|
ATTESTATION
I, SONAGOU TAKAM Yvon Berthet hereby declare that I am the
sole author of this dissertation. I authorize the Higher Technical Teacher
Training College (H.T.T.T.C), Bambili to lend this thesis to other institutions
or individuals for the purpose of scholarly research.
I understand the notion of plagiarism, and I am aware of
university policy on this.
I certified that this dissertation reports original work by me
during my university project, except for the paragraphs, sentences, titles and
subtitles already referenced (see References, webography or bibliography) on
this work.
Date:
Signature:
CERTIFICATION
CERTIFICATION
I hereby certify that this dissertation entitled
Design and implementation of sustainable development web portal in
Cameroon has been carried out by M. SONAGOU TAKAM Yvon Berthet,
with registration number 13T0788 in the Department of Computer Sciences, and of
the option Information and Communication Technology (ICT) of the Higher
Technical Teacher Training College (H.T.T.T.C) Bambili, University of
Bamenda.
The work is therefore approved for a contribution to
scientific knowledge and literacy presentation for the award for the
«Higher Technical School Teacher Post Graduate Diploma (DIPET II)
option Information and Communication Technology».
Date: Date:
Supervisor: Head of Department:
DEDICATION
DEDICATION
To the memory of my Father TANKAM David
(1961-2015)
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
At the end of my dissertation, I would like to thank all those
people who madethis possible and an unforgettable experience for me:
· I wish to express my sincere thanks to Dr. DADA
Jean-Pierre, my supervisor, for his patience, motivation, enthusiasm, and
immense knowledge, for providing me with all the necessary facilities for the
research.
· I place on record, my sincere thank you to M. ATANGANA
Romain,Head of Department, for the continuous encouragement.
· I am also grateful to the Teachers of the Department
for sharing their expertise, for their guidance and encouragement extended to
me.
· I take this opportunity to express my gratitude to Pr.
AKUME Daniel AKUME, Director of the H.T.T.T.Cfor the availability of all the
resources of his institution to our formation.
· I also thank my parents for the unceasing
encouragement, financial support and attention.
· I would like to thankmy classmates and friends who have
supported and encourage me through the duration of the dissertation project.
· I also place on record, my sense of gratitude to one
and all, who directly or indirectly, have lent their hand in this venture.
ABSTRACT
ABSTRACT
This dissertation, entitled «Design and
implementation of sustainable development web portal in Cameroon " is
intended as a solution to problems of communication between the actors of
sustainable development in our country since the establishment of such a
development model requires communication and information tools powerful and
reliable. Thus this work was completed at the H.T.T.T.C ofBambili during the
academic year 2014-2015.
Accordingly, the construction of such an application required
a design phase which is made using the MERISE method leading to the selection
of tools to help us achieve our web application. The web portal for sustainable
development thus constructed provides to Cameroonians anews service, a library,
a system of external hyperlinks, a forum service, a members area with internal
mail, an internal search engine, a Google custom search just like a content
proposal system..
Keywords: Web portal, sustainable development, web, web
application.
RÉSUMÉ
RÉSUMÉ
Ce mémoire, intitulé « Conception
et réalisation d'un portail web de développement durable au
Cameroun » se veut une solution aux problèmes de
communication entre les acteurs du développement durable dans notre pays
vu que la mise en place d'un tel modèle de développement exige
des outils de communication et d'information puissants. C'est ainsi que ce
travail fut mené à l'E.N.S.E.T de Bambili durant l'année
académique 2014-2015.
Partant, la construction d'une telle application a
nécessité une phase de conception qui s'est fait à l'aide
de la méthode MERISE débouchant sur le choix des outils devant
nous permettre de réaliser notre application web. Le portail web de
développement durable ainsi construit met à la disposition des
camerounais un service d'actualité, une librairie, un système de
liens externes, un service forum, un espace membres avec messagerie interne, un
moteur de recherche interne, une recherche personnalisée Google, tout
comme un système de proposition de contenu.
Mots clés : Portail web, développement
durable, web, application web.
TABLE OF CONTENT
TABLE OF CONTENT
ATTESTATION
Erreur ! Signet non
défini.
CERTIFICATION
ii
DEDICATION
iii
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
iv
ABSTRACT
v
RÉSUMÉ
vi
TABLE OF CONTENT
vii
LIST OF FIGURES
x
LIST OF TABLES
xi
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
xii
CHAPTER ONE: GENERAL INTRODUCTION
1
1. Background and context of the study
2
2. Statement of the problem
3
3. Research questions
3
4. Research hypotheses
4
5. Objectives of the study
4
5.1. General objective
4
5.2. Specific objectives:
4
6. Significance of the study or
achievements
4
7. Scope of the study
5
8. Delimitation of the study
5
9. Importance of the dissertation for
Education community
5
10. Definition of terms
6
11. Overview of Dissertation
10
CHAPTER TWO: LITERATURE REVIEW
11
1. Introduction
12
2. Overview of web applications
12
2.1. History of web applications
13
2.2. The Internet and the Web
14
2.3. Types of websites
17
2.4. Social Medias
20
2.5. Web portals
21
3. Sustainable development and ICT
26
4. Literature review
26
5. Conclusion
27
CHAPTER THREE:RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND
MATERIALS USED
28
1. Introduction
29
2. Web application architecture
29
2.1. The 2tiers architecture
29
2.2. The 3-tiers architecture
29
2.3. The n-tiers architecture
30
2.4. The MVC architecture
30
3. Modules of application web site
30
4. Research design
31
5. Analysis methods
31
5.1. Object Oriented Methods
31
5.2. Functional methods
32
5.2.1. SADT method
32
5.2.2. MERISE method
33
5.3. Choose of a method
33
6. MERISE steps
34
6.1. MERISE levels
34
6.2. Data dictionary
35
6.3. The Data Conceptual Model (DCM)
37
6.4. Data Logical Model (DLM)
43
6.5. From Data Logical Relational Model
(DLRD) to Data Physical Model (DPM)
44
6.6. Data Physical Model
44
7. Materials used
45
7.1. Software
45
7.2. Hardware
50
8. Conception and realization of the
application
50
8.1. Classification of needs of the future
users
50
8.2. Functional specifications
51
8.3. The software life cycle
52
8.4. Structure of the web application
53
9. Partial conclusion
55
CHAPTER FOUR:RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
56
1. Homepage
57
2. Connection / disconnection
57
2.1. Subscribe
58
2.2. Disconnection
59
3. Consult pages
60
3.1. Link page
60
3.2. Article page
61
3.3. Document page
61
4. Search
61
4.1. Search in the website
62
4.2. Google customize search
62
5. Propose content and general
administration
62
5.1. Link
62
5.2. Article
63
5.3. Document
64
6. Forum
64
6.1. Read topics
64
6.2. Read subjects
65
6.3. Read and publish comment
66
7. User space
67
7.1. Private Messages
67
7.2. Profile
68
7.3. User list
69
8. Administration
69
8.1. Forum administration
69
8.2. Users administration
71
CHAPTER FIVE:GENERAL CONCLUSION AND
RECOMMENDATIONS
72
1. Summary of findings
73
2. Difficultiesencountered
73
3. Recommendations
74
4. Suggestions for further studies
74
5. Conclusion
75
BIBLIOGRAPHY
76
APPENDICES
78
LIST OF FIGURES
LIST OF FIGURES
Figure 1: Entities of the project
3
Figure 2: Entities attributes
38
Figure 3: Entity identifiers
39
Figure 4: Associations and cardinalities
40
Figure 5: Complete Conceptual Data Model
42
Figure 6: the table Article
44
Figure 7: final relation schema
45
Figure
8: Structure of the application
54
Figure 9: Visitor Homepage
57
Figure 10: Connection form
58
Figure 11: suscription form
59
Figure 12: Disconnection button
60
Figure 13: Useful links page
60
Figure 14: Library
61
Figure 15: search results
62
Figure 16: new link form
63
Figure 17: new article form
63
Figure 18: new document form
64
Figure 19: forum homepage
65
Figure 20: forum subjects
66
Figure 21: forum comment
66
Figure 22: read messages
67
Figure 23: new message form
68
Figure 24: profile view
68
Figure 25: User list
69
Figure 26: forum management - topics
70
Figure 27: forum comments management
70
Figure 28: user management
71
LIST OF TABLES
LIST OF TABLES
Table 1: Data dictionary
3
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
LIST OF ABBREVIATIONS
ADSL : Asymmetrical Digital Subscriber Line
AJAX : Asynchronous JavaScript AndXML
AOL : American On Line
API : Application Programming Interface
AS : Autonomous System
BGP : Border Gateway Protocol
CDS : Central Depository System
CMS : Content Management System
CSS : Cascading Style Sheet
DBMS : DataBase Management System
DCM : Data Conceptual Model
DLM : Data LogicalModel
DLRM : Data Logical Relational Data Model
DNS : Domain Name Server
DOM : Data Object Model
DPM : Data Physical Model
ENSET : Ecole Normale Supérieure
d'Enseignement Technique
FTP : File Transfer Protocol
GPRS : General Packet Radio Service
GSM : Global System for Mobile
Telecommunication
HMI : Human Machine Interface
HTML : HypertextMarkup Language
HTTP : Hypertext Transfer Protocol
HTTPS : Hypertext Transfer Protocol Secure
HTTTC : Higher Technical Teacher Training
College
ICMP : Internet Control Message Protocol
ICT : Information and Communication
Technologies
IMAP : Internet Message Access Protocol
IP : Internet Protocol
IRC : Internet Relay Chat
ISP : Internet Service Provider
ITU : International Telecommunication Union
IUCN : International Union for Conservation of
the Nature
JSON : JavaScript Object Notation
JSP : Java Server Page
LAN : Local Area Network
MERISE :Méthode de Recherche Informatique
pour les Systèmes d'Entreprise
MSN : MicroSoftNetwork
MVC : Model View Controller
NGO : Non-Governmental Organization
NNTP : Network News Transfer Protocol
OSI : Open System Interconnect
PDA : Personal Digital Assistant
PHP : Hypertext Preprocessor
POP : Post Office Protocol
POP3 : Post Office Protocol Version3
PTOM : Physical Treatment and Operational
Model
SADT : Structure Analysis and Design
Technique
SGML : Standard Generalized Markup Language
SMTP : Single Mal Transfer Protocol
SOA : Service Oriented Architecture
SQL : Structure Query Language
SSI : Small Scale Integration
SSL : Secure Socket Layer
TCM : Treatment Conceptual Model
TCP : Transfer Control Protocol
TLM : Treatment Logic Model
TLS : Transport Layer Security
UDP : User Datagram Protocol
UML : Unified Modeling Language
UNCED :United Nations Conference on Environment
and Development
UP : Unified Process
URL : Uniform Resource Locator
WAMP : Windows Apache MySQL PHP
WebApp : Web Application
WI-FI : Wireless Fidelity
WWW : World Wide Web
W3C : World Wide Web Consortium
WYSIWYG : What You See Is What You Get
XML : Extensible Markup Language
CHAPTER ONE: GENERAL
INTRODUCTION
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
1. BACKGROUND AND CONTEXT OF THE STUDY
The various economic, social and environmental crises that the
majority of countries of planet are experimenting today, seems to be the result
of the capitalist model of development disseminated in the world by the
Occident. Capitalism is this model of development which gives the priority to
the economic growth. Consequently the level of development at the beginning of
the 20th century is being measured with the capacity of the states
to accumulate richness. Later the social factor makes its appearance and one
then will measure the development from an economic and social point of view.
However, with the apparition of the oil crisis in 1973 and
1978, the Occident was become aware of a possible shortage of the natural
resources. Also, a significant parameter of the development had been put on
side: the environment. The model of industrial development seems non-viable.
Therefore, related to the problem of viability which is equity clings, the more
poor undergo more on the ecological crisis which prevails.
The model of development of the moment seems to be highly
consuming non-renewable resources. At the same time, with the multiplication of
ecological crises, it appeared urgent to redefine a new way of development
taking into account all the parameters of a healthy development. This idea
comes out as a result in 1980, from the concept of "sustainable
development" that appears in a report of the International Union for
Conservation of the Nature (IUCN).
In 1992, the United Nations Conference on Environment and
Development (UNCED) published the «Earth Charter», which
outlines the building of a just, sustainable, and peaceful global society in
the 21st century. The action plan Agenda 21 adopted by 173 countries
amongst which the Cameroon for sustainable development identified information,
integration, and participation as key building blocks to help countries achieve
development that recognizes these interdependent pillars. It emphasizes that in
sustainable development everyone is a user and provider of information. It
stresses the need to change from old sector-centered ways of doing business to
new approaches that involve cross-sectorial coordination and the integration of
environmental and social concerns into all development processes.
Cameroun for its part inherited after the independence the
capitalist system characterized by the drainage of the natural resources
towards outside to the detriment of the local population and especially of the
environment. It is in this logic that the multiplication of social crisis as
well as environmental crisis such as: desertification, pollution, climatic
disturbances have occur. Thus, the Cameroonian leaders choose a model of
sustainable development through the adhesion of Cameroon to Agenda 21observable
in many fields particularly those of energy and agriculture. However a rapid
seen of the political flow chart of our country reveals insufficiencies.
Because the sustainable development is based on three principal pillars the
social one, the economy, and the environmental pillar which is disseminated
within many ministries. These ministries overlap remains weak while the
sustainable development requires actions coordinated on all the levels whatever
they are.
