3.2 Description of the Irrigation System at the PHP
Group
4 0 16 9 2 2 28 3 3 40 43
The irrigation system at the PHP Group, Njombé is divided
into three main parts; the pumping stations, the conduits (pipes), and the
distribution network. To develop the
database for the system, a clear knowledge of how the system
looks like and how it functions will be of great necessity.
3.2.1 Pumping station
The entire network is supplied through five pumping stations
(Koumbe 1, Koumbe 2, Koumbe 3, Trou Lac Dia-Dia and Maya) and use 21 pumps for
the lifting of water; 16 of the pumps are situated at the main station at
Koumbe and 5 others situated at Trou Lac, Dia-Dia and Maya. The engine pumps
used have the following characteristics:
Engine Type: 12 cylinder engine
Engine Power: 337 hp
Pump Type: Centrifugal with 5 wheels of diameters 330 mm rotating
at 1800 rpm Pump Flow Rate: 240 m3/h
Total Head: 240 m
Operating Pressures: 24 bars (Koumbe) and 13-17 bars (others)
Water is pumped from the rivers Moumbe, Mboko and Maya as well as
the Dia Dia Lake and Well (about 50 m deep).
3.2.2 The main line (Pipes)
Water is transported from the pumping stations to the
plantation via steel or PVC pipes with diameters between 200 mm and 700 mm.
These pipes are either buried, placed on the surface or have become exposed to
the surface due to erosion. Interconnection between the pipes gives a looped
network such that in case of malfunctioning of one of the pumping stations, the
others could be used for pumping. During the irrigation season, each pipe
operates individually, hence, forming a ramified network. These ramified
networks cover a total distance of about 55 km and each is equipped with a
given set of structures and equipments, which facilitate the use and management
of these networks. Figure 3.4 shows these main conduit and the pumping stations
from which they obtain water.
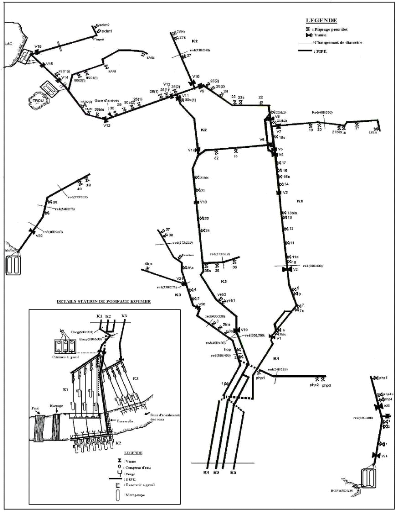
Source: Irrigation department PHP
Figure 3.4: Main lines at the PHP group
3.2.3 Distribution network
This is the set of equipment and structures which transport water
from the main hydrant to the level of the sprinklers. It is made up of:
- Secondary conduits in galvanized steel or polyethylene and with
diameters of 120 mm, 150 mm, or 160 mm,
- Tertiary conduits or antenna with diameters of 120 mm,
- Quaternary conduits with diameters of 40 mm or 50 mm,
- Risers and sprinklers.
This network is characterized by two main irrigation systems;
overhead and Undertree:
a) Overhead irrigation
In this type of irrigation, the sprinklers are situated above
the banana plants. This mode could either be by total coverage with big guns or
by integral coverage with sprinklers.
· Total coverage with big guns
It is the most ancient system used by the Group and usually
gives the ground base for the installation of other systems. It occupies a
surface area of about 410.20 ha. The big guns used are characterized by a flow
rate of 60 m3/h, an operating pressure of 5.5 bars, a horizontal
throw of 54.4m, coverage of 0.5 ha/canon, and an irrigation depth of 10mm/h.
the number of big guns per irrigation plot is between 60-100 big guns, this
gives a spacing of 72 or 78 m in the line and between 66 or 73 m between lines
(72 m*66 m or 78 m*73 m). The advantage of using big guns is the ease of follow
up of irrigation but a great disadvantage lies in the high energy consumption
during pumping.
· Integral coverage with sprinklers
(21*21)
It is characterized by single or twin nozzle sprinklers with
the following features: a flow rate of 1.4 m3/h for single nozzle
sprinklers or 1.9 m3/h for the twin nozzle sprinklers, an operating
pressure of 4 bars, and an irrigation depth of 3.36 mm/h. Evaporation and wind
are the principal setbacks to this system. Compared to big guns however, this
system consumes less energy. It occupies a surface area of 193.46 ha.
b) Undertree irrigation
Two systems are used in this Group; sprinklers with integral
coverage (12*11 m) and the micro jets system.
· Integral coverage
This system is made up of twin nozzle sprinkler heads. It is
a low pressure system (2.5 bars). The nominal flow rate is 0.42 m3/h
with a horizontal throw of 9.5 m per sprinkler. This system is highly prone to
theft and difficult to monitor during irrigation because of the high density
per irrigation plot (200-250 sprinklers/plot). It occupies a surface area of
1250.25 ha.
· Micro Jets
Used mostly in the cluster and twin line spatial arrangement.
The sprinkler heads used are of the type RONDO and RAINBIRD and are
auto-regulated (flow rate does not change with variation in pressure). The
characteristics of these micro sprinklers are; a flow rate of 30 l/h, an
operating pressure of 1.5 and 3.5 bars for horizontal throws of 1.8 and 2.0
bars respectively. Despite the advantage of low energy consumption, it requires
special attention in terms of maintenance due to constant clogging of the
nozzles especially those of the pressure regulators which are very small. It
occupies a surface area of about 1750 ha.
| 


