Thierry SCHILTZ
Control Social Communication
SICA- University BORDEAUX 3
Master's paper
THIERRYSCHILTZ@HOTMAIL.COM
Director of research : Christian Laguerre
 
« E-press : Press in danger or further
information »
2001-2002
THANKS
I first of all hold to thank Mr Frederic Saler way in which it
received me and from time that it devoted to our maintenance carried out.
It enabled me to include/understand well how functions the
Sudouest.com. site.
In the second place, I make a point of thanking Mr Laguerre to
have followed me and have directed at the time of the constitution for this
memory.
And finally, I make a point of thanking all the people who
agreed to answer my questionnaire on the regional daily press on Internet
CONTENTS
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
Methodology of this memory P
07
Introduction first part P 09
I.INTERNET, CULTURAL REVOLUTION AND SOCIAL OR SIMPLY
TECHNICAL REVOLUTION
1. The revolution of Internet
1.1 Origins and the development of Internet
P 10
1.2 Bond between technical progress and social
change p 11
1.3 Undeniable assets P 14
1.4 Transparency P 16
1.5 Cyber-meet P 17
1.6 Inequalities P
19
1.7 Freedom P 20
1.8 Impact on the company P
21
1.9 Analyze assumption P 23
Conclusion first part P 25
Introduction second part P 26
II. PAPER MEDIUM WITH THE ELECTRONIC MEDIUM
1. Compete with or complementarity
1.1 Beginnings of the press on line P
27
1.2 Key figures P
29
1.3 Different assistantships P
32
1.4 Convergence of the two supports P
33
1.5 Interactivity
P 34
1.6 Personalization of the offer
P 34
1.7 Analyze assumption P 35
2. The function journalist is it credible on
Internet ?
2.1 The demonopolisation of information P
36
2.2 Free access to the sources P
37
2.3 Diffusion of information P
37
2.4 Loss of credibility P
38
2.5 Or hyper-credibility P
40
2.6 Analyze assumption P 41
3. Of the journalist to the
cyber-journalists
3.1 A strong deontology P
41
3.2 The writing on the Web P
43
3.3 A more tiring reading P
44
3.4 A new writing because of a new reading
P 45
3.5 Formation P 46
3.6 Analyze assumption P 48
4.Rentability of the press on electronic medium
4.1 Principle of the exemption from payment
P 49
4.2 Publicity on the Web P
50
4.3 E-espionage P 52
4.4 The E-mass mailing P 52
4.5 Press electronic and trades electronic
P 53
4.6 Small advertisements P
54
4.7Etat current of the profitability of the daily
newspapers on the fabric P 56
4.8 Analyze assumption P 60
5. Statute of the press on Internet
5.1Historic of the right of the press P
61
5.2 The statute of the press on line P
61
5.3 Royalties P 67
5.4 Chart of journalist P
69
5.5 Analyze assumption P 71
Conclusion second part P 72
Introduction third part P 73
III. THE REGIONAL DAILY PRESS ON INTERNET
1. Group South-western
1.1 Presentation of the daily newspaper
P 74
1.2 Discussion with Frederic To salt P
78
1.3 Analyze maintenance in connection with the
assumptions P 81
2. Inquire into the regional daily press
2.1 Methodology of the investigation P
82
2.2 Result P 83
2.3 Analyze investigation in connection
with the assumptions P 96
Conclusion third part P 99
Other tracks to be explored P 100
General conclusion P 103
Bibliography P 105
Appendices P 109
GENERAL INTRODUCTION
In one century, technologies of the communication made fast
and vertiginous progress.
One could note how the radio and television succeeded in being
integrated in the company without to make disappear the other existing
media.
Internet is a new media which has just appeared in our
company.
Many people intend a glorious future and strong promises to
him in its connection.
One does not know yet exactly how it will be integrated in our
company and it is thus prone to many probable assumptions in its future.
Our population has a need for information concerning the world
where it is located.
That can be topicality general, economic, sporting or
different which is dependant according to its personal interests.
The media assume this role and one can say until there that
the appearance of the new media like the radio and television were
complémentarisés and converged.
Nevertheless the radio is made up of sounds and television of
a marriage sounds and images whereas Internet diffuses primarily writing such
that the newspaper industry.
The objective of this memory is to measure if this new
technique with the promises which are made to him will prolong the history or
on the contrary to even destabilize to destroy one of the first appeared media
which are the printing works of the newspapers.
Methodology of this memory :
This memory aims to answer six essential assumptions which
turn around the topic of the electronic press.
It was necessary for me thus to find primarily works
theoretical in order to check my assumptions.
The first measure to be taken is thus to go to consult the
various libraries and bookstores of Bordeaux. So several problems quickly
appeared.
First was a small quantity of works which covered this
subject.
The second problem, which was most constraining, comes from
nature from media Internet. This media is in perpetual evolution and the
principal works found in these places were very quickly obsolete.
Indeed a work which was written in 1998 included/understood
certain valid information nowadays but the majority were exceeded by the fast
evolution of this tool and the methods which accompany it.
Nevertheless, a system of filtering on these works not very
recent and the discovery of other works a little more recent made it possible
to draw the fundamental theories to validate or cancel the put forth
assumptions.
It should be noted that the theory which was used to me for
the not-validation of my first assumption resulted almost exclusively from
works.
The second method used to check my assumptions was to go to
take information on the mother of all networks to knowing Internet.
Thanks to and the bond search engines in bonds, it was
possible to direct me towards relevant information to check the assumptions.
This tool gave the possibility of making research on a larger
territory.
There are works and whole reports/ratios of researchers,
teachers and professionals who are at the disposal of the Net surfer.
Moreover Internet allowed me to go to examine the electronic
versions of the daily newspapers in order to analyze if the theory were well
applied by the electronic daily newspapers.
The third method to check my assumptions was of a more
practical nature.
This method had two missions :
- To give an outline of the behaviors of the population
concerning their accesses to the regional press.
- To supplement the theoretical one by two studies on the
ground.
It, initially, was carried out a discussion with a multi-media
journalist with the South-western daily newspaper in order to explain me the
methods of its work to analyze if they were well in adequacy with the theories
drawn to check my assumptions.
In a second place was carried out a survey near the population
of the South Basin in order to analyze the behavior of this population to reach
regional information but there too to make it possible to support the theory
which checks my assumptions.
This memory is composed of three parts.
Each under parts of the first two parts have an assumption
stated in beginning, a theoretical study during its unfolding and a validation
or a not-validation in end.
The Third part relates to primarily research on the ground
which made it possible to support the theory and to give an outline of the
access to regional information in our area.
INTRODUCTION FIRST PART
This first part is devoted not to the press on Internet but to
Internet as a whole.
The purpose of it is to give theoretical elements in order to
check only one assumption whereas the second part aims to check five of
them.
The choice to put only one assumption in this part comes from
a more important need of theory than for the following ones but also because it
will treat Internet as a whole whereas thereafter it is the press on
Internet.
To read the press, to hear the radio, to listen to television,
it seems that all that touches with Internet is developed by a promise of a
better world.
Internet should radically change our company to go towards a
better future.
This part aims to check if this new tool is well intended to
carry out a social revolution.
I.INTERNET, CULTURAL REVOLUTION AND SOCIAL OR SIMPLY
TECHNICAL REVOLUTION
My first assumption, setting ahead in this part, relates to
Internet as a whole.
It emits that Internet is a tool of communication which in the
future will revolutionize our company by modifying there the activities and the
relations of our world population.
1. The revolution of Internet
1.1 Origins and the development of
Internet :
Internet network has soon a quarter century. Indeed, it is
into 1969 that the American ministry for defense undertakes to build a
data-processing communication network which can resist a nuclear attack. It is
still during the time of the cold war and it is thus important for the
government and the soldiers to be able to continue to make communicate, in all
the cases of figures, all the organizations of defense. The original
architecture of the network is explained for this reason : one should not
create a central node, a center of order, which would be likely, if it were
touched, to block the whole of the system.
In system Internet, all the computers connect themselves
through thousands of networks. Also if a network does not function any more, if
it is destroyed by an unfavourable power or so quite simply, it suffers from a
clogging of calls, then information follow another advance to arrive to its
recipient. In a word, Internet is a network of networks.
