CHAPTER FOUR
DATA PRESENTATION AND ANALYSIS
4.0 INTRODUCTION
The main focus of this chapter is the presentation and
analysis of the data collected from the secondary sources. This chapter
embodies presenting and analysing the data collected qualitatively and
quantitatively following the objectives of the research stated in Chapter one.
Our analysis will be organised in two main parts: Analysis of the data
collected and Policies suggestion to financial body to reduce their risks and
increase their profitability level.
4.1 QUALITATIVE ANALYSIS
This refers to the use of tables and graphs to show how
variables have evolved over the years. This will be done for the period
2002-2005.
4.1.1 ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF RISK MANAGEMENT ON CREDIT
RISKS
The qualitative analysis made in this part of the study will
be a study which analyses the evolution of non performing loans as an indicator
to credit risks in the overall Cameroon Banking system.
The following table represents the evolution of non performing
loans and provision for bad loans as an indictor to credit risks.
Table 4.1 Cameroon: Banking system Indicators
(units indicators)
|
Years
|
2002
|
2003
|
2004
|
2005
|
|
Non performing loans
|
15.7
|
13.9
|
13.1
|
12.6
|
|
Provisions ( % of bad loans)
|
81.1
|
81.2
|
85.3
|
85.4
|
Source: Banking commission of Central Africa and
staff calculations.
The table above represents the key indicators of the banking
sector in Cameroon given as aggregates. More so it shows the evolution of non
performing loans over the years 2002-2005. The amount of non performing loans
are represented here as a percentage of the sum total of loans given out by the
banking sector. Going by the diagram, we can see that over the years the amount
of non performing loans (credit risk) is reducing .In 2002, the credit risk was
15.7 and in 2005 it was 12.6 indicating a reduction of credit risks of 3.1%.
This decrease can be explained by the action of the management team in their
effort to risk reduction.
A- Trend Analysis
In this section, we are going to represent graphically the
data in the table 4.1 above in relation to the amount of non performing loans
which is presented as a percentage.
The following expression can therefore be derived:
Credit risks = (Amount of bad debt/ Amount of total
credit granted) X 100
This rate should be as low as possible since it the goal is to
minimise risks in order to make investments more profitable. The following
illustrates diagrammatically the evolution of credit risks.
FIGURE 4.1: Evolution of credit risk from 2002 to 2005
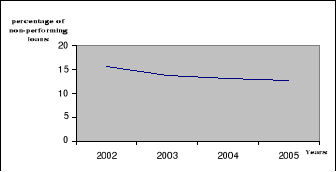
Source: Banking Commission of Central Africa and Staff
Calculations (COBAC), 2005.
The slope of this curve is negative showing that over the
years the amount of non performing loans is reducing. This therefore means that
the risk management has an impact on the credit risk, by reducing the size of
the non performing loans. This can be achieved for instance through an
effective credit policy.
4.1.2 ASSESSING THE IMPACT OF RISK MANAGEMENT ON LIQUIDITY
RISKS
a) Table Analysis
Our analysis in this part of our study will be based on the
table below, which represents the evolution of maturity transformation defining
the liquidity level of Cameroonian banks over the long run.
Table 4.2: Cameroon Banking system indicators
(unit indicators)
|
Years
|
2002
|
2003
|
2004
|
2005
|
|
maturity transformation
|
3
|
3
|
5
|
4
|
Source: Banking Commission of central Africa and Staff
Calculations, 2005
The maturity transformation is the ratio of the overall
solvency of the banking sector. By this ratio a company can determine how
liquid it is and how far it is coping with its long term obligations based on
its assets.
The following expression represents the ratio of maturity
transformation.
Maturity transformation = Long Term Assets / Long Term
Liabilities
The trick of this ratio is that organisations and of course
financial institutions must keep this ratio greater than one. This indicates
that if this ratio is higher it is a sign of solvency of the organisation,
since it can meet its long term obligations.
Going by the table above, we can say that the solvency ratio
in 2002 was 3 and that it has increased to 5 in 2004 and 4 in 2005, which means
that over the years the organisations are getting more solvent by increasing
their liquidity level.
Here the liquidity risk is lesser since it is expressed when
the solvency ratio tends to 0 or to a negative value. We ca therefore affirm
that the risks management of Banks in Cameroon is aware of the negative impact
of liquidity shortages and keep a high liquidity ratio in order to avoid
illiquidity. In brief the higher the liquidity ratio, the lesser the liquidity
risks.
b) Trend Analysis
The figure below is represented on the data given in table4.2
above, which represents the evolution of maturity transformation for the entire
banking sector in Cameroon for the Period 2002-2005.
Figure 4.2 The evolution of Maturity Transformation, 2002-2005
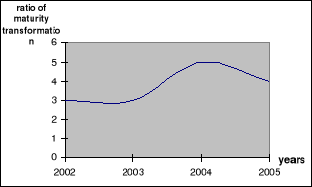
Source: Banking Commission of Central Africa and Staff
calculations, 2005.
The curve drawn above represents the evolution of the
liquidity ratio of the Cameroon Banking sector over the years 2002-2005. In
2002 and 2003 the curve is constant meaning that the liquidity level remains
unchanged. But due to the action of risks managers in their tasks to maintain
adequate liquidity level, the ratio will increase in 2004 to 5 and decrease to
4 in 2005 while remaining higher than in 2002 and 2003. Given that the curve is
positive, the liquidity risks are diminished since adequate liquidity is kept n
Banks and Bankers can meet sudden upsurge withdrawals of creditors while not
affecting the overall profit of the financial institutions.
| 


