I.1.8.3. Oxidative stress,
endothelia dysfunction and diabetes
Oxidative stress is caused by a relative overload of oxidants,
i.e., reactive oxygen species especially from glycation or lipoxidation
processes and decreased enzymatic and non enzymatic antioxidant defence system.
Evidence has accumulated suggesting that diabetic patients are under oxidative
stress and that complications of diabetes seem to be partially mediated by
oxidative stress (Hadi et al., 2007). Several
mechanisms seem to be involved in the development of an oxidative stress in the
presence of elevated glucose concentrations, namely glucose autoxidation,
protein glycation, AGE formation and the polyol pathway (Hadi et
al., 2007). Thus, it has been shown that oxygenated free radicals
are able to alter vascular function (endothelia dysfunction), especially by
inhibiting synthesis and action of nitric oxide (NO
·). Endothelia
dysfunction comprises a number of functional alterations such as impaired
vasodilatation, inflammation activation and increase plasma level of endothelia
products all of which are usually associated to cardiovascular disease. A key
feature of endothelial dysfunction is the inability of arteries and arterioles
to dilate appropriately in response to stimuli. This limits the delivery of
nutrients and hormones to the distal tissues (Wineke et al.,
2009). Insulin resistance may be associated with intracellular
production of free radicals which in turn could be responsible for
deterioration of insulin action thus leading to a vicious cycle
(Ghufran et al., 2011).
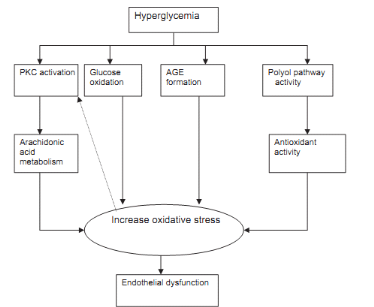
Figure 6 : Hyperglycemia induced
endothelial dysfunction (Hadi et al., 2007)
I.1.9. Prevention and Management
of type 2 diabetes mellitus
I.1.9.1. Strategies for
treatment and control of diabetes
There exist a primary, secondary and tertiary prevention of
diabetes mellitus. Primary prevention of type 2 diabetes is possible and
includes Lifestyle changes aimed at weight control and increased physical
activity. The benefits of reducing body weight and increasing physical activity
are not confined to type 2 diabetes, they also play a role in reducing heart
disease and high blood pressure.
Secondary and tertiary preventions are keys to reducing the
risk of costly diabetic complications, as well as their associated disabilities
(Craig et al., 2009). The primary purpose of
secondary prevention activities such as screening is to identify individuals
without symptoms who already have the disease, who are at high risk of
developing complications related to the primary disease, and where intervention
could have a beneficial effect.
Tertiary prevention of diabetes includes every action taken to
prevent or delay the consequences of diabetic complications, such as blindness,
foot amputation and adverse pregnancy outcomes. Strategies for tertiary
prevention involve prevention of the development of complications by strict
metabolic control, education and effective treatment. They also involve
screening for early stages of complications, when intervention and treatment
are generally more effective (Craig et al., 2009).
Diabetes mellitus type 2 should not be managed based on symptoms alone.
The goal of treatment of diabetes mellitus is to control blood
glucose and ultimately prevent long-term complications. Provided hyperglycemia
is mild in type 2 diabetes, patients may be given at least a one month trial of
diet, exercise and weight management in order to control hyperglycemia. If this
regimen does not lead to adequate blood glucose control, the physician will
need to prescribe oral anti-hyperglycaemic agents and/or insulin
(Reaven et al., 2009). It is now well established
that multiple metabolic abnormalities associated with insulin resistance and
increased cardiovascular risk, such as dyslipidemia, obesity and hypertension,
are already present at diagnosis. Results of many intervention studies have
demonstrated marked benefit from antihypertensive, lipid-lowering and
anti-platelet therapy (Reaven et al., 2009).
Exercise is extremely important in the management of diabetes
because of its effect on blood glucose and free fatty acids. Exercise burns
calories and helps to control weight, eases stress and tension, and maintains a
feeling of well-being. In addition, regular exercise improves the body's
response to insulin and may make oral anti-diabetic drugs and insulin more
effective. It also promotes circulation, and lowers cholesterol and
triglyceride levels, thus reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease
(Eldor et al., 2009).
| 