This method of construction facilitated the development of the
system. Dice 1972 the network « ARPANET » is set up. It
allows the connection of a score of military and university centers. For qu
`Internet becomes a broader mean of communication, it will be necessary to
await 1982, date on which, the access to the network is granted free.
The following year the National Science Foundation (NSF)
American finance the setting in network of sixty American universities and
three European. In 1985, the network of the NSF is integrated into Internet.
One estimates then at 5000 the number of users of the network.
Especially the speed transmission increases gradually and, in
1986, the network is connected on the public lines. Consequently, Internet
touches the whole of the scientific community. In 1987, 100.000 computers are
connected and more than 3000 research centers dialog on Internet. Gradually
Internet was diverted of its military function to interest the researchers and
the academics. A community of user was born, who has his own culture where mix
taste for data processing, is delirious of researcher and pleasure of the
dialog.
The appearance of software of access to Internet, under
Windows, for micro the computers, facilitates the approach of the Net. More
known, mosaïc, will be distributed free to all the users of the
network.
Moreover, with the progress of numerical compression, it video
makes its entry on Internet. The networks on line thus approach the graphic
quality of the CD-ROM.
But, it is especially since 1992, that the blow of accelerator
is given. The conditions with Internet, for the private companies, are
softened, so that all those which have the equipment necessary can propose
services.
Commercial companies are installed on the network to sell
services and time of connection. Consequently, of new actors appear on the
network, of the thousands of people connect themselves. Internet becomes a
phenomenon of company.
1.2 Bond between technical progress and social
change :
I first of all make a point of specifying that these
reflections made to check this assumption were theoretically drawn from the
works of Domenica Wolton « Internet and afterwards » but
also of Breton Philippe « The worship of the Internet.
For thirty years a waltz of progress of the tools of
communication has taken place. The men vis-a-vis the techniques of
communication are pressed, always late and seek fast progress.
One thus has, now, of the means of communication which are
fast and without border.
Internet has been for a few years a tool which is proposed.
Many people regard it as a tool which will upset positively and radically the
company.
It must enable us by a better freer, more interdependent
communication to be and to decrease the social inequalities.
It is a tool which will increase the capacity of our
democracy, from its possible interactivity, but it is also a door towards a
world unification.
One thus attends a race of technical progress to arrive at a
better company.
The press, body which is easily skeptic, is, him also,
accordingly of the race to progress.
Since ten years, it published an incalculable number of
supplements written or audio-visual on new technologies, quoting constantly the
United States like models it to follow and denouncing the delay of French
mentalities.
The idea of Domenica Wolton1(*) is to relativize this revolution.
According to him « these visions technicists of the
future are all founded on the idea, dominant in the United States, of the
primacy of technology on the company. Their greater defect is to ignore the
history... Obnubilated by technology, they do not know which the human
societies were always more complicated than the most sophisticated
technologies. »
Indeed it thinks that technical progress does not suffice for
him to only reveal a change of the communication and culture.
It thinks that if a technique of communication plays an
essential part, it is because it symbolizes a radical rupture existing
simultaneously in the cultural order in the company.
It is not the printing works, which in oneself upset Europe,
but it is the bond between the printing works and the deep movement of
questioning of the catholic church. It is the reform which gave its direction
to the revolution of printing works and not the printing works which allowed
the reform.
In the same way the radio, then television had this impact
only because they were related to the deep movement in favor of the democracy
of mass.
If the techniques are the visible element of the
communication, essence is the cultural model which they convey, and the project
concerning the role and the organization of the communication system of a
company.
Another example which Domenica Wolton in2(*) his theory quoted is what it
calls the European desert of the communication.
It explains us why to wonder about European mutual
comprehension does not limit itself to a technical interrogation.
Indeed Europe is made up of 370 million inhabitants and it is
not while placing inter-connected computers and televisions that one will solve
the problem of the European cause.
It will be necessary to re-examine the history, the symbols,
the representations, the ideologies, the stereotypes... and the performance of
the tools appears ridiculous.
The European countries have all a strong culture and identity
but if they had suddenly had a will of really living then the techniques
jointly would join to carry out this bond but one returns from there to the
dependence of the techniques compared to a cultural model and to a social
project.
Internet is thus not, with its analysis, a revolution as much
declare it but it is clear that new technologies have assets which are
undeniable and which attract a primarily young public.
1.3 Undeniable assets
There is a certain psychological dimension which, indeed, is
essential in the attraction of new technologies because those Ci join the deep
movement
of individualization of our company.
They are the symbol of freedom and the capacity to control
time and space, a little as the car in the Thirties.
One can summarize this attraction in three words which
are : autonomy, control and speed.
Each one can act, without intermediary, when he wants, without
filter nor hierarchy and in real time.
I do not wait, I not acted and the result is immediate. That
gives a feeling of absolute freedom and even of power, whose account well the
expression returns « surfer on the Net ».
An open world accessible to all, and which finally gives
a chance to each one, whatever its route and its diplomas.
And it is for one of these reasons that new technologies
acquire a social dimension, because they make it possible to give a new chance
to those which missed the first.
It is not only the abundance, the freedom and the absence of
control which allure but also the possibility of a possible car-promotion
without school, without Master and control.
One can according to Philippe Breton3(*) distinguish three positions
concerning attraction for Internet.
There are the partisans of whole Internet, the partisans of a
reasoned use and the technophobes.
The partisans of whole Internet will deploy all their energy
to try to make develop Internet which they see like the future of the man and
our company.
Internet is for them a new world.
The partisans of the reasoned use see Internet as a tool
equipped with considerable assets to exploit but they do not place it in optics
to make a social revolution.
The technophobes are those which are opposed to the new
techniques of communication and more particularly to Internet.
Indeed it can be related on the ignorance and the frustration
of the new techniques.
The inequality of the personal and professional situations,
and the inequality of education can cause this phenomenon.
After illiteracy the i-electronism is added.
There are also those which are irritated by the apology made
by the media on Internet and which prefer to refuse it in block without them
having really value judgments.
The partisans of whole Internet speak to us about promises of
a better world.
For example Bill Gates4(*) speaks to us, in his work « the road
ahead », that Internet will be able to enrich our leisures and our
cultures, that it will attenuate our urban tensions since each one will work at
his place or in a country house.
He promises that one will learn with better controlling our
life in all these aspects thanks to the new communication networks.
He makes, already there, a rather considerable promise, but
one can quote another character who accentuates his remarks.
Pierre Lévyest5(*) author of multiple tests, on this topic, which will
have a great influence in the mediums of new information technologies and
beyond.
Levy does not hesitate to evoke it « total
reconnection of the mankind with itself » that Internet will
allow.
It thinks that the true destination of the man is to be a
planet gear, taking an active part in the collective intelligence of its
species.
Internet represents one accordingly « citadel of
light ".
All its remarks speak to us about the true finality of new
information technologies. All occurs as if Internet had the capacity to reduce
the tensions, to build a more harmonious and conflict social bond. The
imaginary world that its speeches propose to us calm, luminous and is
pacified.
It is a also question of being able to do everything at home
without moving of its armchair. All the activities there will thus be found
that one exerts downtown like some other news.
1.4 Transparency
The topic of the transparency frequently returns in the
mediums of new technologies.
This value even made irruption in the world of the policy,
which certainly under the old government, Lionel Jospin had declared at the
time of the ten ninth summer school that « the entry of our country
in the company of information corresponded to more access to the knowledge and
the culture, more employment and of growth, more public utility and of
transparency, more democracy and of freedom ».
The transparency is here on the same level as other values
considered to be fundamental.
The concept of transparency is sometimes comparable with the
Utopia of a social harmony, without secrecy neither lie, opposition nor
conflict.
The fact of making more harmonious the world by Internet
implies to give up the conflicts, the oppositions, division, criticism, the
power plays.
For that, the continuation of an ideal of transparency implies
that Internet is a completely open network.
It is necessary that there is a generalized interconnection
and that one lets pass what about is deprived, from the close friend, of the
secrecy.
In Ohio6(*), an experiment was made.
Six friends are in a house 24h on 24 and all that they make is
filmed on the Net and available in the whole world.
