ANNEXE3
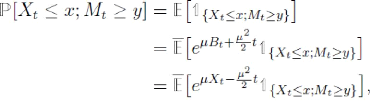
et d'âpres le principe de réflexion :
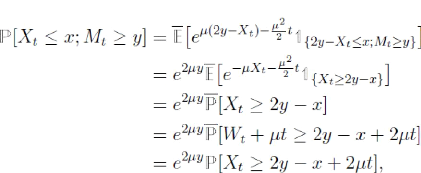
car W est un e -mouvement brownien. Ceci achève
la démonstration
Bibliographie
Vivien BRUNEL- Benoît ROGERT-version: September 23, 2009
Risque de crédit-Ecole Nationale des Ponts et Chausses
Couverture des risques dans les marchés financiers
Nicole El Karoui Ecole Polytechnique, CMAP, 91128 Palaiseau
Cedex
Aurelien ALFONSI, Thèse de doctorat ,L'ECOLE NATIONALE DES
PONTS ET CHAUSSÉES,
David KURTZ & Thomas B. PIGNARD,Modélisation du risque
de crédit, DEA de Statistique et Modèles
aléatoires en économie et finance Université
Paris 7 -- Université Paris 1
[1] Aven (T.). A theorem for determining the compensator of a
counting process. Scandinavian Journal of Statistics, 12(1), pp. 69-72
(1985).
[2] Bielecki (T. R.), Rutkowski (M.). Credit Risk : Modeling,
Valuation and Hedging. Springer (2002).
[3] Bomfim (A. N.). Credit Derivatives and Their Potential to
Synthesize Riskless Assets. The Journal of Fixed Income December 2002,
Vol. 12, No. 3, pp. 6-16 (2002).
[4] Crosbie (P. J.). Modeling Default Risk. KMV Corporation, San
Francisco,
www.kmv.com (1997).
[5] Dellacherie (C.) Meyer (P.A.). Probabilités et
potentiels, chapitres I `a IV, Hermann, Paris (1975).
[6] Duffie (D.), Filipovi_c (D.) & Schachermayer (W.).
Affine Processes and Applications in Finance. Annals of Applied
Probability, Vol.13, No 3, August 2003 (2003).
[7] Duffie (D.). A Short Course on Credit Risk Modeling with
Affine Processes. Working Paper. Stanford University and Scuola Normale
Superior (2002). Disponible sur http ://fibonacci.dm.unipi.it/ finance/duffie
notes.pdf.
[8] Duffie (D.), Lando (D.). The Term Structure of Credit
Spreads with Incomplete Accounting Information. Econometrica 69, pp.
633-664 (2001).
[9] Duffie (D.), Pan (J.), Singleton (K.). Transform Analysis
and Asset Pricing for Affine Jump Diffusions. Econometrica, Vol. 68,
pp. 1343-1376 (2000).
[10] Duffie (D.), Singleton (K. J.). Modeling Term Structure of
Defaultable Bonds. The Review of Financial Studies Special 1999 Vol.
12, No. 4, pp. 687-720 (1999).
[11] Duffie (D.), Singleton (K. J.). Credit Risk .
Princeton University Press (2003).
[12] _Emery (M.). Classical Probability Theory : An Outline of
Stochastic Integrals and Diffusions. Quantum Probability Communications, QP-PQ,
Vol. XI,World Scientific (1999). Disponible sur http ://
www-irma.u-strasbg.fr
[13] El Karoui (N.) & Mazliak (L.). Backward Stochastic
Differential Equations. Pitman Research Notes in Mathematic Series
(1997).
[14] Geske (R.). The valuation of compound options. J.
Finan. Econom. 7, pp. 63-81 (1979).
[15] Hull (J. C.), Nelken (I.), White (A.). Merton's Model,
Credit Risk, and Volatility Skews. Working Paper. University of Toronto
(2003).
[16] ISDA 2003 Credit Derivatives
Definitions.
www.isda.org.
[17] Krylov (N. V.). Introduction to the theory of diffusion
processes. American Mathematical Society, Providence.
[18] Laurent (J.-P.). I will survive. Risk, June
2003. www.risk.net (2003).
[19] Leland (H. E.). Corporate debt value, bond covenants, and
optimal capitalstructure. J.Finance 49, pp. 1213-1252.
[20] Longstaff (F. A.), Schwartz (E. S.). A simple approach to
valuing risky fixed and floating rate debt. J. Finance 50, pp. 789-819
(1995).
[21] Merton (R. C.). On the pricing of corporate debt :The risk
structure of interest rates. J.Finance 29, pp. 449-470 (1974).
[22] Pan (G.). Equity to credit pricing. Risk, November
2001. www.risk.net (2001).
[23] Protter (P.). Stochastic Integration and Differentiel
Equations. Springer (1990).
[24] Pye (G.). Gauging the Default Premium. Financial
Analyst's Journal, January-February, pp.49-50 (1974).
[25] Credit Derivatives Survey. Risk, February
2003. www.risk.net (2003).
[26] Roncalli (T.). La gestion des risques financiers.
Cours du DESS de Gestion des risques et des actifs de l'universit'e d'
Evry.
gro.creditlyonnais.fr.
[27] Rudin (W.). Real and Complex Analysis.
McGraw-Hill, New York, third edition(1987).
[28] Schonb
·ucher (P.), Rogge (E.). Modeling Dynamic
Portfolio Credit Risk.Working Paper. ETH Z·urich (2002). Disponible sur
www.schonbucher.de.
[29] Schonb
·ucher (P.), Schubert (D.). Copula-Dependent
Default Risk in Intensity Models. Working Paper. University of Bonn (2000).
Disponible sur
www.schonbucher.de.
[30] Vasicek (O.). Credit Valuation. Working Paper. KMV
Corporation. www.kmv.com
(1984). Merton R. (1974). On the pricing of corporate debt : The risk structure
of interest
rates, Journal of Finance, Vol. 29, pp. 449-470.
Black F., Cox J. C. (1976), Valuing corporate securities : Some
e_ects of bond indenture provisions, Journal
of Finance, Vol. 31, pp. 351-367..
Laure Coutin, Laboratoire de Probabilités-Statistiques,
Université Paul Sabatier Toulouse,
Jean-Claude Gabillon, Groupe de Finance, ESC Toulouse,
Laurent Germain, Groupe de Finance, ESC Toulouse,
Monique Pontier, Laboratoire de Probabilités-Statistiques,
Université Paul Sabatier Toulouse,
Clémentine Prieur, Laboratoire de
Probabilités-Statistiques, Université Paul Sabatier Toulouse,
Anne Vanhems, Groupe de Finance, ESC Toulouse
Correspondant du projet: Laurent Germain, ESC Toulouse.
| 