At the same time, the Internet Word Stats reproduced a report
of the International Telecommunication Union (ITU). This report, taking into
account the proliferation of computer science and Internet, observed that there
are 1,006,000 Cameroonians which uses Internet in June 2012. This number
represents at this time nearly 5? of the population. Today this percentage is
re-examined, so, according to the World Bank more than 6.4? Cameroonians go on
Internet in 2013 what testifies a constant penetration of Internet within
Cameroonian society. Also one of greatest attractions of Internet is web
portal, shown by their proliferation in Cameroon treating in general of
subjects like employment, news, economy and even of Internet. Another important
thing to note is that amongst the 10 favorite websites of Cameroonians 6 are
web portals according to Internet Word Stats.
2. STATEMENT OF THEPROBLEM
The sustainable development from its scale (the fact that it
puts forward all the actors of the life of a nation) requires the existence for
this model of development of tools of communication and information reliable
and powerful. Therefore, the popularization of the computer science and
especially of Internet makes us foresee a web portal as solution to this
problem. Hence the web portals from the diversity of the services which can be
associated to him come out like one of the serious alternatives for the
diffusion of the sustainable development in our country. The construction of a
Web portal having to be used as platform of information, communication and
exchanges, training for the public services, the private academics, NGOs,
companies and individuals look necessary.
3. RESEARCH QUESTIONS
For this research we can formulate the following questions:
· Is it possible to ameliorate the interchange of
information among all the actors of sustainable development in Cameroon through
a web application?
· What should be the impact of such amelioration?
4. RESEARCH HYPOTHESES
We can formulate the following hypothesis,
· The actual economic and social growth, change of
environmental conditions in Cameroon ask to improve the level of web services
specially in the domain of sustainable development ;
· Sustainable development improving knowledge and
communication should have an impact on the way people perceive their society
and their environment.
5. OBJECTIVES OF THE STUDY
5.1. GENERAL OBJECTIVE
The general objective of this work is to build a user-friendly
web application, actually a web portal, in order to improve communication and
information amongst the different actors of sustainable development in
Cameroon.
5.2. SPECIFIC
OBJECTIVES:
By the end of this dissertation, with the appropriate use of
database software and software, we should be able to:
· Identify all the actors of the sustainable development
in our country;
· Put in place a news page on sustainable development
which can be update online;
· Build a sharing space forum on varies theme concern by
sustainable development;
· Put in place a library in relation to our topic from
which users must be able to download document.
6. SIGNIFICANCE OF THE STUDY OR
ACHIEVEMENTS
Although there already exists in Cameroon many web portals,
and that many researches have already been carried on the construction of web
application, this research project aims the construction of a web application
in the field of sustainable development which remains inexistent in our
country. This project goes beyond initiation to scientific research and of the
mastering of web programming tools to contribute to future work which will be
carrying on the building of applications web and also those concern by
sustainable development of which it could be used as platform of collection of
information.
7. SCOPE OF THE STUDY
This study is based on analysing the general way web developer
used to design and implement web application, taking into consideration the
particularities of web portals.
The research also takes as important parameter the main
aspects of sustainable development, his main component or pillars (economic,
social, environment).
8. DELIMITATION OF THE STUDY
This work is for all people, Cameroonian or not interested by
sustainable development.
It intends to create a web portal for the following :
- An information space;
- An online library with downloadable documents;
- A page for useful links;
- A registration and connection space;
- The ability to registered user to propose content;
- Discussion space or forum with private space for registered
members;
- The capacity of members to send private message inside
forum;
- A specialized search engine;
- An administration space for the webmaster to update the
website, and to manage the forum.
9. IMPORTANCE OF THE DISSERTATION FOR
EDUCATION COMMUNITY
By putting in place a web portal of sustainable development we
may improve communication and information amongst all the actors and person
interested by sustainable development in our country. This subject is also an
opportunity to master the tools and languages related to web programming.
For educational community it can be a tool for improving
knowledge and exchanging of point view.
10. DEFINITION OF
TERMS
To conclude this study the definition of key concepts comes as
of first need.
· Sustainable development
The United Nations World Commission on Environment and
Development in its 1987 report Our Common Future defines sustainable
development as the : "Development that meets the needs of the present without
compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs." Under
the principles of the United Nations Charter the Millennium Declaration
identified principles or pillars and treaties on sustainable development,
including economic development, social development and environmental
protection. Broadly defined, sustainable development is a systems approach to
growth and development and to manage natural, produced, and social capital for
the welfare of their own and future generations. The concepts of sustainable
development and sustainability derive from the older forestry term "sustained
yield", which, in turn, is a translation of the German term
"nachhaltigerErtrag" dating from 1713. Sustainability science is the study of
the concepts of sustainable development and environmental science. There is an
additional focus on the present generations' responsibility to regenerate,
maintain and improve planetary resources for use by future generations.
Sustainable development is defined as development process that
balances ecological, economic and social and establishes a virtuous circle
between these three poles: it is a development, economically efficient,
socially equitable and ecologically sustainable. It is respectful of natural
resources and ecosystems, life support on Earth, ensuring economic efficiency,
without losing sight of the social purposes of development such as the fight
against poverty, against inequality, against exclusion and search for equity. A
strategy for sustainable development must be winner of this triple point of
view, economic, social and ecological.
Sustainable development requires that human decisions and
behavior in reconciling what appears to many irreconcilable, manage to expand
their vision: it requires to open our time horizon over the long term, that of
future generations and our spatial horizon in taking into account the
well-being of everyone, whether a resident of the South or the North, a nearby
region of the city or neighbouring district.
Different domains have been identified for research and
analysis of sustainable development. Broadly defined, these include ecology,
economics, politics and culture as used by the United Nations and a number of
other international organizations. As a working definition, sustainability can
be defined as the practice of maintaining processes of productivity
indefinitely (natural or human made) by replacing resources used with resources
of equal or greater value without degrading or endangering natural biotic
systems.
Sustainable development is based on research integration and
alignment of sectorial policies set imposes joint processing of economic,
social and environmental effects of any policy or human action. Such an
approach requires integration of multi-partnership approaches and
interdisciplinary. Its success is based on partnership and cooperation between
actors from different disciplines (economics, sociology, ecology) from
different sectors (transport, water, waste, natural environment, social
development) and different environments (entrepreneurial, associative,
institutional, administrative, commercial, trade union), acting at different
territorial levels, from international to local level.
Sustainable development is in fact based on a new form of
governance, where the mobilization and participation of all actors of civil
society in decision-making should take precedence over the mere exchange of
information. Sustainable development aims to promote participatory democracy
and restore civic approach. Access to information and transparency are
prerequisites.
· Internet
Internet is a world system of interconnection of network,
using a standardized whole of protocol of transfer of data. It is therefore a
network of network, composed of million networks as well public, private,
university, commercial and governmental. Internet transports a broad spectrum
of information and allows the development of applications and services varied
like the electronic mail, the instantaneous messenger and the World Wide
Web.
Internet having been popularized by the appearance of the
World Wide Web, both is sometimes confused by the public. The World Wide Web is
however only one of the applications of Internet.
The access to Internet can be obtained through an Internet
service provider via various means of communication: either telegraphic (ADSL,
optical fiber to the residence), or without wire (WIMAX, by satellite).
· World wide web
The World Wide Web, commonly known as the Web, sometimes the
Web, literally the "web (spider) World" is a public hypertext system operating
on the Internet that provides access with a browser, uploaded pages in sites.
The image of the web has hyperlinks that link web pages together.
The Web is only one of the Internet applications, with email,
instant messaging, Usenet. The Web was invented several years after the
Internet, but the Web has made the mainstream media attention to the Internet.
Since the Web is often confused with the Internet; in particular, the word is
often used Canvas very ambiguously.
The World Wide Web is and has been designated by many
synonymous names and acronyms: WorldWideWeb, World Wide Web, World-wide Web,
Web, WWW, W3, Web of Spider World, World Wide Web, Web.
The name of the original project was WorldWideWeb. The words
were quickly separated into World Wide Web to improve readability. The name
World-Wide Web was also used by the Web inventors, but now recommended by the
World Wide Web Consortium name separates the three words without a hyphen.
Spelling World Wide Web and the Web abbreviation are now well established.
Surfing the web is like walking into an endless jungle. We
never see the end so there websites, and found it absolutely everything.
Anyone can publish information on the web.
· Web site
According to Wikipedia a website is a set of related web pages
typically served from a single web domain. A website is hosted on at least one
web server, accessible via a network such as the Internet or a private local
area network through an Internet address known as a Uniform resource locator.
All publicly accessible websites collectively constitute the World Wide Web.
A website can be defined as a set of linked websites together
by hyperlinks, accessible through the Internet using a web address (URL) from
the same domain name. Sometimes the term is used website, which is equivalent
(Internet is the network which supports the web, but the shade is not of
fundamental importance in this case).
A website consists of web pages as' they are in a computing
resource available on the Internet and read by a web browser (Firefox, Chrome,
Internet Explorer). In general, when talking about web page, we think of a html
document containing text, images, videos or any other type of resources.
However, a simple image with a URL (therefore accessible through the Internet)
may be considered by extension as a web page. The web is primarily based on the
connection between multiple pages that make references to each other. This is
called hypertext links (or hyperlinks). We find these links in the navigation
menus or in the body of web pages.
It is possible to make connections between the pages of a
website in the same way we can to point these links to web from other websites
pages. We talk in a case of internal links in the other external links.
· Web portal
The web portal term draws its origin from Latin Medieval
"portale", meaning the main entrance of the city.
Portal sites are websites whose primary purpose is to provide
users with resources and services related to a theme, a profession, a
geographic area or community.
Resources may be links to other sites reference discussion
forums or blogs, but can also consist of editorial content specific to the
gate. These services can be of different types: Engine Specialized searches;
email.
The term portal is a good metaphor to describe these web
portals to a "dedicated universe."
We still define a web portal as a web site trying to offer the
broadest pallet of information and possible services in only one site. It is a
web site which offers a single door of entry on a broad range of resources and
services (electronic mail, forum of discussion, spaces of publication, search
engine) centered on a field or a particular community. The users have most of
the time the possibility of being register and to connect later on and use the
whole of services suggested to them. A web portal provides also services such
as the capacity for the user to personalize his workspace. The user thus has
access to the activity of current purse, the weather report, the profiles of
other users who use the gate, and several types of information according to the
individual interest of the user.
We can distinguish 02 main classes of web portals: vertical
web portals constitute an entrance point specialized in a specific place of the
market or a domain of industry, it is the case of forbes.com. Horizontal web
portal is used like a platform for several organizations and covers a variety
of information in various sectors (yahoo.com for example).
So, according to Wikipedia we have many types of web portal:
personal portals, government web portals, cultural portals, corporate web
portals, stock portals, search portals, tender portals, hosted web portals,
domain-specific portals.
The web portal is distinguished from the web directory on two
aspects:
- It does not offer only links to third party websites from
one category but offers related services and editorial content it owns.
- Allows usually (but not always) the user to register in
order to be able to customize its interface and use the associated services.
- 11. OVERVIEW OF
DISSERTATION
To achieve our general objective, the present study is
organized around five chapters.
The first chapter, entitled «General
introduction» was already been done. It contained the context and
background of the study, the problem statement, the objectives, the questions
of research, the hypothesis, the objectives of research as well as the
delimitation of the subject.
«Literature review and materials used» is
the title of chapter two. Here will be devoted to the preceding studies
undertaken by other researchers. We will be focused on documents relating to
the construction of a Web application or better on the construction of a web
portal.
The chapter three, Methodology of research and materials
used, in this part, the procedures that were applied to collect data. Data
processing techniques and the research design are also presented. This chapter
ends with materials (software and hardware) we will use to implement our web
portal.
Chapter four is concern by «Results and Findings and
discussion». Then the chapter five shall carry on the summary,
conclusion, recommendations and suggestions for further studies.
The last chapter entitled «General
conclusion» will help us to summarize all our findings, a small
conclusion is done. We will list some recommendations ad suggestions for
further studies in relation with this topic.
CHAPTER TWO: LITERATURE
REVIEW
LITERATURE REVIEW
INTRODUCTION
It is nowadays quite undeniable that the internet has
revolutionized the world since its effects will soon spread into the lives of
everyone at all levels. The explosive growth of the Internet has given place to
the creation of new businesses that have relied on a plethora of services on
the powerful programming languages as well as web application development
quality steadily to accustom user needs to.
Web applications are about to revolutionize the way we
communicate throughout the world. The communication rules are thus upset
because the distance is no longer one of the key factors. And besides, internet
through web applications is one of the major communication tools to promote a
considerable time, a variety of services, and easier access to information.
Thus, the construction of a reliable web application involves the fairly clear
understanding of what a web application on the one hand; and secondly a look
will be devolved to the principal that has been identified for the construction
of web portal. This chapter begins with an overview of web applications, and
finishes with some ideas coming from dissertations.
1. OVERVIEW OF WEB APPLICATIONS
A web application also called a dynamic website (since a
static website is more like a tool of communication which do not allow
interaction with users) is a software application manipulated through a web
browser. In the same way that web sites, web application is usually placed on a
server and handles by activating widgets using a web browser via a computer
network (Internet, intranet, LAN).
The Webmail, content management systems (CMS), blogs are web
applications. Search engines, e-commerce software, online games, forum software
may be another form of web application. Network devices including routers, for
example are sometimes equipped with a web application in their firmware. Thus a
web application aims to accomplish specific task like when we make a research
on Google. The impact of web applications on how to operate a business, to
transmit and receive information, and even on people's lives, is considerable
and in more than four decades programmers have tried to jump the barriers
between traditional applications and web applications.