For the fundamentalist ones of Internet, the ideal of a
transparent world incarnates itself in one « village
total », without border, law, unconstrained. Freedom of movement in
is imperative, and any standard which makes obstacle with this freedom of
movement is perceived a such enemy with this transparency.
The hacking is also sometimes compared to this desire of
transparency. The attacks which were made in 2000 against the gate of yahoo was
not to divert confidential data but it was well the active worship of the
transparency, the opening, the suppression of the secrecy which can explain
such behaviors.
According to Pascal bubble7(*), author of an article in release in February
2000, the bibliographies of pirates are rare, but the little which one has
resembles. For saying that in their youth, they dismounted all the objects in
order to try to include/understand how they functioned.
Even impassioned Internet in general adopted this attitude
being children.
1.5 Cyber-meet
Internet is a mother of all networks which allows, if it be
thorough at the end, to separate the men and to exempt them of any direct
meeting.
The most direct partisans of Internet affirm, which to profit
from the promises which Internet offers to reach this new world, then, it will
be necessary to transfer to it the majority from the activities that up to that
point we realize differently : work, leisures, television, trade,
relations with others, the prayer, and for more the extremists sexuality.
Any communication, any meeting, any relation must from now on
pass by the network.
A concept which is put in parallel is that the desire of a
better world can come owing to the fact that our current world is marked by
violence.
The goal is to go towards a pacification while moving away
from the other. Each one among us wants to be locked up in a bubble and a
pacified universal communication : all advantages of the communication
without its risks.
All the relations will be done since at home, in fact
cybers-relations would exempt the direct relations and their disadvantages.
Internet would bring peace in a disturbed world which does not
see how to make peace.
Often the partisans of Internet have evil to come into direct
contact with people. A Net surfer can spend the hours in a cybercafé to
communicate on the Net and to have a large difficulty in come into contact with
his neighbor of left.
It is necessary to pay attention to this multi connection,
because no matter what say the partisans of Internet, always a moment ago when
it will be necessary to release the machines and to learn how to speak with
somebody directly .
The cyber-world is technically possible but appears not very
probable to apply.
The chiefs D `state has all the means to communicate
between them by the machines but it is seen that they take the plane to make
thousands of kilometers in order to have a direct relation.
1.6 Inequalities
A promise of Internet is that, from its access to the
universal culture, and from its possibility of planetary communication, it will
be a tool which will cause a drop in the inequalities.
This remains to be proven and of the studies show the
opposite.
Indeed according to Domenica Wolton8(*) and Breton Philippe9(*), Internet is a tool which will
reinforce the inequalities.
There is already five million illiterate in France to which
will be added the i-electronism. Everyone is not familiarized with the tool of
new technologies and the schools just start to teach it.
The problem is especially in the Third World countries where
the population has less the occasion to be familiarized with these new
technologies.
We are very far from the speeches of « reunification
of the conscience universal » and nearer to the traditional
figure of the increase in the domination of some, because of control of the
tools of communication.
Moreover Internet, contrary on television and with the radio
which offer same information for everyone, is a tool where the person must go
to seek her own information.
The problem is that it is already necessary to have assets to
go to seek information.
Somebody who arrives on the site of the museum of the Louvre
or the library of Paris must have a minimum of knowledge to know what to
ask.
He thus y will have a difference in use of Internet according
to the sociocultural level.
It is not all, information on Internet, which will have an
added value, risk in the future to become more and more paying then will be
added in more one financial selection.
Jean-Paul Fitoussi10(*) wrote a work on this subject, « the new age
of the inequalities », which represents this thought well.
1.7 Freedom
Freedom is a concept which by the use of Internet is likely to
be threatened under certain aspects.
One often speaks about the network level denounced in a
report/ratio of the European Parliament. 11(*)
The national sécurity agency is shown to devote itself
to an activity of systematic interception of the world communications, in
particular those which forward by Internet.
Freedoms are also threatened by a development of the aspects
of the electronic trade.
Such is the topic of the report/ratio 1999 of the national
commission on data processing and freedoms (CNIL)12(*) in France which worries about
the development of the cyber-monitoring and the conditions about the electronic
trade.
The suppression of the mediations in the trade makes the
things easier.
Simple clicks and one passes to the decision of purchase and
with the payment on line, the impulsive ones may find it beneficial to be
controlled.
Moreover and as he is written a little more explicitly in the
continuation of this memory, the controls of publicities try with certain
successes to violate the private life of the Net surfers.
The principle is simple and it did not await new communication
and information technologies for that.
More the advertizing executive knows the life, the tastes, the
practices of that to which it is addressed more it will be able to adapt its
message and to increase the chances to allure its interlocutor and thus to
sell.
There is by the attack with freedom.
Another point, as one saw it is necessary to be wary of the
multi connection so that it does not decrease too our direct relations but
there is another consequence to take into account.
Indeed, a man who has his various portables, his electronic
mails, his soon marketed faxes and other services will be unceasingly
reachable.
It is enough to already see the slave system which represents
a portable telephone. There is there too a mistrust to have on our freedom.
1.8 Impact on the company
It is difficult to know how Internet will develop that it is
in a remote future or near.
One saw by these various analyzes that a propaganda on the
topic of « revolution Internet » invaded the media since
the end of 90.
That Ci announces a revolution of the ways of life and
company.
It would seem that reality wants to relativize this
revolution.
Indeed Internet is a tool which, from its technical
performance, is able to revolutionize a company but it would be necessary for
that that our company has a strong and general will of modification to go in
this direction.
If it has this general will then it will be able to take
support on Internet to do what one calls a social revolution.
Even under the social pressure of the media and their
promises, it is very probable that a company any Internet as the strongest
partisans see it is not possible.
It appears clear that our company does not wish to digitize
the whole of its activities.
On the other hand even if Internet is not a revolution as
promised, it is very probable that the technical potentiality of this tool will
attract part of the population.
It thus will not be a social revolution but it will modify and
create part of the economic activities and social.
Internet will cause social positive assets but it is also
likely to involve perverse effects.
This enormous data base which constitute the mother of all
networks can be seen like a formidable tool of transparency for the
population.
She will have access to many information but one of the risks
is that, which one calls, it « No man' S Land legal » does
not encroach on the intimate and private field of the people.
One also speaks about communication even of universal thought.
Internet can allows all one each one to communicate with which one wishes, in
real time, and to the other end of the world. The problem is that this
technique will not remove our identity and our culture which is attached to our
country.
Internet is also as one saw previously a tool which allows
car-promotionner. The mother of all networks makes it possible to circulate
there freely and at high speed. It is a new world where one can feel main.
It is a positive side for the recognition of oneself even.
Concurrently to that, one also saw the possible obstacles
where freedoms and the risk of inequalities have as a probability of being
accentuated with Internet.
The challenge is not with dimensions communication system but
with dimensions of the differences and cohabitation i.e. the capacity to manage
its differences. The race with the new techniques is likely to be frustrating
because the stake of the communication is not the with dimensions one of the
technical performance but of with dimensions of the test of the others.
Moreover the fundamentalist ones and the media push us towards
Internet so much towards with dimensions to be it together world but also
towards a singularisation.
The ideal life would be that where we would be separate, where
the direct meeting would be reduced, it should be paid attention, because
by-there, one already threatens a social bond in difficulty.
A study13(*) carried out by the team of Robert Kraut near 256
people over two years with Pittsburgh showed that the use of Internet decreases
the circle of the social relations close and remote, loneliness increases,
increases the depressive feelings.
Recluses of a new kind appear everywhere, who maintain nothing
any more but one report/ratio informational and instrumentalized in the world
which surrounds them. These people build a social bond which is not completely
any more that of a human society.
1.9 Analyze assumption
The assumption was to check that the media of Internet was
going in the future to carry out in addition to its current technical
revolution, a social revolution.
One understands by social revolution a general upheaval of the
activities and relations of the people in our company.
According to these analyzes, it seems that this assumption is
not completely checked and it is advisable to say that Internet will probably
not be a social revolution but which it all the same will fit in our company
and will deploy some positive and negative points there. Internet is all the
same a tool with enormous potentialities which is worth really the sorrow to be
interested in it.
On the near future, the development of access to Internet is
calculable with much difficulty. One could say « who will live will
see ». The immense din which is reflected everywhere, on television,
in the media, publicity, the political speeches as well as in the daily
conversations, « it is necessary that I put myself at it »,
one in the mouth of many people hears, give more the impression to yield to a
social pressure than to have a real need for it.
