respondents (52%)
indicated that Foreign Aid leads to dependency syndrome on the part of the
Rwanda Government. The remainder 48% felt people use the Aid for sustainable
development activities. These positions reflect earlier perceptions which have
been attributed to varying levels of literacy and cognitive sophistication.
However, there were more females (56%) compared to 50% males who indicated that
there is no
correlation between donor aid and consumer dependency and this
again buttresses the earlier observation as more women are generally less
literate than their male counterparts, especially in third world countries such
as Rwanda. These varying levels of literacy were again reflected in the
participants? awareness of Millennium Development Goals (MDGs). This
corroborates findings by UNDP (2007) who assert that the issue of poverty has
some multiple interpretations; hence the so-called gendered nature or
feminisation of poverty and aid too.
4.1.2.7 Knowledge of the existence of MDGs in
Rwanda
Figure 4.4:
The survey results show that the majority of the respondents
(96%) were aware of the MDGs in
85
Rwanda and nearly all of them had learnt from the Government?s
sensitization and mobilization programs (publications) and open public
discussions on the country?s Vision 2020. On the other hand, a very strong link
(85%) between the Rwanda?s ruling class political ideology and MDGs exists. The
ruling class political ideology of Rwanda has programs and strategies such as
Economic Development and Poverty Reduction Strategy (EDPRS) and Vision 2020 to
address MDGs. It was therefore necessary to find out more about the
participants? awareness of MDGs
by asking them to rank them according to their own priorities.
It can therefore be concluded that the instrumental role of MDGs as a weapon to
fight poverty is overlooked hence the need to acquaint people with critical
issues regarding this concept.
4.1.2.8 Ranking of MDGs according to priority
Figure 4.5:
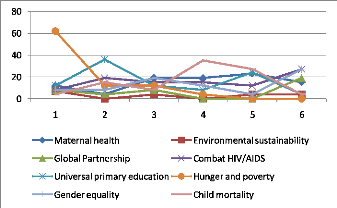
The study findings indicate that of all the MDGs Rwanda is
prioritizing the eradication of extreme poverty and hunger most with a number
one ranking. A lot of effort is also being put in trying to improve maternal
health and combating HIV/AIDS, malaria and other diseases in order of priority,
respectively. Findings also revealed that the Rwandan Government is trying to
achieve universal primary education for all its citizens as its fourth
priority. However issues of gender equality, empowerment of women and global
partnership still need greater articulation.
h
This was supported by data from FGD were one respondent
echoed:
Global Parnership Combat HIV/AIDS
Genr qy
«The issue of eradication poverty and extreme hunger has
become a universal priority across all d ty
nations in Third world.»
Based on this, it can be interpreted that the issue of
prioritising MDG 1 may seem to go along the assumptions of modernisation
theorists who insist «in order to develop, third world nations must copy
western models of development (Sanderson, 1991)
4.1.2.9 Rating of Poverty Eradication
Strategies
Figure 4.6:
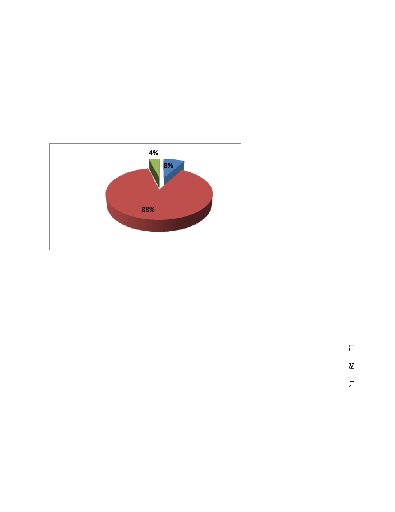
The study findings of the above pie-chart reveal fact that
EDPRS is mostly used in Rwanda as a
strategy to eradicate poverty. Based on
the findings, it can be argued that strategies as means to
an end are always critical in as far as eradicating of poverty is
concerned, thus without user-8%
friendly strategies poverty cannot be ameliorated. The
Economic Development and Poverty Reduction Strategy (EDPRS), adopted in 2007
together with Rwanda?s Vision 2020 and Constitution, provides a clear statement
of the government?s high level priorities and a consistent set of principles.
The EDPRS grew out of the Rwanda?s first Poverty Reduction Strategy Paper
(PRSP), adopted in 2002 and agreed with donor partners as a
necessary step towards receiving PRSP EDPRS N
debt relief under the Heavily Indebted Poor Countries initiative.
ODI, (1999)
85
| 