It is important to note that the success of web applications
is due to many advantages that can be summarized through several points:
· In terms of time, the implementation and deployment of
a web application is faster, the flow and sharing of data between users as
optimized as much as we enjoy the most intuitive applications and easier to
handle (to through the web browser).
· In terms of accessibility, access can be done through
many types of devices (PC, phone), operating systems constraints do not exist
here; work or access can be done from anywhere in the world and as a bonus the
data is accessible 24hour / 24 and 7days on7.
· In terms of costs, access to web applications at a cost
entirely predictable based on the subscription chosen by the customer and many
features are free of charge.
· In terms of security, user data is stored in large
processing centers (Data Center) very reliable.
· As bonus, web applications are steadily increasing and
dynamism they have shown is unparalleled.
1.1. History of web applications
The interactive web applications slowly revolutionized the way
we use the Internet. The concept of web application is not recent. Indeed, one
of the first programming languages for web application development was the
"Perl". It was invented by Larry Wall in 1987 before the internet became
accessible to the general public. But it was in 1995, when the programmer
RasmusLerdorf made the PHP language available to all that the Web application
development really took off. Today, even most of the famous of these web
applications are developed in PHP including Google, Facebook and Wikipedia.
A few months later, Netscape, ancient and popular web browser,
announced a new technology, JavaScript, allowing programmers to dynamically
change the content of a Web page that was, until now, static text. This
technology allowed a new approach in the development of Web applications, which
were now, and still today, much more interactive for users. For example, the
Google Instant feature for displaying search results even as the letters of the
word is typed, makes heavy use of JavaScript.
The following year, in 1996, two developers, Sabeer BHATIA and
Jack Smith, launched Hotmail an online messaging service. This allowed (for the
first time) to the general public to access and check e-mail anywhere users
could be on the planet and thus away from their workstation (computer).
Then came the famous Flash platform for adding interactive
content to websites. Flash came on in 1997 under the name of Shockwave Flash.
Later, after being acquired by Macromedia and now by Adobe, Flash became a
development platform for interactive Web applications.
Subsequently the use of web applications will know many
bouncing including online journalism beginning that will place internet as an
entire media. So, things were greatly facilitated by Google in 1998, when the
company launched its first online search engine which by its new way to index
Web pages, greatly facilitated the search for information on the internet.
Google continued to innovate and became one of the most prolific companies in
terms of Web applications, listing the popular Google Maps, Google Docs, Gmail
and others.
However, it is until 2004, at a conference on "Web 2.0" that
appears for the first time the concept of "Web as a platform." This innovation
paved the way for future web applications, that is to say, the software that
takes advantage of the internet and moving away from the traditional use of the
desktop.
1.2. The Internet and the Web
Internet is a worldwide system of interconnected computer
network, using a standardized set of data transfer protocol. This is a network
of network without nervous center, composed of millions of networks public,
private, academic, commercial and governmental. Internet carries a wide band of
information and allows the development of applications and various services
such as email, instant messaging, and the World Wide Web.
Internet access can be obtained through an Internet Service
Provider through various means of electronic communication, either wired
(telephone network, ADSL, fiber) or wireless (WIMAX, satellite). An Internet
user at that time is designated by the term "surfer".
Internet is constituted of the plurality of networks spread
worldwide and interconnected. Each network is attached to a separate entity
(ISP Internet) and is associated with a unique identifier called Autonomous
System (AS) used by the routing protocol BGP (Border Gateway Protocol). In
order to communicate, network exchange data, either by establishing a direct
link, or by attaching to an exchange node (peering point). These exchanges may
be limited to traffic between their respective users (called peering) or
include third traffic (it is then transit agreement). An operator that provides
Internet transit service to other service providers is called carrier. These
peering are free; they are not subject to regulation by a central authority.
Each network is connected to one or more other networks. When
data is to be transmitted from one computer to another belonging to a different
AS, it is then necessary to determine the way to perform among the networks.
Routers, charge of traffic between the AS usually have a complete routing table
(Full routing table) of more than 330,000 routes in 2010, and send traffic to a
neighbour router closer to the destination after consulting their routing
table.
To access the internet you must have an IP device and a
connection to an ISP. For this, the user uses the following hardware and
software:
· A personal computer or other network terminal
equipment:
- Personal Assistant
- Video-game console
- Mobile phone
· A communication channel to the service provider:
- Fiber Optic
- Fixed telephone line: analog line, ADSL
- Mobile Phone Line:4G , 3G, Edge, GPRS, GSM
- Satellite
- Wi-Fi
· An Internet service provider (ISP)
Software's are required to operate Internet following uses:
· E-mail software: SMTP and POP client or IMAP offered by
Mozilla thunderbird, Microsoft outlook.
· File Transfers software: a client or FTP (File Transfer
Protocol). They may include Filezilla
· World Wide Web: a Web browser
· Peer to peer: one of many P2P software based on use
(sharing peer-to-peer files, Distributed Computing).
Internet operates on a layered model similar to the OSI model.
The elements belonging to the same layers use a communication protocol to
exchange information. A protocol is a set of rules that define a language for
communicating multiple computers. They are defined by open standards.
Each protocol has its own functions and together they provide
a range of ways to respond to the multiplicity and diversity of needs on the
Internet.
The mains are:
ï IP (Internet Protocol) network protocol that defines
the primary mode of exchange between participating computers to the network by
giving them a unique address on the network.
ï TCP (Transfer Control Protocol): responsible for
establishing the connection and control of the transmission. It is a reliable
delivery protocol. This ensures that the recipient has received the data.
ï HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) protocol used for
the loading of web pages.
ï HTTPS (Secured HyperText Transfer Protocol): for HTTP
navigation in secure mode.
ï FTP (File Transfer Protocol): protocol used to transfer
files over the Internet.
ï SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer Protocol) mode of exchange
of e-mail sent.
ï POP3 (Post Office Protocol version 3): mode of exchange
of e-mail reception.
ï IMAP (Internet Message Access Protocol): another email
exchange mode.
ï IRC (Internet Relay Chat): instant chat protocol.
ï NNTP (Network News Transfer Protocol) message transfer
protocol used by Usenet discussion forums
ï SSL (Secure Pocket Layer) or TLS (Transport Layer
Security): secure transaction protocols, used in particular for secure online
payment.
ï UDP (User Datagram Protocol): to communicate,
unreliable but lightly in small datagrams.
ï DNS (Domain Name System): Internet name resolution
system.
ï ICMP (Internet Control Message Protocol): IP control
protocol.
1.3. Types of websites
Basing the classification on the technologies used while
building the websites and the interaction with the user, we can have the
following types of websites:
· Static website
A static website is made up exclusively of website files
stored on a server and sent directly to the client browser to enable the
display of pages. Updating a static site is performed by the addition of HTML
files in the storage site. There is no back office. The daily management of
such a site can quickly become laborious: To add a link to a new page, add this
link to all existing pages and therefore modify each file one by one. This is
made easier by specialized software, but it is tedious.
Primarily a static site is coded in Hypertext Mark-up Language
(HTML). Cascading Style Sheets (CSS) are used to control appearance beyond
basic HTML. Images are commonly used to affect the desired appearance and as
share of the main content.
This kind of website usually displays the same information to
all visitors. Similar to handing out a printed brochure to customers or
clients, a static website generally will provide consistent, standard
information for an extended period of time. Although the website owner may make
updates periodically, it is a manual process to edit the text, photos and other
happy and May require basic website design skills and software. Simple forms or
marketing examples of websites, Such As classic website, a five-page website or
a brochure website are often static websites, because they present pre-defined,
static information to the user. This may include information about a company
and its products and services through text, photos, animations, audio / video,
and navigation menus.
Static websites can be created of edited using the following
categories of software:
- Text editors, such as Notepad or Text Edit, where HTML codes
are manipulated directly from the program editor
- A WYSIWYG (What You See Is What You Get) offline editor,
such as Microsoft FrontPage and Adobe Dreamweaver with which the site is edited
using a GUI (Graphical User Interface) and the final HTML codes is generated by
the editor software automatically.
- WYSIWYG online editors, used to create rich media online
presentation like web pages, widgets, blogs, and other documents.
- Template-based editors, such as Rapid Weaver, which allow
users to create and upload quickly web pages to a web server without detailed
HTML knowledge, as they pick a suitable template from a pallet and add pictures
and text to it in a desktop publishing fashion without directly handling of
HTML code.
Static websites may still use Server Side Includes (SSI) as an
editing convenience, such as sharing a common bar across many pages menu. As
the website's behaviour to the reader is still static, this is not considered a
dynamic site.
· Dynamic website
A dynamic website is one that changes or customizes itself
frequently and automatically, here, clients can interact with each other and
with the application, the information is automatically updates and sometime
those website offer an administration space.
Server-side dynamic pages are generated "on the fly" by
computer code that produces the HTML and CSS. There are a wide range of
software systems, such as CGI, Java Servlets and Java Server Pages (JSP),
Active Server Pages and ColdFusion that are available to generate dynamic web
systems and dynamic sites. Various web application frameworks and web template
systems are available for general-use programming languages like PHP, Java-EE,
Perl, Python, and Ruby, to make it faster and easier to create complex dynamic
web sites. But amongst all those languages PHP is the most used and belong to
the ten most used programming languages in the world with Java.
When interviewing a website, a server sends an HTML/CSS code
for your browser displays the web page you request. To build the HTML/CSS code,
the server can use two methods:
- It only reads files present on a hard drive (this is called
static site)
- It builds the code from a model (static part) and data
stored on a database (the dynamic part)
· Benefits of dynamic websites
- Ease of Use: Dynamic websites are more frequently used.
Indeed, they allow users, for example through the use of CMS, to easily add to
and edit a website without having to intervene directly in the source code for
it.
- Construction of elaborate web sites: Thanks to the use of a
database, it is possible to produce pages that can adapt to the user request,
which may otherwise also contribute content. One can for example propose
research with custom criteria, or the opportunity to comment on a page.
· Disadvantages of dynamic websites
- Slower than a static site:
The main disadvantage of a dynamic site is that it is slower
than a static site. Indeed, it must go through an intermediate step of querying
the database, wait for data and send them to the user after compilation.
- Server Resource Consumption
For the same reasons, dynamic websites require more resources
to operate machine. This is what drives some organizations to turn to static
sites like Jekyll systems.
- Greater complexity
Dynamic web sites might be more convenient to use for users,
they are nevertheless much more complex computer systems perspective. A static
site requires zero maintenance and is easy to install, but a dynamic website
should be regularly updated to work and requires more complex starting
configurations (eg for the connection with the database). A dynamic site also
requires additional resources to operate (PHP).
- Less Security
Of course, from the moment it is possible to connect to a site
management system (back office) and where there is connection to a database,
the security holes are more than a static site. We must therefore ensure the
integration of security aspects in the design of a dynamic website, including
and especially when using a CMS like WordPress or Joomla market.
· Full flash website
Flash is a vector animation system developed by Adobe editor.
To play a flash animation, a plug-in (Flash Player for example) must be
installed on your browser. The full flash websites have only one web page
index.html. Calling this page from the server causes the page to load a flash
file like "animation.swf". Thus the index.html page contains a link to the
animation file that contains all the animations of the site. So the full flash
websites may have the following characteristics:
- They create vector animations of great quality;
- They offer the ability to create interactive applications by
using action script
- This technology is still the preferred way to add video
content on sites
- There are no compatibility issues when that flash technology
is installed on the browser
- By creating a flash animation, it is ensured that the design
will remain the same from one computer to another or from one browser to
another.
Note that flash animations are already used on many website
but partially like on YouTube where it is used to display video content.
· Site 2.0 with AJAX
This category of web site is based on the AJAX architecture
(Asynchronous JavaScript and XML).
In a web application, the conventional method of dialogue
between a browser and a server is as follows: at each manipulation made by the
user, the browser sends a request containing a reference to a web page and the
web server performs calculations and sends the result as a web page to the
browser. This will display the page he has just received. Each manipulation
results in the transmission and display a new page. The user must wait for the
answer to perform other manipulations.
Using Ajax, the dialogue between the browser and the server
takes place mostly in the following way: a program written in JavaScript
programming language, embedded in a web page, is executed by the browser. It
sends in the background requests to the Web server, and then changes the
content of the page currently displayed by the web browser based on the result
received from the server, thus avoiding the transmission and display of a
complete new page.
Instead, the operation of Ajax programming requires JavaScript
exchanges between the browser and the Web server. It also requires you to
program the changes to make in the Web page to receive responses; otherwise the
dialogues are unknown to the user.
Ajax requests are made asynchronously: the Web browser
continues to run JavaScript program while the application is part he does not
expect the response sent by the web server and the user can continue to perform
manipulations during this time.
1.4. Social Medias
According to Wikipedia, Social media is media using highly
accessible communication technologies to facilitate social interaction.
Social networks are groups of individuals or organizations
that discuss, speak, and interact with each other. They share opinions, ideas
or content. On the web, social networks are greatly favoured by the advent of
platforms such as Facebook, Twitter, YouTube and Linked In.
In fact, there are hundreds of platforms that create community
between people and / or businesses. This is why it is important, before
embarking on your "conquest" of the web, to determine where your customers, so
by extension what platforms to use.
There are several "families" of social networks:
· Personal social networks:
Here, we talk about networks like Facebook (with over 1
billion users to date, this is the best known and most popular). They allow
finding the knowledge, family members or friends. We can exchange photos and
videos, chat with them, organize events.