Passed a certain threshold of diffusion, a technical object
becomes essential, even if it is not wished and if its use poses problem.
Once reached this threshold, it will become difficult to do
without from a computer and Internet under penalty of insulating the
recalcitrant ones socially.
It is to reach this threshold that publicity aims initially
the sensitive layers, in particular youth, targets privileged promise of a new
world.
CONCLUSION FIRST PART
In conclusion of this part, It is important to say that it is
necessary to relativize the concept of social revolution that some let
claim.
Internet will not manage to create a company where any
information would circulate freely and peacefully. It will not manage either to
change the social reports/ratios considerably.
It is a powerful tool which will help us in many activities
which they are economic, cultural, communication and different but it will not
upset our world company basically.
It is a tool which is not inserted yet in our company and
which seeks to take its place.
Its development is certainly far from being with maturity, but
it does not seem to have for destiny to create a new and better world.
INTRODUCTION SECOND PART
This part aims to check five assumptions which relate to
primarily the setting in electronic version of the daily newspapers of the
French newspaper industry.
Internet, associated its promise of development, made us
reflect on the possibility of a fall, even of a replacement of the newspaper
industry by the electronic press.
This part will allow us, by theory, to analyze this point and
to have an outline on the paradigms of the electronic press.
It is a question of analyzing the possibilities, operation,
the actors, the statute and the state of the current market of this new
activity of press by checking five assumptions.
It thus in this part five pennies left there
including/understanding each one an assumption checked theoretically one after
the other.
Once after having validated or not the assumptions then we
will have made the theoretical turn of this analysis.
II. PAPER MEDIUM WITH THE ELECTRONIC MEDIUM
Many daily newspapers on paper medium created a version on
electronic medium.
This second assumption states that the electronic version will
compete with the version paper of the current daily newspapers.
1 . Compete with or complementarity
1.1 Beginnings of the press on line
The beginnings of the press on line go up to 1992 in the
United States; in France, it is necessary to wait until 1995. The first
experiment of setting on line was made by Chicago Tribune at the
beginning of the year 1992. But the daily newspaper which has the appearance of
an academic case is Mercury News, created in May 1993 by a daily
newspaper of Silicon Valley, San Jose Mercury News. Its fast success
is to be put in relation to the quite particular characteristics of the
Californian valley: more than 60% of the hearths have a computer and the
economic and cultural life is centered on research and new technologies.
The example of Release. At the
beginning of the year 1995, Libération14(*) launches a weekly
supplement devoted to multi-media (appearing Friday). Noting the success of
these pages, the direction of the daily newspaper decides to put the
multi-media book on line. Since, the contents of the site largely developed:
headings especially designed for the electronic version, rich iconography,
paying files of the newspaper.
Thereafter of many regional daily newspapers or nationals
launched out in adventure Internet like the South-western daily newspaper,
Western France, the World....
According to a study of Benchmark Group15(*) of April 2001, out of 3400
titles of French press, more than one third's is from now on present on
Internet.
The debate on the future of the traditional newspaper industry
currently oscillates between happy optimism and apocalyptic vision. Some
prophesy the death of the newspapers and even that of the journalists, while
others refuse to intend to speak about the numerical support and the
consequences which rise from its use.
Before trying to examine the changes, the constraints and
the assets which represent the emergence of the new interactive support, a
remark is essential: in the history of the communication, never an innovation
did not make disappear technologies which preexisted to him. Only the modes and
the instruments of production changed. Thus, the arrival of the radio and
television influenced becoming to it newspaper industry, but this one therefore
did not disappear.
It is one of the first questions which comes to mind, namely
the consequences which the press one line can cause with the newspaper
industry.
As opposed to what certain people say, who place Internet
above all, the newspaper industry will have beautiful days still in front of
it. It should be known that per hour when begins the emergence of the press on
line, the written world press consumes it, nearly 53 million tons to paper each
year including more than 2 million for France16(*).
Internet is still a new media which sulfur of a weak rate of
equipment of microcomputers. What involves that only still a minority of the
French population has access to the mother of all networks.
Thus let us make, initially, a first point on the equipment of
the households, which will make it possible to make thereafter a comparison
with the other media. This will enable us to show itself, in the current state,
the place which Internet in the households takes.
1.2 quantify key
Internet :
|
17(*)
|
2nd sorting 2002
|
1st sorting 2002
|
4th sorting 2001
|
3rd sorting 2001
|
2nd sorting 2001
|
|
A number of hearths equipped microcomputer
|
8.894.000
that is to say 36,1%
hearths
|
8.806.000
that is to say 35,7%
hearths
|
8.685.000
that is to say 35,6%
hearths
|
8.680.000
that is to say 35,6%
hearths
|
8.420.000
that is to say 34,5%
hearths
|
|
A number of hearths having access to Internet
|
5.410.000
that is to say 22,0%
hearths
|
5.384.000
that is to say 21,9%
hearths
|
5.196.000
that is to say 21,3%
hearths
|
4.387.000
that is to say 18,0%
hearths
|
4.445.000
that is to say 18,2%
hearths
|
36.1% of the hearths are equipped out of
microcomputers and 22% have access to Internet.
|
2
|
June 2002
|
May 2002
|
April 2002
|
March 2002
|
|
A number of 11 year old individuals and more informant to have
connected itself to Internet during the last month, whatever the place of
connection
|
16.528.000
that is to say 32,5%
of the French
|
16.970.000
that is to say 33,4%
of the French
|
16.591.000
that is to say 32,6%
of the French
|
16.472.000
that is to say 32,4%
of the French
|
There are 32.5% of the population which at
least once states to have been connected in the month.
ACCOUNTS Of ACCESS A Internet OPENED BY the
MEMBERS Of the AFA18(*)
|
19(*)
|
Individual subscriptions
(paying or credits at 40 days/particular and professional)
|
Hours of connections
(Commutated Telephone Network)
|
|
March 2002
|
7 725 000
including 734 500 accesses high flow
|
80.895.000
|
|
December 2001
|
6 986 500
including 601.500 access high flow
|
73.640.000
|
|
Sept. 2001
|
6.318.000
including 420.000 access high flow
|
69.072.000
|
|
June 2001
|
6.177.000
including 351.000 access high flow
|
67.558.000
|
|
March 2001
|
5.968.000
|
71.393.000
|
|
December 2000
|
5.263.000
|
54.600.000
|
|
September 2000
|
4.590.000
|
40.007.000
|
|
July 2000
|
4.281.000
|
33.786.000
|
|
April 2000
|
4.105.000
|
34.811.800
|
|
January 2000
|
3.030.000
|
25.265.000
|
|
October 1999
|
1.925.000
|
17.025.000
|
|
July 1999
|
1.642.000
|
14.050.000
|
|
April 1999
|
1.500.000
|
12.930.000
|
|
January 1999
|
1.280.000
|
11.200.000
|
|
October 1998
|
960.000
|
8.000.000
|
|
July 1998
|
802.000
|
6.140.000
|
|
April 1998
|
697.000
|
5.200.000
|
|
January 1998
|
540.000
|
4.000.000
|
|
September 1997
|
400.000
|
3.000.000
|
|
September 1996
|
150.000
|
600.000
|
7.725 00 subscriptions opened by the members
of the AFA.
In these tables one can thus realize that it there A 22 %
is 5.410.000 of hearths having access to Internet and that there was an
increase of 4% in one year.
In addition one can compare this figure with the rate of
equipment of two other media.
Television :
Histogram20(*) Ci below shows us that there is 93% of the hearths
which are equipped with a television.
|
RATE Of AUDIO-VISUAL EQUIPMENT OF the HEARTHS BETWEEN
1981 AND 2001
|
|
The radio :
Equipment by hearth of six stations on average.
For the press one cannot speak about equipment since everyone
is supposed capacity to buy a daily newspaper. Nevertheless, there is according
to media pocket, approximately 42% of the French population which read
at least a daily newspaper. These figures already reveal an essential point,
Internet is a media which, compared with the others, still has a weak rate of
penetration in the hearths.
Internet is still a new media but it should be specified that
it is in constant evolution, it is enough to see the number of subscribers with
the AFA to realize that one passed from 150.000 subscribers in 1996 to
7.725.000 in 2002.
