2.5 Zio valley morphology
Geomorphology sketch interpretation (fig. 11) carried out
starting from the air photographs of the study area made it possible to
recognize that the morphology of the Zio valley in the sedimentary basin which
is delimited in the West by the plate of Agoènyivé, in the East
by those of Kpogan and Tsévié and in the South by the offshore
bars. These covered geomorphologic units little vegetation are the main
sediments providers of course water.
2.5.1 Zio basin plates
- Agoènyivé plate, extending
approximately on 45 km with average altitude 40 m, is lengthened with the
sinuous edge, delimits right river bank;
- Kpogan and Tsévié plates,
respectively average altitude 30 m and 90 m, they are laid out the first and
are almost parallel to separated by the LAMA depression; they extend
approximately on 50 km with slopes to the convexo-concave pace.
2.5.2 Inshore bars zone
Showing the sea sand cords internal and external primarily
made up at constant sand; they are below laid out plates of soil bar and
average height varying between 4 and 6 m (BLIVI, 1993). Zio drains the offshore
bar interns on 14 km where it is carried out many meanders justifying river
erosive dynamics and the flatness of the valley in the mouth.
2.5.3 Zio river sediment terraces
From the morphological point of view, the alluvial terraces
is a system of projecting ledges or stages below deposited in slopes of valley
by a river. The top of the projecting ledges is covered with sediments
corresponding to the bottom of the river successive beds. The valleys generally
show three kinds of levels at knowing, high, average and low terrace. Also,
these terraces are differenced by their conservation degree, iron oxidation and
hard sedimentary material which compose them.
While basing itself on these criteria of terraces
recognizing, the study zone presents the gravel terraces in Assomé
(GNONGBO, 1989) and those alluvia in Togblékopé (AKIBODE, 2000)
located at about thirty kilometers at the South-east of the first. There is
transition zone with approximately 3 km between these two alluvial formations
where sedimentary material in extraction is a mixture of gravels, clays, and
sands.
A transect from Agoènyivé plate to
Togblékopé shows the space provision of the terraces with alluvia
(fig.10); deposit of these terraces was done in a discontinuous way. This
diagram is almost the same to Dévégo but with two alluvial
terraces levels below the internal offshore bar.
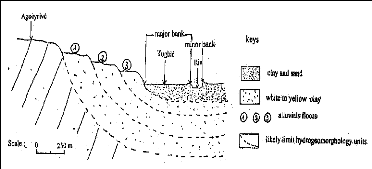
Figure 10: Zio alluvia terraces space provision
2.5.4 Zio low alluvial plain: flooding zone
It is a plain of accumulation of surface corresponding to the
low valley top fill; weak slopes, results from the contributions
plio-quartenary made up of alluvia with clay and sand texture.
Slightly boxed, Zio valley presents unevenness from 1 to 2 m
and slopes ranging between 0,2 to 2%. This topography shows that the low valley
is old silting clogged by alluvia coming from the high basin following the
deterioration of the crystalline rocks (GNONGBO, 1989). It is in these alluvia
that easily flooded zones are extended arms and spreading out river bed.
- Major bed, it is the bed which the river
can cover by current alluvia after flood; furrowed of old axes of drainage and
supplied with colluviums, it extends on average on 1 km and receives water of
exceptional, unforeseeable risings. To up horizontal topography, this bed is
related to the minor by banks of average unevenness 3 m.
- Minor bed, in the shape of ?U`` or in
cradle and broad 10 m on average, this bed presents a slightly tilted flat
bottom in direction of the south. Current channel of Zio flows, its
convexoconcave banks are cut in sandy and clay material. Concave sectors, of
slopes precipice are indication of water strong erosive activity. At the end of
the dry season, the minor bed apparently merges to the bed at low water which
is encumbered many sand banks of dimensions variable and intercalated by
ponds.
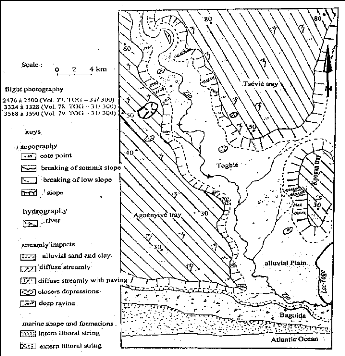
Figure 11: Recognizing geomorphology sketch of Zio valley in
coastal sedimentary basin
(Akibodé, 2000)
| 