· Social entertainment networks:
They allow to share and stream music or videos. Among the best
known include among others as YouTube and MySpace (who just a facelift). These
are portals that can among others allow artists to make them known.
· Social business networks:
Linked In is a good example. This network allows you to
connect with colleagues in offices, suppliers, business partners or potential
employers. By creating a profile, they can include their resume and
accomplishments. We can also interact by discussing our industry.
Social networks today represent the majority of exchanges
messages in the world through internet outpacing mail service. A web portal can
also out of respect be compared to social media because many times offered by
web portals services make them social media forums like the service..
1.5. Web portals
Portal sites are websites whose primary purpose is to provide
users with resources and services related to a theme, a profession, a
geographic area or community.
Resources may be links to other sites reference discussion
forums or blogs, but can also consist of editorial content specific to the
portal.
These services can be of different types: specialized search
engine, email, personalized weather, calculation tools.
A web portal is most often one specially-designed web page
which brings information together from diverse sources in a uniform way.
Usually, each information source gets its dedicated area on the page for
displaying information (a portlet); often, the user can configure which ones to
display. Variants of portals include mash ups and intranet "dashboards" for
executives and managers. The extent to which content is displayed in a "uniform
way" may depend on the intended user and the intended purpose, as well as the
diversity of the content. Very often design emphasis is on a certain "metaphor"
for configuring and customizing the presentation of the content and the chosen
implementation framework and/or code libraries. In addition, the role of the
user in an organization may determine which content can be added to the portal
or deleted from the portal configuration.
A portal may use a search engine API to permit users to search
intranet content as opposed to extranet content by restricting which domains
may be searched. Apart from this common search engines feature, web portals may
offer other services such as e-mail, news, stock quotes, information from
databases and even entertainment content. Portals provide a way for enterprises
and organizations to provide a consistent look and feel with access control and
procedures for multiple applications and databases, which otherwise would have
been different web entities at various URLs. The features available may be
restricted by whether access is by an authorized and authenticated user
(employee, member) or an anonymous site visitor.
Examples of early public web portals were AOL, Excite,
Netvibes, iGoogle, MSN, Naver, Lycos, Indiatimes, Rediff, and Yahoo. See for
example, the "My Yahoo!" feature of Yahoo which may have inspired such features
as the later Google "iGoogle". The configurable side-panels of, for example,
the modern Opera browser and the option of "Speed Dial" pages by most browsers
continue to reflect the earlier "portal" metaphor.
1.5.1. Types of web portals
According to Wikipedia, we can have the following types of web
portals:
· Personal portals
A personal portal is a web page at a web site on the World
Wide Web or a local HTML home page including JavaScript and perhaps running in
a modified web browser. A personal portal typically provides personalized
capabilities to its visitors or its local user, providing a pathway to other
content. It may be designed to use distributed applications, different numbers
and types of middleware and hardware to provide services from a number of
different sources and may run on a non-standard local web server. In addition,
business portals can be designed for sharing and collaboration in workplaces. A
further business-driven requirement of portals is that the content be presented
on multiple platforms such as personal computers, personal digital assistants
(PDAs), and cell phones/mobile phone/mobile phones. Information, news, and
updates are examples of content that would be delivered through such a portal.
Personal portals can be related to any specific topic such as providing friend
information on a social network or providing links to outside content that may
help others beyond your reach of services. Portals are not limited to simply
providing links. Outside of business intracet user, very often simpler portals
become replaced with richer mash up designs. Within enterprises, early portals
were often replaced by much more powerful "dashboard" designs. Some also have
relied on newer protocols such as some version of RSS aggregation and may or
may not involve some degree of web harvesting.
· Government web portals
At the end of the dot-com boom in the 1990s, many governments
had already committed to creating portal sites for their citizens. These
included primary portals to the governments as well as portals developed for
specific audiences. Example of government web portal in Cameroon may include:
the web portal of the government in relation to the service of the prime
minister (
www.spm.gov.cm); the web portal of the
presidency of the republic of Cameroon.
· Cultural portals
Cultural portal aggregate digitized cultural collections of
galleries, libraries archives and museums. This type of portals provides a
point of access to invisible web cultural content that may not be indexed by
standard search engines. Digitized collections can include books, artworks,
photography, journals, newspapers, music, sound recordings, film, maps, diaries
and letters, and archived websites as well as the descriptive metadata
associated with each type of cultural work. These portals are usually based
around a specific national or regional grouping of institutions. Examples of
cultural portals include: Cameroun-Plus (
www.cameroun-plus.com)
a portal for touristic information.
· Corporate web portals
Corporate intranets became common during the 1990s. As
intranets grew in size and complexity, webmasters were faced with increasing
content and user management challenges. A consolidated view of company
information was judged insufficient; users wanted personalization and
customization. Webmasters, if skilled enough, were able to offer some
capabilities, but for the most part ended up driving users away from using the
intranet.
Many companies began to offer tools to help webmasters manage
their data, applications and information more easily, and through personalized
views. Portal solutions can also include workflow management, collaboration
between work groups, and policy-managed content publication. Most can allow
internal and external access to specific corporate information using secure
authentication or single sign-on.
Java Specification Request (JSR168, 2001), standards allow the
interoperability of portlets across different portal platforms. These standards
allow portal developers, administrators and consumers to integrate
standards-based portals and portlets across a variety of vendor solutions.
The concept of content aggregation seems to still gain
momentum and portal solution will likely continue to evolve significantly over
the next few years. The Gartner Group predicts generation 8 portals to expand
on the Business Mashups concept of delivering a variety of information, tools,
applications and access points through a single mechanism.
With the increase in user generated content, disparate data
silos, and file formats, information architects and taxonomist will be required
to allow users the ability to tag (classify) the data. This will ultimately
cause a ripple effect where users will also be generating ad hoc navigation and
information flows.
Corporate Portals may also offer customers & employees
self-service opportunities. Examples could be the portal of Orange Cameroon (
www.orange.cm) or the portal of MTN
Cameroon.
· Stock portals
Also known as stock-share portals, stock market portals or
stock exchange portals are web-based applications that facilitates the process
of informing the share-holders with substantial online data such as the latest
price, ask/bids, the latest News, reports and announcements. Some stock portals
use online gateways through a central depository system (CDS) for the visitors
(ram) to buy or sell their shares or manage their portfolio.
· Search portals
Search portals aggregate results from several search engines
into one page.
· Tender portals
A tender portal is a gateway for government suppliers to bid
on providing goods and services. Tender portals allow users to search, modify,
submit, review and archive data in order to provide a complete online tendering
process.
- Using online tendering, bidders can do any of the
following:
- Receive notification of the tenders.
- Receive tender documents online.
- Fill out the forms online.
- Submit proposals and documents.
- Submit bids online.
· Hosted web portals
Hosted web portals gained popularity and a number of companies
began offering them as a hosted service. The hosted portal market fundamentally
changed the composition of portals. In many ways they served simply as a tool
for publishing information instead of the loftier goals of integrating legacy
applications or presenting correlated data from distributed databases. The
early hosted portal companies such as Hyperoffice.com or the now defunct
InternetPortal.com focused on collaboration and scheduling in addition to the
distribution of corporate data. As hosted web portals have risen in popularity
their feature set has grown to include hosted databases, document management,
email, discussion forums and more. Hosted portals automatically personalize the
content generated from their modules to provide a personalized experience to
their users. In this regard they have remained true to the original goals of
the earlier corporate web portals. Emerging new classes of internet portals
called Cloud Portals are showcasing the power of API (Application Programming
Interface) rich software systems leveraging SOA (service oriented architecture,
web services, and custom data exchange) to accommodate machine to machine
interaction creating a more fluid user experience for connecting users spanning
multiple domains during a given "session". Leading cloud portals like Nubifer
Cloud Portal showcase what is possible using Enterprise Mash up and web Service
integration approaches to building cloud portals.
· Domain-specific portals
A number of portals have come about which are specific to the
particular domain, offering access to related companies and services; a prime
example of this trend would be the growth in property portals that give access
to services such as estate agents, removal firm, and solicitors that offer
conveyance. Along the same lines, industry-specific news and information
portals have appeared, such as the clinical trials-specific portal.
2. SUSTAINABLE DEVELOPMENT AND ICT
Promoted by some as the ideal solution to all environmental
problems, criticized by others as a growing source of concern and negative
impacts on our planet, ICT and their relation to sustainable development is a
subject that leaves no one indifferent.
Thus it is quite undeniable that ICT has many negative impacts
on our planet and it is mainly the energy consumption (Datacenter are big
energy consumers), the production of difficult to recycle electronic waste.
However it is equally undeniable that the contribution of ICT to sustainable
development places it as a leading actor. Indeed technological innovations that
come one after the other changing our ways of working, exchange, access to
entertainment. This contribution can be enjoyed on many levels corresponding to
a crossover approach to the pillars of sustainable development:
· At the level of governance: ICT is widely used at this
stage as the decision support tools. Many software are used to provide analysis
and even future projections.
· The establishment of competence networks: this can be
seen for example as the capacity offered through many internet web portal to
bring together experts in various fields to promote the exchange of
expertise;
· From the day before the first application of ICT
(information systems) to sustainable development has led to the search for
information to better understand the ins and outs of sustainable
development.
This means that this work is placed straight on the objectives
of ICT facing sustainable development. Because in addition to promoting
sustainable development, it also puts the computer science forward, where the
concept of "green IT".
3. LITERATURE REVIEW
This section will consider the various works that focused on
building a web platform so that we can learn from them, is to say that a
critical analysis is made.
Patrice Zangue GOGUIA (2013), designed and implemented a
communication platform for Cameroonian teachers. This means that he has
developed a web application to facilitate collaboration between teachers
regardless of their place of residence. This work is based on information
gathered from school activities, as well as a methodology and a common approach
to web applications (UML) to achieve a web application, a platform equipped
with a forum, a messaging service, and a database.
Prince MUJUMBE SALAMA (2012), designed and developed a web
portal for all the Burundian actors (businessmen, farmers, lawyers and others).
His work aims to promote dialogue between actors from different horizons
allowing a cultural mix and a stronger national cohesion. He made use of the
UML modeling method and numerous programming languages like PHP. However,
building a portal to a broad range of people and offering a large amount of
resources may prove to be in use to be a failure.
The «Portail du
DéveloppementDurable»of the BNF (BibliothèqueNationale
de France) is a portal that shows its functions just the way forward in
building the portal that will be ours, by presenting personalized functions
such as internal research. Let us recognize that many of the functions referred
to our portal are not included.
CONCLUSION
The chapter takes an end allowed us to highlight the shapes of
the subject of ours broadening our scope of knowledge of web applications and
the relationship between sustainable development and ICT. This means that the
subject is not ex nihilo and belongs to its time and the part that was so well
illustrated advantage will help us in refining our research methodology as well
as the selection of tools that will help us.
CHAPTER THREE:RESEARCH
METHODOLOGY AND MATERIALS USED
RESEARCH METHODOLOGY AND MATERIALS USED
INTRODUCTION
Any research necessarily involves several steps. This means
that once the preliminary investigations have been conducted, it is to choose a
methodology that will drive the project to completion. Thus, the abundance of
computer methods demands a rigorous examination of all possible choices. Also,
in the context of this application this chapter fits like a logical
continuation of the above will determine its content.
1. WEB APPLICATION ARCHITECTURE
In computing, the architecturerefers to the overall structure
inherent in a system, the organization of the different elements of the system
(software and/or hardware and/or humans and/or information) and relations
between elements. The Web architecture is the branch of the information system
architecture that is interested in web applications. There are currently a
large number of architectures used for the web.
1.1. The 2tiers architecture
It is composed of two parts, a client and a server. This
architecture can also be represented with a database server (DBMS).
In this type of architecture, the customer assumes
presentation tasks and communicates only with the application server. This type
of architecture can be developed very quickly depending on the complexity of
the project. There are a very large number of development languages and tools
for 2tiers architectures.
From the standpoint of convenience, the problem of
scalability, maintenance and implementation in complex projects must be taken
into account.
1.2. The 3-tiers architecture
Here the customer consists of a web browser and communicates
with the server.
This architecture consists of three elements or three
layers:
· The presentation layer (top level) often called HMI
(Human Machine Interface) is the visible and interactive part. This part is
designed for the Web in HTML usually with JavaScript, Flash.
· The business layer (second-level) is the functional
part of the application. The operations to be performed, the data access
functions and treatments are available to users and raised by their requests.
To provide these services, it sometimes relies on the data access layer and in
turn refers to the presentation layer the results it has calculated.
· The last layer (third level) manages access to system
data. These data can be stored on the same system (files, XML files, databases,
images ...) or other systems. Data access is transparent to the business layer
and is the only concern of the data access layer.
1.3. The n-tiers architecture
N-tiers architecture has been designed to overcome the
limitations of 3-tiers architectures and develop powerful applications and
simple to maintain. From a theoretical point of view, this architecture allows
to solve the following problems:
· It allows the use of rich clients.
· It clearly separates all levels of the application.
· It facilitates the management of sessions.
· It provides great expandability.
One possible definition of this type of architecture is: a
3tiers architecture in which the data processing (data access layer or
middleware) itself contains several layers multiplying the third.
1.4. The MVC architecture
The MVC architecture proposed by Sun is the server-side Web
development solution that separates the logical part / business part of the
presentation in a Web application. This is an essential part of development
projects because it allows the team to work separately (each has its files,
software development and its components).