One needed forty year so that the radio reaches an audience of
50 million and close to about fifteen for television, Internet is to 7 million
in 5 years.
1.3 Different assistantships
Not more than the radio and television did not put at the
rammer the press and the edition, Internet will not supplant the printed
newspapers.
It is on the contrary a means for the newspaper industry to
diversify and meet new needs.
In a first point, the editions on line of the newspapers often
make it possible to touch readers who do not read the edition paper.
For example, in the case of the daily newspaper the
Echoes21(*),
60%22(*) of the readers do
not read the edition paper. In the same way, nearly two thirds of the
subscribers of Wall Street Journal23(*) interactive are not subscribed with the
traditional newspaper.
It should be known that one of the dramas of the newspaper
industry is in the little of interest which the younger generations carry to
him. The more so as the reading of a daily newspaper concerns a practice which
is learned very early in the life, if not it is only acquired very with
difficulty. The Net surfers are precisely younger than the traditional reader.
It is a new unhoped-for public for the daily newspapers too often reserved for
« dad ». The Web must be able to federate these two
generations, in their proposer more credible and gravitational information.
It even announces that the young French Net surfers, the 15-34
years, are those which most frequently go in a newspaper kiosk to buy a
magazine or a daily newspaper. It is what reveals a made study public end 1999
by bva/diffusion controls24(*). Surfer on information would incite them finally
more, that theirs
elder, to divide into sheets the newspapers before buying
them. More half of the Net surfers are subscribed with newspapers whereas the
others are only only one third.
1.4 Convergence of the two supports
Indeed the press on the fabric will allow the newspaper
industry to diversify by touching a new public while meeting another need for
its usual assistantship.
The press on the fabric will come complémentariser the
printed newspaper industry and one can already give certain great advantages
which give this new complementarity.
Modernity. The arrival on the fabric of the
newspaper industry confers a new image of modernity to him which was the
prerogative of television before and, to a lesser extent, of the radio. It
becomes possible to associate with the writing, to make it more reactive
gravitational, of the sound and the images.
Valorization of the data base. The services
in line of many newspapers place at the disposal of the reader part of their
files. Research is facilitated by a classification set of themes and the use of
search engines. The setting on line also makes it possible to develop the data
base of the newspapers by the access to the data bases developed by the
services of documented and the journalists.
Depth of information. Thanks to the
hyperlinks, information acquires a new dimension, a new depth. One connects the
article to complementary documents such as geographical charts, biographical
notes, official texts, information of an economic nature, cultural, former
articles... The journalist can also place at the disposal of the reader part of
his sources, in order to support what it advances. The newspaper industry is
freed, in some kinds, of the constraints space time and can hope to increase
its credit near the readers. The arrival on the Fabric of the newspaper
industry widens the contents of information offered: the Web sites of the
newspapers are from now on capable to propose at the same time, like specifies
it Domenica Wolton25(*), of «information event» and
«information knowledge». One also finds, on the sites of the
newspapers, «information service» and «information
leisure», which can sometimes pose a problem of confusion between what
concerns the practice of the journalism and that of the trade.
1.5 interactivity :
The interactivity
between the journalist and his reader was not born with Internet since, since
the invention of the transmitter, letters to the Editor and receiver dialog.
But Internet gives a new broadth to the interactivity, transforms the
relationship between the journalist and his reader. Thanks to the electronic
mail, the reader can react on an article, request precise details from his
author.
by-there same, the Community function of the newspaper (and
fidelity for the publication) are reinforced, as the multiplication testifies
some to the forums of discussions on the Web sites of the newspapers. The
discussion relates to topics launched by the newspaper or even by the
readers. The fact that the reader is increasingly critical, and especially that
it lays out from now on means of announcing his reaction, obliges the mediator
to seek a greater reliability, to show larger serious.
An example of interactivity on Aftonbladet Online26(*): Dag Kättsröm,
journalist Internet with the Swedish daily newspaper, went to Japan to cover
the Olympic Games with Nagano in December 1997. Beyond the images, sound and
video, its intervention as a multi-media journalist consisted in reaching daily
Internet thanks to its portable computer and animating forums of discussion
(cats) by calling on various sporting champions present over there. The Net
surfers could directly put questions with the sportsmen.
1.6 Personalization of the offer
The almost paradoxical force of the Internet is to
address themselves, like any mass media could not do it so far, with the
greatest number, but also to be able to hold the attention of public targeted
well to offer specific or personalized information to them. The press one line
can thus combine maximum audience and microphone-assistantships. Internet marks
the advent of « one to one ». This new practice
arrival of direct marketing could make followers in the
editors tempted to deliver on line a single edition for each reader, according
to his needs.
With the practice personalized of
« push », the telenetspectator was born.
Nevertheless, the practice of the push, in particular
starting from the mailing lists, can be a restriction on the freedom of the Net
surfer to reach the contents of its choice when it is used without its
preliminary assent. This warning was formulated by the higher council of
audio-visual which considered nevertheless this technique as a progress since
it is implemented with the assent of the Net surfer.
For example, the second French economic daily
newspaper, the platform27(*),
proposes an annual subscription of 185 euros which includes/understands in
particular the possibility of building its own newspaper personalized according
to its favorite headings, its preferred topics and the required names of the
companies. Without forgetting the automatic reception in
« push » of its « newsletters » daily
and to be able to manage its stock exchange wallet remotely.
The newspapers on line can also find in the realization
and the periodic sending of electronic letters a means of alerting, of
fidéliser and of informing the Net surfer on the evolutionary contents
of their site. Many newspapers on line also propose, in order to facilitate the
spot of the Net surfer, to send every morning all or a large part of the
edition one line. The Net surfer does not need even more to go on the site to
have the daily newspaper.
1.7 Analyze assumption
This second assumption is not checked either ; in the
sense that the answer shows that Internet is a new media complementary to the
newspaper industry and that it offers new possibilities to that Ci. All the
assets previously were seen that offer this new media to the daily
newspapers.
For that the newspaper industry should not be confined to
reproduce on the Net exactly the printed version. It must turn to a new form to
deliver its information.
One thus will turn with this new media to a new form of
journalism but the question which comes us is to know if the information
transmitted by these journalists on the Web remains as credible as the
traditional newspaper industry.
2. The function of journalist is it credible on
Internet ?
This third assumption emits that the journalistic information
transmitted on Internet is less credible than the information transmitted by
the traditional newspaper industry.
In the world of the
press on line, the journalistic function loses its traditional reference marks.
If the majority of the big national dailies launched out on the network, none
delivers an identical counterpart of the edition paper. As one saw previously
it is preferable for them contrary to offering to the reader differentiated
contents, nouveau riche thanks to the resources which the new support offers.
Article, the journalist must pass to the multi-media treatment of the
subject: linear structure, it passes to the star structure, its style
approaches orality, the subjects are given in context and especially, the
journalist loses the monopoly which it held on the access to the sources of
information and consequently the monopoly of their diffusion.
2.1 The demonopolisation of information
The journalist
loses his privileges. The access as the diffusion of information is
democratized and opened to all at lower cost on the network. And that
constitutes one of the major challenges for the profession. The
demonopolisation information is the direct consequence of the capacity of
the World Wide Web. The Fabric indeed gives access to all kinds of data, coming
from the origins most various and accessible by one clicks of mouse to
everyone. And it is precisely this logic of diffusion of overall information
which calls in question certain of the traditional attributes of the
journalist. Initially, it loses its monopoly of access to the official sources
of information which are the news services. In the second place, the diffusion
of information can from now on be done without the driving belt that are the
journalists: no matter who has the right to put on line an informative site
proclaiming itself, and each actor of the topicality (political, economic,
trade-union, cultural...) can diffuse directly and with a great facility
information relating to it or related to its sphere of activity.
2.2 Free access to the sources
Internet put an end in a final
way with what was often perceived like an unjustified privilege: the monopoly
of the journalists on the access to the dispatches of the official news
services. Traditionally, in the newspaper industry, the draftings followed hour
per hour the important events which proceeded throughout the world thanks to
wire of press of the great agencies like AFP28(*). For a long time, the journalists benefitted from
this advantage which enabled them to limit the competition of information
within the bodies of press. Thus, the private individuals not having access to
these sources of information, only the media, juridically recognized like
bodies of press, were entitled and materially able to disseminate information.