This architecture has its origins in the SmallTalk language
early 1980. The main objective is to divide the application into three distinct
parts: the model, view and controller.
2. MODULES OF APPLICATION WEB SITE
In a comprehensive way, the modules can be defined as the
constituent parts of a system. In terms of IT, a program usually consists of a
set of sub-programs (modules) that form a whole. Web applications are no
exception to the rule, and more dynamic web site pages more likely it is to
have modules. Therefore, our portal will also have many modules that are
consistent with its objectives.
3. RESEARCH DESIGN
Here, reference is made to the conceptual framework in which
the desired project is completed. Thus, the objectives have already been
located, however, point out that the data used in the whole process are
secondary data. The major source of information is without doubt the
internet.
4. ANALYSIS METHODS
4.1. Object Oriented Methods
Object modeling is to create a computer model of the user's
system (a computer system). This model can bring both elements of the real
world concepts or ideas around business or field which will be part of the
system.
4.1.1. UML method
UML (Unified Modeling Language) is a graphical modeling
language based on pictograms. He appeared in the world of software engineering,
as part of the "object-oriented design." Commonly used in software projects, it
can be applied to all kinds of systems are not limited to the IT sector.
4.1.1.1. Advantages
· The standardization of object concepts, which have
clear benefits in terms of computer applications.
· The reusability of software components,
· Ease of maintenance,
· The ease of prototyping and extension of
applications.
4.1.1.2. Limits
· The time it takes to manage and maintain the UML
diagrams is too long;
· A large additional work is necessary to synchronize the
code with the diagrams
4.1.2. UP method
Unified Process (UP)
is a management method of the life cycle of software development and
therefore, for the object-oriented software. This is a generic method,
iterative and incremental.
4.1.2.1. Advantages
It is adapted to the work context, the needs of the user, the
library reuse opportunities or "bricks" preexisting.
UP method has a bidirectional architecture that minimizes the
risks against the grain to the needs and the risk of infinite developments,
indefinite, unclear or incomplete: Here the user can correct itself on
prototypes, turn that takes development. From the beginning of operations,
tangible results are obtained even if they are only prototypical.
4.1.2.2. Limits
The development of the architecture is coarse and independent
of use case
4.2. Functional methods
4.2.1. SADT
method
Structured Analysis and Design Technic (SADT) is a method of
American origin, developed in 1977, it spread in the late 1980s as one of the
standard graphic description of a complex system down by functional analysis,
that is to say that the analysis travels from the general to the specific and
detailed. SADT is a systemic approach to modeling a complex system or operating
process.
4.2.1.1. Advantages
· Structure hierarchical level by allowing clarification
and analytical breakdown of the complexity of a system.
· Timeless Diagram.
· Saves time.
4.2.1.2. Limits
· No sequential representation.
· Lack of operation in Boolean logic (AND, OR).
· Inability to a global view, except "the highest
level"
4.2.2. MERISE
method
MERISE is a French acronym, «Méthode de
Recherche Informatique pour les Systèmes d'Entreprise». It is
a method of analysis, design and IT project management. MERISE has been widely
used in the 1970s and 1980s to the massive computerization of organizations
4.2.2.1. Advantages
MERISE method has as undeniable advantage of allowing a clear
definition of the overall information system and to define correctly the
perimeter.
The strength of the MERISE method is to structure the needs of
decision makers in a simple and understandable way. MERISE improves
communication between different actors in the development process. This method,
thanks to its models, oversees the project and thereby protects the speakers of
a possible development irrelevant.
Follow this intellectual journey may also help the company to
better know, understand each other better and thus communicate better.
4.2.2.2. Limits
MERISE method is ill-suited to distributed environments where
multiple external applications to a domain come interact with the application
to model. Moreover, it is not able to model the semantic identifiable
information (documents).
4.3. Choose of a method
MERISE should definitely match the research work of ours as
it is true that his grip does not require a lot of time as its application to
the project given the constraints and requirements are ours.
5. MERISE STEPS
5.1. MERISE levels
5.1.1. Conceptual level
The conceptual level is to design the SI disregarding all
technical and organizational constraints and these both in terms of data
treatment.
The conceptual level answers the question What? (On what to
do, what with data).
The MERISE formalism used is:
· The Data Conceptual Model (DCM).
· The Treatment Conceptual Model(TCM)
5.1.2. Organizational level
The organizational level's mission is to integrate the
analysis criteria related to the organization studied. The organizational level
will define the notions of temporality, chronology of operations of unity of
place, will define the workstations, access to data bases.
The questions at the level of treatment are:
· Who?
· Where?
· When?
The MERISE formalism used is:
· The Data Organizational Model (DOM).
· The Treatment Organizational Model of Treatment
(TOM).
5.1.3. Logical level
Logic is independent of hardware, programming languages and
data management. This is the answer to the question What with?
The formalism will:
· The Data Logical Model (DLM).
· The Treatment Logic Model (TLM).
5.1.4. Physical level
The physical level defines the actual organization (physical)
of data. It provides technical solutions, such methods of storage and access to
information. This is the answer to the question What?
The formalism used is:
· The Data Physical Model (DPM).
· Physical Treatments and Operational Model (PTOM)
5.2. Data dictionary
The data dictionary is a document that allows identifying,
classifying and sorting all the information (data) collected during interviews
or study the documents. The dictionary can be more or less elaborate depending
on the desired level of granularity. The dictionary data generally includes the
following information:
· The name of the data: the name that will be used to
represent the data in the database and the computer program
· Description: This field gives the meaning of the
element;
· The type of data: this field represents the data type
to use for the backup of each element;
· Nature: This setting will help in the representation of
data in the database;
· Size: the representation of the maximum amount of data
that will contain every element;
· The observation shows the importance of the given
degree.
On our portal for sustainable development, we have the
following data dictionary:
Table 1: Data
dictionary
|
N0
|
Name
|
Description
|
Type
|
Nature
|
Size
|
Observation
|
|
1
|
Doc_id
|
Document id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
2
|
Doc_name
|
Document name
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Obligatory
|
|
3
|
Doc_description
|
Document description
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Facultative
|
|
4
|
Doc_path
|
Document path
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Obligatory
|
|
5
|
Link_id
|
Link id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
6
|
Link_name
|
Link name
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Obligatory
|
|
7
|
Link_description
|
Link description
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Facultative
|
|
8
|
Link_url
|
Link url
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Obligatory
|
|
9
|
Art_id
|
Article id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
10
|
Art_title
|
Artcicle title
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
100
|
Obligatory
|
|
11
|
Art_content
|
Article content
|
Text
|
AN
|
|
Obligatory
|
|
12
|
Art_author
|
Article author
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Facultative
|
|
13
|
Art_date
|
Article publication date
|
Date
|
y/m/d
|
|
Facultative
|
|
14
|
Art_media
|
Article media file
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Facultative
|
|
15
|
Sug_id
|
Suggested content id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
16
|
Sug_type
|
Suggested content type
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Obligatory
|
|
17
|
Sug_author
|
Suggested content author
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Obligatory
|
|
18
|
Sug_cont
|
Suggested content contain
|
Text
|
AN
|
|
Obligatory
|
|
19
|
Sug_date
|
Suggested content date
|
Date
|
Y/M/D
|
|
Facultative
|
|
20
|
Sug_media
|
Suggested contentmedia file
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
100
|
Facultative
|
|
21
|
Mess_id
|
Message id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
22
|
Mess_send
|
Message sender
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
23
|
Mess_recei
|
Message receiver
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
25
|
Mess_cont
|
Message content
|
Text
|
AN
|
|
Obligatory
|
|
26
|
Mess_date
|
Message date
|
Date
|
Y/M/D
|
|
Facultative
|
|
27
|
User_id
|
User id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
28
|
User_name
|
User name
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
100
|
Obligatory
|
|
29
|
User_loc
|
User location
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
50
|
Facultative
|
|
30
|
User_prof
|
User proffession
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
50
|
Facultative
|
|
31
|
Top_id
|
Topic id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
32
|
Top_title
|
Topic title
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
100
|
Obligatory
|
|
33
|
Top_descr
|
Topic description
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Obligatory
|
|
34
|
Top_sub_nbr
|
Number of subjects
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Facultative
|
|
35
|
Sub_id
|
Subject id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
36
|
Sub_title
|
Subject title
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
100
|
Obligatory
|
|
37
|
Sub_descr
|
Subject description
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
255
|
Obligatory
|
|
38
|
Com_id
|
Comment id
|
Int
|
N
|
10
|
Obligatory
|
|
39
|
Com_author
|
Comment author
|
Varchar
|
AN
|
100
|
Obligatory
|
|
40
|
Com_cont
|
Coment contain
|
Text
|
AN
|
|
Obligatory
|
|
41
|
Com_date
|
Comment date
|
date
|
AN
|
|
Facultative
|
5.3. The Data Conceptual Model (DCM)
The DCM is based on entity concepts and association and on
the concepts of relationships. Graphing, simple and accessible, allowing a
non-IT to participate in its development. The basic elements of a conceptual
data model are:
· Properties;
· Entities;
· Relations.
5.3.1. Entities
The entity is defined as a management object considered of
interest to represent the activity model (eg user entity) and each entity
carries one or more simple properties, including one called atomic, unique and
discriminant is designated as an identifier.
The establishment of this portal requires the following
entities:


Figure 1: Entities of the
project
5.3.2. Properties
The properties are the basic information of the information
system. They are essential and basic information.
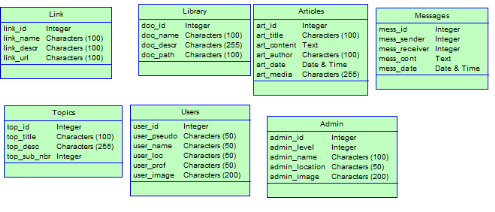 
Figure 2: Entities
attributes
5.3.3. Occurrence
An instance is the value taken by an attribute. Thus, each
entity has a case.
5.3.4. Identifier
One of these properties has a specific role, it is also known
as the key identifier. The identifier is used to find a safe and unique way all
the properties involved in the entity. We must find or invent a property when
its value is known allows the knowledge of all the values attached to it
formally.
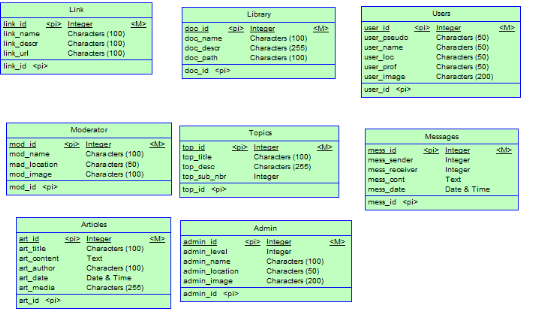
Figure 3: Entity
identifiers
5.3.5. Associations and
Cardinalities
The association is a semantic link between one or more
entities: the association can be reflexive, preferably binary, and ternary
sometimes or even higher dimension. It may also be a carrier of one or more
properties.
The association is enriched by the notion of cardinality, it
indicates the minimum and maximum number of times any occurrence of an entity
can participate in an association, and we can have:
· Minimum Cardinality
- 0 if an occurrence of the entity may exist while not
interfering in any occurrence of the association
- 1 if an occurrence of the entity can exist only if it occurs
in at least one occurrence of the association
- N: Rare cases to avoid
· Maximum cardinality
- 1 if an occurrence of the entity cannot be involved in more
than one occurrence of the association
- N whether an instance of the entity cannot be involved in
more than one occurrence of the association
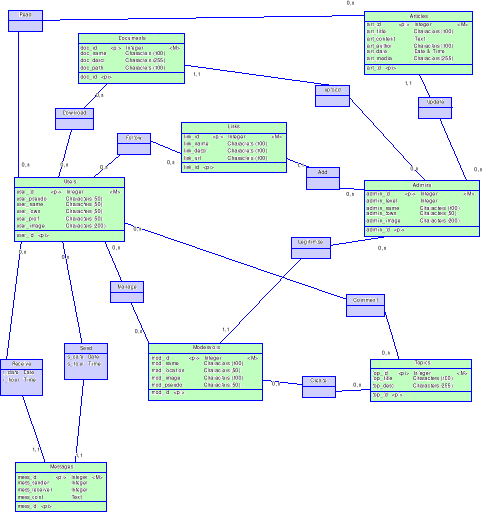
Figure 4: Associations and
cardinalities
5.3.6. Normalisation rules
This is about the rules to be observed the relationship
entity association to be valid.
·
Normalisation of names
The name of an entity, his attributes and the name of the
association between the entities must be unique. Two entities can't have the
same attribute name.
·
Normalisation of identifier
A good identifier should avoid too much attributes, and should
have the lesser number of characters as possible.
·
Normalisation of attributes
It is recommended to avoid entities with too many attributes
by replacing those attributes with associations.
·
Normalisation of attributes of associations
The associations attributes must directly depend of the
identifiers of the table that the association link.
·
Normalisation of associations
Associations should be materialise with verb in the infinitive
form or eventually in the passive form.
5.3.6.1. First Normal Form (1NF)
A relation is in first normal form if:
- All attributes contain only one atomic value (not
divisible).
- The attributes do not contain repetitive values.
5.3.6.2. Second Normal Form (2NF)
A relation is in second normal form if:
- She is in first normal form.
- If all the non-key attributes do not depend on a part of the
primary key.
In other words, any property of the relationship must depend
entirely of the key.
5.3.6.3. Third Normal Form (3NF)
A relation is in third normal form if:
- She is in second normal form.