The mother of all networks calls all that into question by placing at the
disposal of the Net surfers the entirety of the information distributed by the
news services. Everyone can from now on reach as well as a journalist these
essential sources of information.
2.3 Diffusion of information
With this demonopolisation
of the access to the sources the demonopolisation of the diffusion of
information is added. Insofar as the access to the sources of information is
opened to all, it is not materially any more necessary to be juridically
recognized as journalist to disseminate information. Which need would there be
to enter a profession which lost its privileges? The creation of a webzine is
free and not very expensive. Whoever can car proclaim cyber-journalist.
Moreover, thanks to the low cost which the creation of a Web site supposes, the
majority of the actors of the political, economic, social events... can from
now on disseminate and exchange directly their original information without
necessarily passing by the driving belt of the press and the subjective filter
of the journalists.
Thus, the majority of the administrative institutions obtained
a Web site for better answering the questions and requests of the French. In
the same way, the political companies or parties have all their site in order
to be able to communicate directly with the voter or the consumer. What is also
interesting, it is to note that in addition to these sites related to permanent
institutions, very many sites are created from day to day, according to the
topicality, to react, express opinions or to bring further information on the
events. The actors of the topicality find on Internet the advisability of
being able to easily express a right of reply to the rumors or opinions
revealed on their subject.
Thus,
Internet gives access to the world up to now prohibited of the press releases,
the dispatches, the legislations, the administrative reports/ratios and makes
it possible each one to play journalist. However, the possibility open to all
to proclaim journalist raises many difficulties. In addition to being a
formidable source of information, the network can also be a dangerous tool of
misinformation.
2.4 Loss of credibility
The superabundance
and the absence of control of information are likely to make Fabric a kind of
Pandora's box. The network conveys, indeed, a very great number of infos or
propaganda, rumors of not checked what leads certain observers to think that
Internet would be perverse media even dangerous bus demolishes of any control
and without unified deontology. One can give for example to mention Drudge
Report29(*) like the
prototype of the revealing site of the information based on rumors; this type
of address, which multiplied since the business Monica Lewinski, is
absolutely condemnable even if it is recognized as a rule of the game that all
information is not true (Drudge acknowledges that 20% of its information are
false). Indeed, these reporters car-proclaimed offers to the readers a mixture
of infos and intox that nothing makes it possible to separate. They thus take
the responsability to carry unduly reached to the dignity of people mediatized
by sowing the doubt in the spirit of the reader. And this doubt is all the more
accentuated because of credibility which Matt Drudge acquired by starting
Monicagate.
The Salinger business also constitutes an example of
misinformation caused by Internet. Salinger, former Secretary of State of
Kennedy, had, on the faith of a document circulating on the network, alleged
that the plane of the TWA which had been crushed close to New York in July
1996, had been descended by a missile from the American army.
Another danger lies in the falsification of documents
facilitated by the immense technological possibilities which digitalization
offers. It becomes easy truly to handle information, to create false events
with photographs, films or bands audio with the support. The network can
let pass a considerable quantity of matter sectarian, heinous, terrorist
receipts, pornographic images, plots, ideas revisionists...
Very easy control out of newspaper industry remains mainly
ineffective on the Web.
Lastly, information can sometimes be narrowly mixed with the
electronic trade with the risk with a confusion with the kinds. Indeed, the
newspapers on line, for the majority available free, seek means of becoming
profitable and the practice of the electronic trade commissioned in is one. The
newspapers on line can make from the agreements with commercial sites and
propose with their readers to become purchasers. The idea which raises
difficulty is to propose for example, at the end of a critical article on a
book or a disc, to acquire it by simple clicks (and a number of blue chart).
The correspondence between the information and the proposal for a purchase,
source of income for the newspaper, raises obviously the question of the
credibility and the independence of information. One can wonder whether a
journalist is not tempted to be obliging, if its intentions are likely to
increase the profits of its company, or if the subjects are not likely to
be selected according to their capacity to make sell.
2.5 Or hyper-credibility.
Against these
various kinds of attack to the credibility of the information disseminated on
the network, this last has capacities of resistance. Initially, it allows an
instantaneous response any attack based on the misinformation. The false noises
can be thwarted by sites being registered into false against a rumor and this
all the more easily as they would have to them-even in addition a stronger
legitimacy. It is probable that a nonfounded rumor launched by Matt Drudge
would be quickly decredibilized if Washington Post30(*) contradicted it. In
addition, the network offers a new capacity to the reader to check all the
assertions. One of the guarantees of the veracity of information is in their
handing-over in context, by the means of the bonds hypertexts. The articles on
line often provide the addresses of their sources and leave to the reader the
leisure go up with rough information. Credibility is very often measured with
the degree of transparency of the sources of information.
The direct access since the article to the press releases, the
dispatches and other documents original can only provide one increased
credibility, even compared to the traditional newspapers. The article on line
from now on is accompanied by historical files, or a great diversity of texts
produced on the subject.
Lastly, Internet makes it possible to mix information
resulting from the daily newspapers, the radios, the chains television, the
news services and puts thus fine at unicity sources. As for the traditional
press, the journalist on line, to be credible must prove reliable. The big
national dailies paper which have creates an edition on line offer to the
latter all the credibility of their name.
It is logical that the image of credibility reaches on the
written support continues on support Internet. The question of the credibility
of information basically returns to the social mission of the journalist who
consists in weighing, to measure, to interpret the various sources. The
abundance of the data available on the Net does nothing but point out the need
for the function of mediator of the journalist.
2.6 Analyze assumption
Indeed by this analysis, this assumption tends to be checked
even if it were seen that the network offers possibilities of
crédibiliser all the same this information.
Indeed the credibility of information is touched by nature of
this media. This gigantic data source accessible to everyone, that is there to
diffuse or y to take information, involves a fall of the veracity of this
information.
3. Of the journalist to the
cyber-journalist
This fourth put forth assumption states that the trade of
cyber-journalist is a profession with whole share.
I.e. that it is a profession which requires a formation and an
experiment to exert it.
It is not enough to be a very good journalist on paper medium
for also being a very good journalist on numerical support.
3.1 A strong deontology
Not only the journalist
does not have any right immanent with the monopoly of information, but it
should not fear that the public has from now on access to rough sources of
information without passing by them. Quite to the contrary, the quasi unlimited
number of information available on the Web and the difficulty in evaluating
their credibility make more necessary than ever the function of mediator whom
the journalist must play. This last must thus bring beneficiation on
information available on line. And that does not seem possible that within a
precise framework deontologic.
The superabundance
of information available thanks to the Web makes crucial the function of
journalist. We saw it, the infos on Internet are various qualities. And on a
subject which the reader knows little about, it will have the invaluable need
for a mediator to ensure the sorting of the data, the validation of the
sources, the handing-over in prospect for the events... The journalists must
take up the essential duty of critic of the cyberspace so that it is not about
an immense hold-all, in which to seek credible information would amount
searching for a needle in a haystack.
To distinguish truth from the forgery, to thwart a intox or a
misinformation of propaganda are an extremely difficult work and which proves
to be of a great utility in a space where control is weak. Internet is a
privileged place of the freedom of expression and it is advisable not to
confuse the expression of an opinion with rough information. Among the thousand
trades of the communication which find a ground favourable with their function
on the Web, the journalist must assume the responsibility to keep a critical
eye on the unit of their diffusion and must for that process the data with more
care and more rigor.
Thus, the added value that the journalist brings to
information becomes very invaluable in this new context. The need for an
intelligent sorting is done more pressing in this rain of information. Many
search engines take up already a duty of sorting based on criteria given by the
Net surfer. That makes it possible to be made quickly deliver a great number of
documents on a selected subject. However, in good data-processing machine, the
search engine is not capable to distinguish truth from the forgery and to make
a qualitative selection of the data. It thus falls to the journalist
qualitatively to classify information and to present it purified. In this
manner, information will be able to have various qualities.
And so today, the weakness of the request, the principle of
the exemption from payment of the Net in general prevents the newspapers in
line from being paying, it seems that short-term the added value of information
becomes expensive. Internet is likely to become a class media.
The quality of information will have its price. Those which will be
able to pay will have access to sorted information and handing-over in
prospect; the others will be delivered to their own understanding in the jungle
of common information. Already, of the sites like the platform31(*), the echoes32(*) or Wall Street
newspaper33(*)
propose information
financial and economic expensive.
It is the same with the general topicality with for
example the world34(*) which sells part of its contents.
At all events, the journalist must for the moment to distinguish
his information from the freedom of expression of all one each one.
3.2 The writing on the Web

The writing on the Web as the newspaper industry has its own
rules which one can already release the relationships with the traditional
media.
The Web is close to the newspaper industry from its method of
production: put on page, creation and renewal of the one are as many stages as
one finds in the newspaper industry. In the same way, with the hypertextuality,
one can be satisfied to read the first level of information. As on paper one
reads the title, the hat and the first paragraphs.
As regards writing, the style has many common points with the
radio. Short sentences, short texts, simple syntaxes seem to be the criteria
most adapted to facilitate the reading on the Net, and thus on screen. The text
on the Web must be percussion than the text on paper. One would approach rather
the standard of approaches, «in short and complete» writing, «a
sentence, an idea».
Nevertheless, the great innovation which these media bring to
us is the hypertextuality.
Indeed the length of information is defined by the leading
team, namely that for example a daily newspaper as South-western35(*) will prefer to decrease
the general topicality in order not to give all the infos that there is in the
version paper on the other hand she will give more information on other
subjects which will be in the additional headings (See discussion with Frederic
Saller with the third part of this memory).
At all events the hypertextuality makes it to the journalists
many possible in order to disseminate their information.
Indeed thanks to the multiple bonds hypertexts, the article of
a journalist can become to some extent it « capsule »
allowing to penetrate in the multi-media galaxy of information. The article is
not any more one end in itself. On the Web, it becomes a window which
half-opens on the world.
The journalistic techniques induced by Internet allow, for the
first time to be able to restore information in its historical, economic or
geographical context, thanks to the documentary bonds activated of simple
« click ».
The Net surfer thus passes, in a wink, information in a state
of knowledge being reported to it.
3.3 A more tiring reading
The text with the screen is different from the text paper
initially because it is with the screen: luminosity and flutter cause tiredness
and can obstruct the reading.
Moreover, with the screen, there is only one sight partial of
the text. No moment it is possible to have an exact physical representation of
the totality of the text, or then it should be printed to find it on paper
medium.
An effort of memory is sometimes necessary, the return behind is
less obvious and less flexible than on the paper medium (it depends completely
on the navigation envisaged by the author).
For little which one uses the possibilities of animation, the
effects of appearance and disappearance, the multi-media writing is thus much
richer than the writing on paper, but more limited also because of the nature
and the size even of the screen.
Moreover, according to Jakob Nielsen36(*), the reading with the screen
is 25% slower than the reading on paper. From where need for being more
«lenient» with reader Internet and for increasing the concision as
well as the highlighting of the texts on line.
There is according to this same study 79% of the users who fly
over the texts and 16% which read word for word.
It appears clear that the reading with the screen is less
comfortable than a reading on paper especially because of luminosity and of the
size of the screen. One has a greater overall picture when it is on paper
medium.
It is an important point with the brakes of the development of
the numerical press.
The comfort of the reading of a press on paper medium will be
replaceable with much difficulty by the electronic medium.
3.4 A new writing because of a new reading
« attack » and it
« fall » any more the limits of a text do not constitute
what involves that the reading will not necessarily any more be done in a
linear way. « framed »,
« under-papers », and others « angles »
of traditional page-setting leave room to bonds hypertexts returning on other
levels of information.
The mode of reading thus will be modified and it is to the
journalists of the Net to succeed in directing it by the descriptive clear ones
and a setting in intuitive line. Page-setting is not any more from now on in
only one dimension.
It is necessary that the bonds is clear and logical and that
it make it possible to the readers to go towards desired information.
It is not enough to be a pro of data processing to know the
behaviors and the practices of a Net surfer. Therefore the journalist of the
Web must know the universe of the Web well to guide his readers there in the
most intelligent possible way.
Four years ago, according to a study carried out by media
source37(*), the
journalist on Internet complained to be only to transform there the version
written numerically, but one realizes that maintaining the big national dailies
the possibilities of this media included/understood and tend towards new
headings which have original contents. The cyber journalist with his new media
is thus being born.
Jacob Nielsen explains that like the reader of the newspaper
industry, the reader one line generally will start by flying over the page
which it rather has in front of him than to read word for word. It is once it
located what interested it that it will start to read the text attentively.
Consequently the journalist must, still there, to use texts
easy to fly over with the naked eye, thanks to key words used like bonds
hypertexts or then coloured, of the explicit subtitles, and an idea by
paragraph.
In all the cases, and at all events of the leading policy of
the daily newspaper, Internet is a media, which like all the others, request a
clean writing and which moreover, by its technicality makes it possible to look
further into information.
The journalist of the Net must manage intelligently to exploit
the assets which Internet offers to manage to give information which is clear,
alive and complete.
It seems that we are still in the premises of this writing but
it is smelled already that the profession starts to develop in this
direction.
One can realize, from the progressive emergence of the
formations which are being born, that cyber-journalism has certainly, need for
qualities of the journalist of the traditional media, but that it has also need
for other qualities for its new profession.
3.5 Formation
The major part of
the journalists who work on the Web received at the beginning any specific
training for this support. They were trained on the job and are distinguished
from those of their colleagues who do not use yet tool Internet by a taste
often pronounced for microprocessing. The example of the person in charge for
the service Web of West France38(*) is significant: professional experienced and
interested by all that touches with microprocessing and information scientific
and technical, Bernard Boudic (head of department of general information) turns
to the interactive support in 1996.
One can also note academic formations which were set up in
order to give a formal training to those which want to be directed towards this
new trade.
There is for example school JMK of journalism in Sweden which
has since 1996 of a course five months baptized Global Electronic Journalism
(GEJ) and dedicated to the formation with journalism on Internet. The
principal center of formation JMK is located at the University of Stockholm and
form to journalism during three years, with from now on the option to be able
to add one six-month period of formation within the GEJ.
This formation with journalism on Internet consists in
teaching to page-setting with format HTML from newspapers one line while taking
as a starting point the the already existing things on the Web, like with
knowing to seek and find information, while sailing on the Web through
the search engines.
Even if the deontology compared to these new media is not in
the middle of this formation, it will sensitize with the manner of processing
the data.
In Spain, the Pamplona university proposes also to a formation
of journalism one line.
In France, it should be noted that the Higher School of
Journalism of Lille had founded the die «journalism multi-media»
which sought to improve the theoretical and technical training of the senior
journalists or coldly graduates. This formation was supposed to make it
possible to the multi-media journalist to better dialog with the other bodies
of operative trade in the services Web of the newspapers: data processing
specialists, graphic designers... It was also supposed to learn how to him to
adapt its know-how as regards data processing to the supports multimedia. The
contents of the formation were complete: history, economy, right,
ethics media and the multi-media one; concept of programming
data-processing and language HTML and Java script; computer graphics...
This formation was stopped at the end of one year only.
3.6 Analyze assumption
This fourth assumption was checked by theoretical research
carried out.
One impassioned of data processing and Internet cannot be
claimed to be a good journalist on the Web, just like a good journalist of the
newspaper industry cannot come to a conclusion to be a good journalist about
Internet.
This trade on the matter consists in having a formation or to
learn by the experiment as for any other trade.
4.Rentability of the press on electronic medium
We have, since the beginning of this part, shown that the
press on electronic medium came complémentariser with the press on paper
medium, that it made lose credibility with the function of journalist and that
it gave place to a new profession. Now, the fifth assumption is to check if by
its low diffusion and production cost, the electronic version will become more
profitable than that of paper.
The passage to a «means of faster transport»,
entering directly in the consumer and requiring loads of manufacture, quite
less compared with printing works, could only interest the press. Indeed, the
costs of the prepress to the impression and the distribution are costs which
are heavy on behalf of the newspapers.
Thus, one of the major assets of the cyber press is due to the
disappearance of physical manufacture. It is not any more the newspaper which
invests in the diffusion, but the purchaser who must be equipped in material
with reception (micro-computer, modem, subscription). This being besides a
brake for the access to the electronic press.