- If all functional dependencies on the key are direct (if
there is no transitive functional dependencies between non-key attributes).
In other words, all of the attributes do not belong to the key
does not depend on a non-key attribute.
5.3.7. Complete CDM
Following the rules stated above, we developed the conceptual
model of the following data:
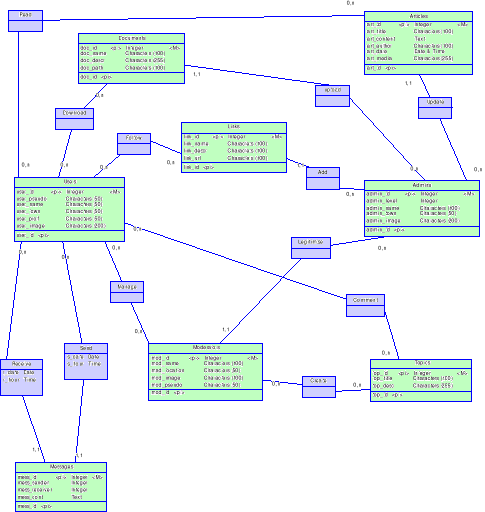
Figure 5: Complete
Conceptual Data Model
5.4. Data Logical Model (DLM)
The DLM is the normal result of MERISE process. Its purpose
is to bring us closer to the physical model. For this, we start from the
Conceptual Data Model and the relationships we remove it within certain
pre-established rules.
5.4.1. Definition of concepts
The LDM provides technical vocabulary again that it is
important to understand well.
5.4.1.1. Tables, columns and rows
So that was an entity Data Conceptual Model is a table in the
DLM. Thus this table is organized in line or column and each column represents
the fields of the table and each line represents the values for each field.
5.4.1.2. Primary and foreign keys of each table
The identifier that had the DCM, DLM is the primary key which
can be recognized by its underlining. Also a table can contain the primary key
of another table that at that moment becomes a foreign key. Which foreign key
is symbolized by a sharp before his name. Thus:
- A table has only one primary key, but can have multiple
foreign keys;
- The foreign key can be made;
- The column of the primary key cannot be empty;
- The foreign key can also be primary key in the table.
.
5.4.2. From DCD to Data Logical
Relational Data Model (DLRM) rules
As mentioned above, the passage of the DCM to DLRM is purely
mechanical, simply meet and set some rules.
5.4.2.1. Entity and table
Each entity becomes a table and therefore, the identifier
becomes the primary key, the properties of the entity become the table
attributes.

Figure 6: the table
Article
5.4.2.2. Binary relation with cardinalities (X,1) - (X,n),
X=0 or X=1
The entity type cardinality 1.1 or 0.1 absorbs the identifier
of the strongest entity (0, n or 1, n). This identifier is then called the
foreign key.
5.4.2.3. Binary relation with the cardinalities (X,n) -
(X,n), X=0 or X=1
Where n is the maximum cardinality of both sides of the
relationship it becomes entity and absorbs identifiers each related entity.
Without enough IDs are the new key of the entity. This new key is formed by the
concatenation of the foreign key related entities.
5.5. From Data Logical Relational Model (DLRD) to Data
Physical Model (DPM)
Building the Physical Data Model is to transform the Logical
Data Model into a series of relationships. This step completes the data
processing process. The implementation of the databases can be performed
optimally.
5.6. Data Physical Model
The Data Physical Model is the final step in the data
management process MERISE method. All analysis was carried out upstream, most
of the work of reflection was framed by the conceptual model, and the
transition to the physical model is a mere formality.
We thus obtain the following diagram:
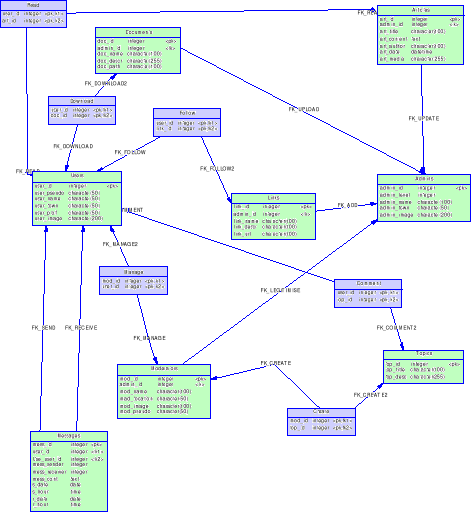
Figure 7: final relation
schema
6. MATERIALS USED
The actual conduct of this project required the involvement
of numerous tools both hardware and software whose role will be declined as
well.
6.1. Software
This refers to a list of software that helped in the
construction of the project and the various programming languages used.
6.1.1. HTML
The Hypertext Markup Language, HTML generally short, is the
data format designed to display web pages. It is a markup language that allows
writing of hypertext, hence its name. HTML also allows structuring semantically
and formatting the page content, to include multimedia resources including
images, input forms, and programmable elements such as applets. It allows the
creation of interoperable documents with varied amenities manner consistent
with web accessibility requirements. It is often used in conjunction with
programming languages (JavaScript) and presentation formats (cascading style
sheets). HTML is originally derived from the Standard Generalized Markup
Language (SGML).
In this work, it is the HTML 5 to be used, this version offers
new attributes and tags and new specifications.
.
6.1.2. CSS: Bootstrap framework
CSS (Cascading Style Sheets) is a computer language used to
describe the presentation of HTML and XML documents. The standard defines CSS
are published by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). Introduced in mid-1990,
CSS is commonly used in web design and well supported by web browsers in the
2000s.
Note that until today, many CSS features are incompatible for
some browsers. And it is the same for the CSS3 version that is used in this
project, even some specifications have not yet been integrated in most
browsers.
Thus, in order to make the development easy, we associate the
Bootstrap framework, which is a CSS framework put in place by twitter to help
in the building of websites. Bootstrap associate JQuery to involve more
performance.
6.1.3. JavaScript
According to Wikipedia, JavaScript is a scripting programming
language mainly used in interactive web pages but also on the server side. It
is an object oriented language by the prototype, that is to say that the basic
language and key interfaces are provided by objects that are instances of
classes, but which are each equipped with builders for generating their
properties, including a prototype property that allows to generate custom
objects heirs.
JavaScript code can be integrated directly into Web pages, to
be executed on the client. This is when the web browser that supports the
execution of these programs called scripts.
Generally, JavaScript is used to control the data entered in
HTML forms, or interact with the HTML document via the Document Object Model
interface provided by the browser (this is sometimes called dynamic HTML or
DHTML). It is also used to perform dynamic services, sometimes pointless,
strictly cosmetic or for ergonomic purposes.
JavaScript is not limited to the handling of HTML documents
and can be used to manipulate documents SVG, XUL, and other XML dialects. On
the contrary, the possibilities of language are seen increased through new
technologies (AJAX, JSON) and many libraries (including JQuery, SeaHorse).
6.1.3.1. AJAX
According to the Web Dictionary, AJAX means software
architecture for creating pages and to interact with the user web applications
and / or other applications without the need to reload page in the web browser
client. This means AJAX relies on technologies present in the different web
browsers, including JavaScript and XML, which are included in the acronym AJAX
"Asynchronous JavaScript and XML".
AJAX does not bring anything new compared to these
technologies, most of which have existed for many years. However it offers a
method to use them together to create dynamic applications executed by
browsers.
6.1.3.2. JQuery
JQuery JavaScript Library is a free, multi-platform created
to facilitate client-side scripting in the HTML code of web1 pages. The first
version was launched in January 2006 by John Resig.
The library contains the following features:
· Browse and change the DOM;
· events;
· Visual effects and animations;
· Manipulation of Cascading Style Sheets (adding /
removing classes, attributes ...)
· Ajax;
· plugins;
· Utilities.
6.1.4. PHP
PHP acronym originally meant Personal Home Page. For
RasmusLerdorf, the author of what became Scripting embeddable server side
throughout XHTML document that we know, this meant adding some functionality to
their personal pages. PHP stands for PHP Hypertext Preprocessor today because
it refers to an XHTML document browser built by the script engine Zend Engine 2
PHP. It allows creating dynamic and interactive Web pages.
PHP's strengths are firstly it is free and allows you to
create powerful web applications, on the other hand PHP since version 5 is
object oriented. It is this version that is used in this work.
Although sometimes attributed to him the characteristic of
being low in terms of safety, PHP has a powerful community, and served to the
world renowned building sites like Facebook.
.
6.1.5. SQL
Structured Query Language (SQL) is a standard computer
language used to perform operations on databases. Created in 1974, the SQL is
standardized since 1986, the language is recognized by the vast majority of
database management systems.
The SQL data manipulation language section allows you to
search, add, modify or delete data in databases. Coupled to the PHP SQL, it
allows the web application to interact with the database.
In addition to the data manipulation language, the language
of data definition to create, edit and organize data in the database, the
transaction control language section allows you to start and finish the
transaction, and data control language section to allow or deny access to
certain data to certain people.
6.1.6. WampServer
WampServer is a web development platform WAMP type, for
operating locally (without connecting to an external server) PHP scripts.
WampServer is not in itself a software, but an environment with two servers
(Apache and MySQL), a script interpreter (PHP) and PhpMyAdmin to administer Web
MySQL databases.
6.1.7. Aptana Studio
Aptana Studio is an integrated development environment
oriented web, multi-platform and open-source. It makes writing code by
providing entry aids for JavaScript, HTML, CSS, PHP and Python.
Aptana is available standalone or plugin in its original
environment: Eclipse. Aptana has several plugins to program for languages /
platforms like specific RadRails, Adobe Air and many others.
6.1.8. Web browsers
A web browser is a software designed to browse the web.
Technically, it is at least an HTTP client. These are complex and evolving
software, mainly in security, as new viruses, spyware and other malicious
scripts continue to emerge, but also in terms of functionality because of new
standards or standards revisions see regularly updated.
The main function of a web browser is to allow the
consultation information available ("resource" in the Web terminology) on the
World Wide Web. The main stages of the consultation of a resource are:
· The user gives to the web browser the web address
resource to consult. There are three ways to give a web address:
- Typing yourself the web address in the browser address
bar;
- Choose a resource in the list of favorites (or bookmark this
page or bookmark), knowing that every favorite is associated a web address;
- Follow a hyperlink, knowing that each link is associated a
web address.
· The browser connects to the web server hosting the
resource referred and downloads. The communication protocol generally used is
http.
· Rendering engine of the browser treats this resource,
downloads any associated resources and displays the result on the user's
screen.
Web browsers will be fully customary in the process of
developing this web application for both tests for debugging. And those used
are the two most popular browsers such as Google Chrome and Mozilla Firefox.
6.1.9. Adobe Photoshop
Photoshop is an editing software, processing and computer
aided drafting edited by Adobe and owned for quite some years after Adobe CS.
It is mainly used for processing digital photographs, but also serves to create
images from scratch. He works mainly on raster images because the images are
made up of a grid of points called pixels (for Picture Element). The interest
of these images is to reproduce subtle gradations of color.
6.1.10. Power
designer
PowerDesigner is a collaborative enterprise modeling tool
produced by Sybase. PowerDesigner runs under Microsoft Windows as a native
application, and runs under Eclipse through a plugin. PowerDesigner supports
model-driven architecture software design. PowerDesigner uses the .pdm file
format.
PowerDesigner provides a single modeling environment that
brings together the techniques and notations of business process and
requirements modeling, data modeling, enterprise architecture modeling, and UML
application modeling.
6.2. Hardware
The main unit use is an HP laptop brand (Pavilion dv7) adopts
a 2.3GHz AMD Dual Core processor. In 3GB RAM, with a resolution of 17.3 inches.
7. CONCEPTION AND REALIZATION OF THE
APPLICATION
7.1. Classification of needs of the future users
A web portal as we have said above is a site that offers a
wide range of resource, a gateway to a specific area. Thus the following
features to respect our portal we seem to be necessary: a news page, a member
area, a messaging system, links to other reference sites, a downloadable
document page and the possibility for a member to propose content.
This means that the objectives for users are clear and
precise. However, these goals can only be achieved with the completion of a
minimum of conditions.
7.1.1. Functional needs
The portal for sustainable development must therefore offer
many features to allow the apotheosis of our goals. And these features are:
· forum
The user must be able to access the different topics discussed
in the forum. It should equally be able to see the comments of website
subscribers. However, the ability to comment in the forum is determined by an
inscription on the site as well as the ability to exchange private messages
with members of the forum. Also registered members on the forum have a visible
profile page of the portal only to members. It must also be possible for these
members to check out the lists of registered members on the site.
· The suggestion to content
Anyone authenticated on the site gets the opportunity to
suggest content. This content can be as much an article, a downloadable
document, or a link to share with the users of the site.
· The consultation paper
These articles that appear year homepage can be read by all
site visitors. Although registered members can receive an e-mail alert if they
agree.
· Hyperlinks
This page of our platform should offer the ability for users
to follow links to better learn about the different areas.
· A library
This page may show downloadable documents in relation to the
portal activities.
.
7.1.2. Non-functional needs
7.1.2.1. Quality requirements
Any site that is an attractive must be coherent and
non-polluting beauty this in order to retain its members. So we must ensure the
usability of the application. So the quality criteria may be stated as
follows:
· Ergonomics:
The need to ergonomic websites has even led to the birth of a
new discipline in web design, ie its importance to our portal. The ergonomic
approach proposes to give the power back to the human being that far from being
dependent objects must instead make use. Therefore our platform has to be
comfortable, simple, and effective.
· Assistance
The user must be able to receive assistance on certain pages
such as those forms so that we ensure that the meaning of each field is clearly
understood.
7.1.2.2. Performance requirements
Achieve a proper and sober application is a good thing, but
it must at all costs be accompanied by a certain performance. Thus we propose
the following objectives:
- The platform must be very reactive, the pages must be able
to refresh automatically;
- Errors must generate understandable messages for users;
- The document catalog must contain more than a thousand
document;
- The number of simultaneous connection must be greater than
1000;
7.2. Functional specifications
Of course the platform must be accompanied by a database.
Which database should be updated automatically from the forms of the portal.
And save each item must contain all necessary references to a possible recovery
to be displayed on a page of the site then be modified or deleted view of the
database. This applies to articles, documents and links.
The personal data of users will be protected just as the
transmission of data to the database.
7.3. The software life cycle
Laurent AUDIBERG (2008) defines the life cycle of software as
all stages of software development, from conception to its demise. The goal of
such a division is to define intermediate milestones for validation of software
development, that is to say, the compliance of the software with the expressed
needs, and verification of the development process, it is -to say the
appropriateness of the methods implemented.
The origin of this division comes from the fact that the
errors have a higher cost as much as they are detected late in the
implementation process. The life cycle can detect errors earlier and thus to
control the quality of the software, the time of its implementation and the
associated costs.
The software life cycle typically includes at least the
following steps:
- Goal Setting: This step is to define the
purpose of the project and its inclusion in a comprehensive strategy.
- Needs analysis and feasibility: that is to
say the phrase, collecting and formalizing requirements of the applicant (the
client) and the set of constraints, and estimate the feasibility of these
requirements.
- Specifications and overall design: This is
the development of specifications of the general architecture of the
software.
- Detailed Design: This step is to clearly
define each subset of the software.
- Coding (implementation or programming): it
is the translation into a programming language features defined during design
phases.
- Unit Testing: They allow you to
individually verify that each subset of the software is implemented according
to specifications.
- Integration: The objective is to ensure
that the interfacing of different components (modules) of the software. It is
the subject of integration testing in a document.
- Qualification (or recipe): That is to say,
the verification of compliance software to the initial specifications.
- Documentation: It aims to produce the
information needed to use the software and further developments.
- Put into production: the deployment
software site.
- Maintenance: It includes all corrective
actions (corrective maintenance) and scalable (scalable maintenance) on the
software.
The sequence and the presence of each of these activities in
the life cycle depend on the choice of a life cycle model between the client
and the development team. The life cycle can take into account the technical,
organizational and human aspects.
7.4. Structure of the web application
Taking into account the objectives of our platform,
architecture and the examples set by other portals of the same type, we have
set up this structure.
USERS SPACE
FORUM CATHEGORYIES
SUGGEST LINKS
SUGGEST DOCUMENT
SUGGEST ARTICLE
LIBRARY
USEFUL LINKS
SUGGEST CONTENT
FORUM
ADMIN
CONTENT SUGGESTED
HOME
INSCRIPTION
UPDATE LINKS
UPDATE ARTICLES
UPDATE DOCUMENT
FORUM SUBJECT
COMMENTS
PRIVATE MESSAGES
USER PROFILE
USERS LIST

Figure 8: Structure of the
application
8. PARTIAL CONCLUSION
So we come to the end of this chapter that wants to be the one
through which all design activities end and gives the way forward for the
construction of the application.
CHAPTER FOUR:RESULTS AND
DISCUSSION
RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In this chapter we will using the screen capture strive to
show the results obtained followed possibly comment.
1. HOMEPAGE
1
The home page presents the hyperlink functions through images
leading to the main parts of our platform. However some pages are only
accessible if the user is identified and also if and only if it is the
administrator
5
4
3
2
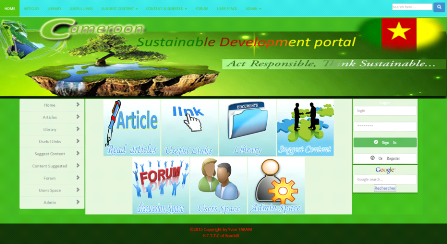
Figure 9: Visitor
Homepage
1- Search form
2- Google customize search form
3- Login form
4- Main menu
2. CONNECTION / DISCONNECTION
The connection is an essential aspect of our portal since it will
regulate access and use of certain parts of our platform. So on the home page
is placed a login form available below with the link to open the registration
page. The figure below show the connection form and the link to the
registration page
1
2
Figure 10: Connection
form
In the figure, the number 1 to 2 represents:
1: connection form using login and a password.
2: Link to access to registration form.
The connection ask to the user to enter his login and password
followed by enter.
2.1. Subscribe
For users who want to enjoy all the benefits, enrolment is a
major step and it is through the following form:
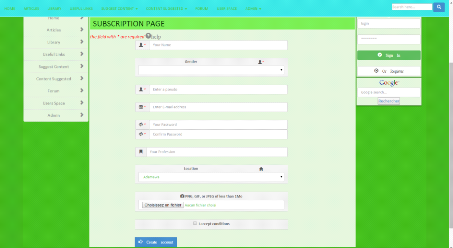
Figure 11: suscription
form
This form illustrated by the figure ask the user to enter some
information like his name, gender, location, picture and to choose a pseudo and
a password to be used next time for login. In case of failure in filling the
form that account will not be created.
2.2. Disconnection
Once connected, the space formally reserved to the login form
is now for the presentation of the current user's photo and his ID while
providing a logout button. This is illustrated by the figure bellow
1

Figure 12: Disconnection
button
The number 1 on this figure represents the disconnection
button.
Then by clicking on this button the current session is ended.
3. CONSULT PAGES
These are pages that allow you to either view the contents of the
portal, or to download the documents available or to follow the available links
to other sites operating in the same field.
3.1. Link page
The figure below presents the useful link pages

Figure 13: Useful links
page
The page is made of three main parts: category, link and
description. Therefore, by clicking on the link the user is automatically bring
on another page.
3.2. Article page
This page show the actuality of sustainable development in our
country trough text accompany by picture or eventually video.
3.3. Document page
Here we have a collection of document related to our topic
which can then be downloaded illustrated by the figure below.
2
1
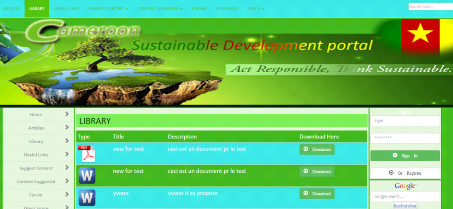
Figure 14:
Library
The numbers on the figure represents:
1- Document type
2- Link button to download the document
The library can contain document which can be downloaded
through the download button.
4. SEARCH
On our platform, we have both sought an engine that is internal
and the other external.
4.1. Search in the website
The research here is done in the items available in the
database. The key words are entered in the top search bar and the results
appear as shown in the figure bellow:
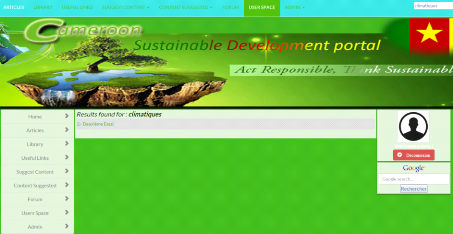
Figure 15: search
results
The results appear in the aspects of numerated links which can
then be followed.
4.2. Google customize search
Google Custom sought is made from the desired form and the
results appear in a Google window.
5. PROPOSE CONTENT AND GENERAL
ADMINISTRATION
It is here given the opportunity to the administrator as the
single user to contribute to the updating of the portal. The forms are the
same, only difference the content offered by a user waits for the validation of
the administrator to be visible.
5.1. Link
Figure below represents the link creation form.

Figure 16: new link
form
To add a new link, the user must provide a title, link,
description, and choose his Cathegory.
5.2. Article
The figure below represents the article creation form.
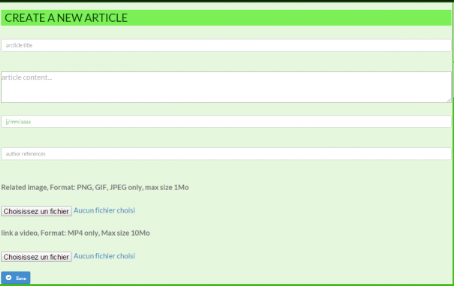
Figure 17: new article
form
The addition of a new article is done by providing a title,
content, author references and the date, then, we can link an image and / or
video.
5.3. Document
The figure below show the new document creation formula:
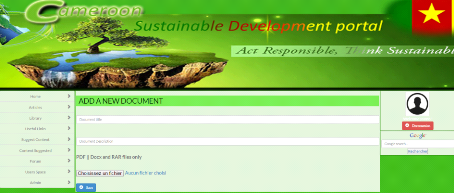
Figure 18: new document
form
To add a new document, you must provide a title and a
description to this document. The document must not exceed 10MB.
6. FORUM
The forum is organized around central themes divided into topics
that can be commented on by users.
6.1. Read topics
The figure below represents the forum welcome page and the
list of topics.
2
1
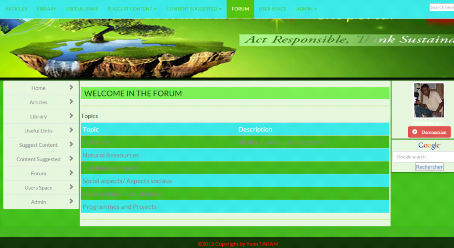
Figure 19: forum
homepage
The number on the figure represents:
1- Topic name
2- Topic description
In this figure appears the list of topic as well as their
description.
6.2. Read subjects
The figure below represents an example of list of subject for a
specific topic.
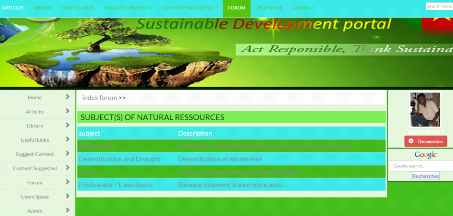
Figure 20: forum
subjects
As for the list of topics, this list has two columns, the title
and the description of the subject.
6.3. Read and publish comment
The figure below show the comments for a specific topic and
the comment form.
2
1
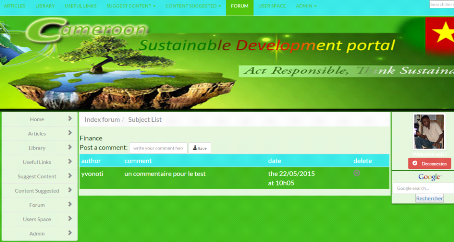
Figure 21: forum
comment
The number on the figure represents:
1- Form to share a comment
2- List of comments with their author and the date of
publication.
7. USER SPACE
7.1. Private Messages
7.1.1. Read messages
The figure below show the message list of the user
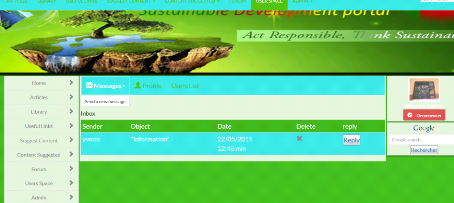
Figure 22: read
messages
As presented in the figure, the user reads his message has the
ability to delete or answer to the message.
7.1.2. Send messages
The figure below represents the new message form.
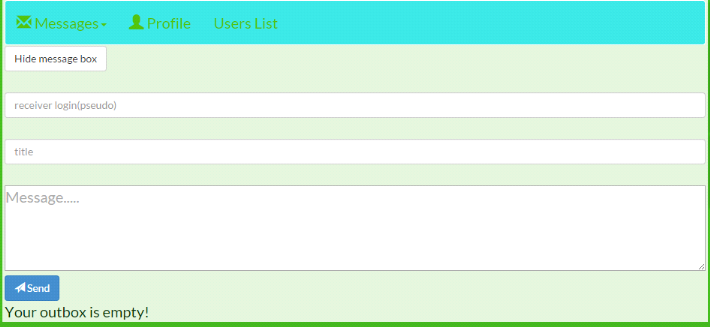
Figure 23: new message
form
To send a new private message, the form must contain the
recipient's pseudo, a title and the content itself.
7.2. Profile
The figure below shows a profile view page
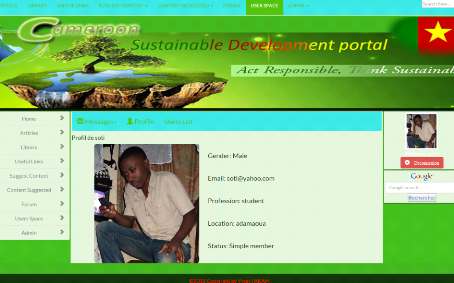
Figure 24: profile
view
Any user can see his profile page which displays his profile
picture and some personal information.
7.3. User list
The figure below shows the user list page.

Figure 25: User
list
Here, we have the list of users with their picture, their pseudo
and their profession.
8. ADMINISTRATION
8.1. Forum administration
The figure below displays the forum topics administration
page.
3
2
1
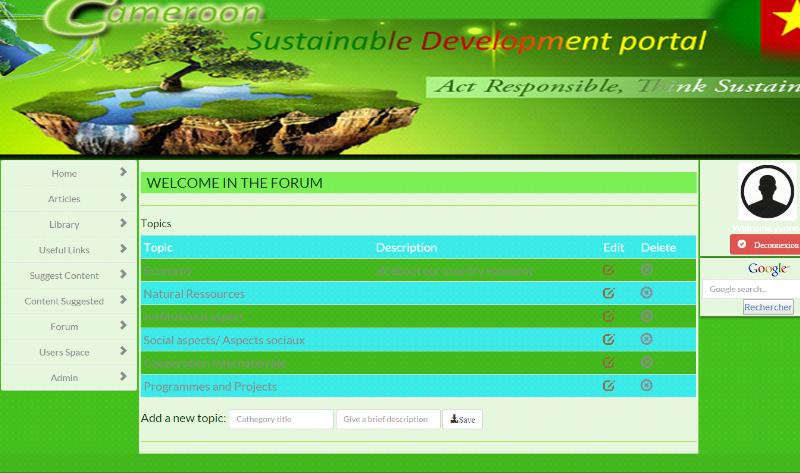
Figure 26: forum
management - topics
The numbers on the figure represent:
1- Edit the topic
2- Delete the topic
3- Create a new topic
The figure below shows the forum comments administration
1
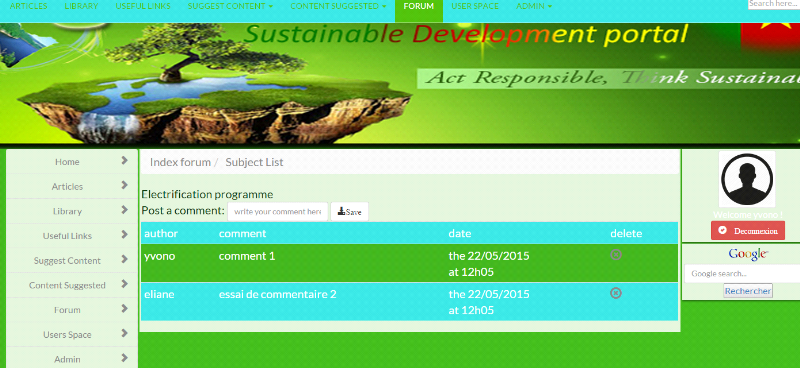
Figure 27: forum comments
management
The number on the figure represents:
1- Delete the comment
Then if the comment is not appropriate it can be deleted.
8.2. Users administration
The figure below displays the user's management page.
1
2
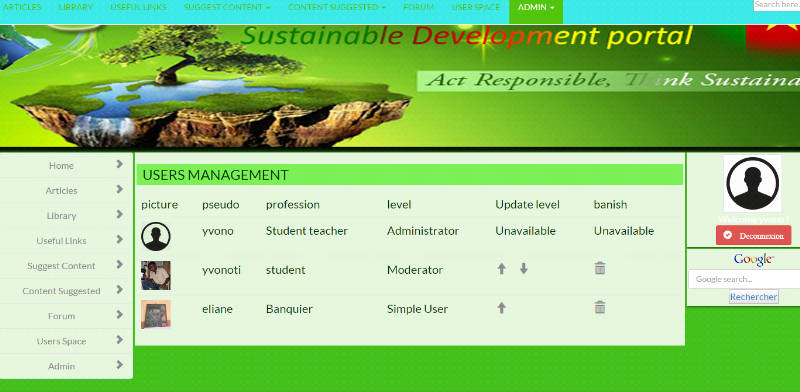
Figure 28: user
management
The numbers on the figure represents:
1- Update the level of a user (upgrade or move down)
2- Banish a user.
CHAPTER FIVE:GENERAL
CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
GENERAL CONCLUSION AND RECOMMENDATIONS
1. SUMMARY OF FINDINGS
This chapter comes as close a logical series which allowed us
to develop a web portal for sustainable development.
Thus we have in this work makes use of MERISE for application
design, an implementation with PHP5, SQL, JavaScript and HTML. This means that
the breakthrough of the Internet in Cameroon provides an unprecedented way to
reach the greatest number of persons with minimal effort. Then, starting from
an elucidation of the problem from the chapter one to a literature review in
chapter two, we come to determine the method and therefore the tools to serve
us in building our portal. A Web portal we shared the results in chapter
four.
This also means that our objectives were reached. Therefore
our platform offers more than an ergonomic interface by associating the
following features:
- A news area through articles, which aims to address the
needs for clear information.
- An electronic library from which can be downloaded documents
previously posted by the administrator;
- A section containing links leading to web site offering
complementary services to our platform;
- A space for discussion or forum that aims to be a place to
share ideas and information about many topics;
- Also, our application has a user space for those who have
registered and are connected. They can exchange private messages while
consulting the directory of registered members of the portal. Our aim was to
engage maximum users of our application warrants the ability given to them to
offer content being articles, links or even documents.
- All this is happening precisely the watchful eye of the
director in his task may decide to give a simple moderator member status to
assist in the forum admin.
2. DIFFICULTIESENCOUNTERED
As in any human endeavor, difficulties were encountered at
several stages of the study. The most important are related to the delimitation
of the subject, the choice of analyses method, the choice of tools as well as
the graphic design of the application.
Sustainable development is a huge topic; the choice of
activities to implement on our portal was not easy.
Also, there is a multitude of web application analyses
approach and to sort out all these methods is a thorough exercise as the
selection of one of them.
Web programming being in constant evolution, select the tools
becomes a rather difficult task because everyone has these benefits and
disadvantages that must be taken into account.
Graphic design meanwhile proved a little more difficult in
regard to the choice of colors, the arrangement of elements of the application
in order to make an ergonomic application.
3. RECOMMENDATIONS
The recommendations address several points here are:
· The security of this application remains one of the
problems we have tried to include it in different parts of the application like
in form validation, in the access rights. Also security is included in
displaying data received from users (login, password).
· The functionalities of our application are complete
according to our objectives. However, many other tools could be incorporated in
this application to make it better like the use of phones.
· In terms of technique and technology employed, these
could equally be improved with: for the technique, a completely MVC (Model View
Controller) could be usedand for the technology a better integration of
AJAX.
4. SUGGESTIONS FOR FURTHER STUDIES
While we we're trying to give this application a much larger
it is, however, appropriate to point out some shortcomings that could be
addressed in future studies. Thus we can highlight:
- The security of the application, security for web
applications is of increasing importance especially since our portal provides a
user space,then, users store on our platform personal information that should
be protected;
- A newsletter system would also be appropriate to alert our
users of all news concerning them or whether new private messages. This could
of course be improved by a warning system with SMS, and Android phone
applications
- Also, the opportunity could be given to users to change
their profile which is not yet the case;
- Better integration of AJAX technology which have only been
used in some parts of the application.
CONCLUSION
The improved exchange of information between the different
actors of sustainable development in our country is what guided this work.
Thus, we were concerned to provide students, educators or government
authorities as well as expert a tool to exchange, to learn, to communicate
using a web portal.
The steps leading to the realization of this web application
enabled us to master the best web development tools. So this work was an
opportunity for us to put into practice the knowledge acquired in application
design as web materials regarding the approach tools. So our programming skills
have been increased including server side programming with PHP as client side
interactivity with JQuery (JavaScript Framework). However, this application
can't alone be the solution to a more global problem which is a sustainable
development for our country.
REFERENCES
[1]- Jean Luc BAPTISTE (2010).
MERISE guide pratique (Modélisations des données et des
traitements : langage SQL). Paris : ENI. PP 19-77
[2]- Philippe RIGAUX (2009). Pratique de MySQL et
PHP. 4ième édition. Paris : DUNOD.
PP :102-166
[3]- Maurice CHAVELLI (2014). Prenez en main
Bootstrap. Paris : OpenClassrooms. PP : 74-124
[4]- Francois-Xavier BOIS (2008). PHP5 - le guide
complet. 3ièmeedition. Paris : Micro
Application.PP: 331-334
[5]- David Sawyer McFARLAND (2014).JavaScript and JQuery:
the missing manual. 3rd edition.Gravenstein: O'Reilly PP:
186-202
[6]- Wesley HALES (2013). HTML5 and JavaScript Web
Apps. USA: O'Reilly. PP : 29-41
[7]- Québec. développement durable:
repères historiques.
http://www.cndp.fr. 0 02 january
2015 ;
[8]- Jean Engels (2009). PHP5 Cours et Exercices. 2e
édition. Paris : Eyrolles. PP : 212-225
[9]- BorkoFurht (2010). Handbook of Social Network
Technologies and Applications.Springer. PP : 117-129.
[10]- Patrice Zangue GOGUIA (2013). Conception et
réalisation d'une plateforme de communication pour les enseignants
camerounais. Bamenda : H.T.T.T.C of Bambili. PP : 7-30
[11]- Prince MUJUMBE SALAMA (2012). Conception et
réalisation d'un portail web à l'intention des différents
acteurs burundais. Université Lumière de Bujumbura - Licence
2012 Informatique et Télécommunications PP 5-20
[12]- Aurelie BOUCHER (2009). Ergonomie web. 2e
édition. Paris : Eyrolles.PP: 89-223
[13]- Microsoft. Designing web application.
https://msdn.microsoft.com.
Retrieved the 18 of January 2015
[14]- Microsoft. Procédure pas à pas:
création d'une application web simple.
https://msdn.microsoft.com.
Retrieved the 18 of January 2015
[15]- Wikipédia. Web browser.
https://en.wikipedia.org. Retrieved the 13th of January 2015.
[16]- Wikipédia. Sustainable development.
https://en.wikipedia.org. Retrieved the 13th of January 2015.
[17]- Wikipédia. WorldWideWeb.
https://en.wikipedia.org. Retrieved the 13th of January 2015.
[18]- Wikipédia. Web application.
https://en.wikipedia.org. Retrieved the 13th of January 2015.
[19]- Jerôme CHAMBARD (2014). Le dictionnaire du
web. Edition 2015. PP : 627-628
APPENDICES
APPENDICES 1: Databasecreation script
-- Base de données: `portail_dev_du`
-- Structure de la table `articles`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `articles` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`state` set('0','1') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
`title` varchar(200) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`content` text COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`photo` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`video` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`date` varchar(30) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`author` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=10 ;
-- Structure de la table `categories`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `categories` (
`cat_id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`cat_title` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`cat_description` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`cat_id`),
UNIQUE KEY `cat_title` (`cat_title`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=9 ;
-- Structure de la table `comments`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `comments` (
`com_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`id_sujet` int(11) NOT NULL,
`auteur` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`contenu` text COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`date` varchar(30) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`time` varchar(10) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`com_id`),
KEY `id_sujet` (`id_sujet`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=1 ;
-- Structure de la table `document`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `document` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`description` text COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`type` enum('.pdf','.docx','.rar') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT
NULL,
`reference` varchar(150) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`status` set('0','1') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=4 ;
-- Structure de la table `links`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `links` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`title` varchar(150) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`description` text COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`reference` varchar(150) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`cathegory`
enum('formation','etat','ong','international','autre') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT
NULL DEFAULT 'autre',
`status` set('0','1') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL DEFAULT '1',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `title` (`title`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=6 ;
-- Structure de la table `messages`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `messages` (
`mess_id` bigint(20) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`status` enum('0','1') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL DEFAULT
'0',
`title` varchar(255) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`content` text COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`date` date NOT NULL,
`hour` time NOT NULL,
`sender_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`receiver_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`mess_id`),
KEY `sender_id` (`sender_id`,`receiver_id`),
KEY `receiver_id` (`receiver_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=1 ;
-- Structure de la table `sujets`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `sujets` (
`id_sujet` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`cat_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
`title` varchar(200) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`description` varchar(200) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id_sujet`),
UNIQUE KEY `title` (`title`),
KEY `cat_id` (`cat_id`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=12 ;
-- Structure de la table `users`
CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS `users` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`gender` enum('m','f') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`pseudo` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`pass` varchar(100) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`picture` varchar(150) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`email` varchar(150) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`location` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`profession` varchar(50) COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL,
`level` enum('1','2','3') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL DEFAULT
'1',
`status` enum('0','1') COLLATE utf8_bin NOT NULL DEFAULT
'1',
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
UNIQUE KEY `email` (`email`)
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8 COLLATE=utf8_bin
AUTO_INCREMENT=14 ;
-- Contraintes pour les tables exportées
-- Contraintes pour la table `comments`
ALTER TABLE `comments`
ADD CONSTRAINT `comments_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`id_sujet`)
REFERENCES `sujets` (`id_sujet`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
-- Contraintes pour la table `messages`
ALTER TABLE `messages`
ADD CONSTRAINT `messages_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`sender_id`)
REFERENCES `users` (`id`),
ADD CONSTRAINT `messages_ibfk_2` FOREIGN KEY (`receiver_id`)
REFERENCES `users` (`id`);
-- Contraintes pour la table `sujets`
ALTER TABLE `sujets`
ADD CONSTRAINT `sujets_ibfk_1` FOREIGN KEY (`cat_id`)
REFERENCES `categories` (`cat_id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE CASCADE;
/*!40101 SET CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT=@OLD_CHARACTER_SET_CLIENT
*/;
/*!40101 SET CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS=@OLD_CHARACTER_SET_RESULTS
*/;
/*!40101 SET COLLATION_CONNECTION=@OLD_COLLATION_CONNECTION
*/;
APPENDICES 2: Homepage script
<?php
require_once("php/config/db_connect.php");
require_once"php/classes/article.php";
require_once"php/templates/header.php";
?>
<article class=" col-sm-8 col-xs-12 home" id="section">
<div class="row" id="elastic_grid_demo">
</div>
</article>
<?php
require_once"php/templates/left.php";
require_once"php/templates/footer.php";
?>
| 