4.1 Principle of the exemption from payment
It is enough to sail on the majority of the daily newspapers
on the Net to realize that the majority of these newspapers on line gave up
founding a subscription at the entry.
The exemption from payment was essential with Internet because
it was the spirit even university and scientific pioneers to freely share
between them information on the mother of all networks.
Jean Miot in his report/ratio on « effects of new
technologies on the newspaper industry » declares that
« the original tare of Internet is the exemption from
payment ».
One could almost compare that with the radio which, it either,
is not paying to obtain information. The problem it is as one saw at the
beginning of the part, a hearth has on average six radio sets without counting
the cars almost all equipped with a radio inside.
Internet is present to him in only 22% of the hearths.
If the press on line wants to be profitable while remaining
free, it will be needed that it primarily draws its resources from publicity
and thus to interest the advertisers, it must have a strong audience, which
currently, compared to the other media is not the case.
The rate of 10% of the hearths having access to Internet is,
according to the institute of study Jupiter Communications39(*), a minimal threshold from
which the persons in charge marketing estimate that it is worth to invest in
publicity on Internet.
These 10% were exceeded but the price of the stringcourses
remains weak, from the weak audience.
It is already for one of these reasons and as one will see it
later, than many daily newspapers chose the mixed version, i.e., to make pay
part of their newspaper and to leave another free part.
The paying part will be of course of the information which
will have a value added compared to the free part. That can be by better a
hierarchisation, be personalized, more relevant, more difficult to find, more
complete....
For Philippe Jannet, person in charge for the Web site for
« Echoes », the access paying to information on Internet
falls under the direction40(*). «It is logical: one cannot give information.
When information is given, it is that there is a problem on the quality even of
information. Publicity is not sufficient to finance all that. If one wants to
really have products of quality or updated assessments the every day, that is
worth money», estimates it. Apart from «information with added
value», which is paying, the remainder is free. To know: titles and
summaries of all the articles of the Echoes.
4.2 Publicity on the Web.
Emile of Girardin was the founder of the modern press but also
of publicity.
Indeed it is thanks to him and to finance its newspaper that
the first publicity appeared on its daily newspaper it
« press ».
After, with the wire of times, each media which appeared, also
made him publicity since the possibility offered by a media is to touch a broad
part of the population.
Each media, from its nature, will have its own operation for
publicity (radio : spots of 20s, press :advertizing insert...)
whereas it is press on Internet.
To start, Internet makes it possible to the advertisers to
have access on line to plannings of reservation of the newspaper paper and the
Web site, like with the periodic follow-up of the results of their advertizing
countryside.
Indeed tools like « dart » of doubleclik
and « open AD stream » of real media allow and the editor
and the advertiser to know instantaneously the progression of the impact of a
campaign in line, even if it means to adjust the message or to change site in
the course of road.
The advertisers have from now on the right to require
immediate results on their investments Internet, finished the studies post
campaigns, place with « rate of click » recorded by the
stringcourse and calculated compared to the numbers of visitors.
An advertiser thus will calculate with how much returns to him
one clicks and will choose the site or the cost of one clicks is the least
expensive.
This process seems to be well for the advertisers which can
calculate the impact of these campaigns but certain editors are currently
raising a debate against this method.
Their remarks are that this system makes it possible to obtain
receipts only when the Net surfers click on the advertizing stringcourse of the
advertisers which encumber the sites. Applied on television, this concept would
amount paying TF1 only if the televiewers ruaient themselves in the stores of
the advertisers right after the diffusion of their spots.
It should be known that the rate of click average on the
banners of the sites of newspaper industry is lower A 1%41(*).
There is on Internet of the stringcourses placed on the site
but there also exists of other forms of publicity on the Web.
Another form is what one calls it « pop
up », this publicity consists in automatically starting the opening
of a Web page which generally takes the place third of the screen.
There are also them « interstitial » which
are also pages of pub but which them will open in full screen during a short
time before arriving at truths sites required by the Net surfer.
Here how in general information publicity in the press one
functions line.
4.3 E-espionage
Internet makes it possible to the editors to measure the exact
audience their sites with the Net surfer meadows.
It can also analyze the behaviors of readings bonds by bonds
and headings by headings.
This possibility can be seen as a temptation to manage
information according to the objective of audience to be reached, guard should
be taken.
These analyzes also will allow the editor and the advertiser
to be able to target and measure with more performance the advertisements.
For example an organization as doubleclick42(*) will observe the practices of
the million Net surfers and will know their characteristics to place the
advertizing stringcourses of the advertisers at the strategic place for him.
A reader who goes on the site is likely to leave information
on his centers of interests, his needs for information, his leisures, even his
standard of living and his socio-professional category.
These data are often collected without its knowledge and will
make it possible to better target the advertizing or different impacts.
E-espionage is quite present on the World Wide Web.
4.4 The E-mass mailing
Indeed, which did not receive in its letter-box what one calls
of the mailing ? They are letters personalized with standard words.
On Internet occurs the same phenomenon with limp E-mails.
Indeed to subscribe with the newspaper or for other reasons,
the Net surfer will leave its limps E-mail with the editor who will classify it
in a data base.
It is enough for him after, to send an electronic mail, by
proposing for example new methods of subscription and to insert a bond there
towards an advertiser.
Generally the daily newspaper takes all the same the trouble
under the terms of the protection of the private life to give the possibility
more of not belonging to the list of this electronic mass mailing.
Indeed in 1999, New York Times used E-mail of its
subscribers to send to them an electronic mass mailing with the name of its
advertisers.
For the same period Wall Street newspaper43(*) was used of its 400.000
subscribers to sell his data base with advertisers.
Indeed this data base was interesting since it described to
the maximum the characteristics of this public, namely their professions, the
size of the company, stock exchange transactions etc....
If a newspaper can send information personalized to its
subscribers it is that he knows their centers of interests well.
There is also the phenomenon of
« cookies » which being small files sent on the computer of
the Net surfer without it realizes some and which make it possible to see its
traceability on a Web site.
That makes it possible to create data bases on the behavior of
the Net surfers and thus to better target them.
4.5 Press electronic and trades electronic
Indeed the press on Internet with the possibility of making
partnerships with large tradesmen in order to give information on such or such
product and thereafter propose a bond to buy this product .
This new convergence between media and trade, calls at the
same time into question the role of the journalist and that of the reader: the
first is transformed into salesman, with the risk to lose the objectivity which
its work requires, as for the second, it would tend to read his electronic
newspaper as a catalog of sale is divided into sheets.
The World44(*) thus gives the possibility on its site of buying
books in partnership with Alapage. It is not all, still in partnership with the
FNAC it gives the possibility of buying music, DVD, software, plays, places of
spectacles .....
All is thus set up to allow the Net surfer to get information
then to consume, of the same gesture, while supporting before all the
«purchases of impulse». Of course, the site of press receives a
commission on each sale actual with its readers.
Certain groups of press
preferred to avoid that and create other sites which are dedicated exclusively
to commercial purposes as the South-western group which one will treat a little
further.
4.6 Small advertisements
Great source of income for the printed media, the small
advertisements represent between 30 and 50% of the incomes of the
newspapers45(*). However
the interactive possibilities return the advertisements on the Fabric much more
interesting and effective that in the newspapers.
It is indeed much easier to manage small advertisements on the
Fabric than on a printed support, because their renewal and their update can be
done almost immediately. Moreover, the references by bonds hypertexts give to
the reader the possibility of knowing some more than the first text does not
say any: presentation of the company making offers employment, visits in three
dimensions of an apartment on sale.
Moreover small advertisements from now on are not limited any
more to the only perimeter of diffusion of the printed newspaper.
These advantages did not pass unperceived to the eyes of the
editors of press: indeed, to reinforce their offer, six daily newspapers
American (Boston Platform, Chicago Platform, Los Angeles Times, New
York Times, San Jose Mercury News and Washington Post) opened, in
mid-October 1995, a common service on Internet, Career Path, which makes it
possible to consult the whole of classified advertisements published by
the six titles. In this way, the newspaper industry provides to the advertisers
a complete service. The small advertisements published in the written support,
can return to a further information on Internet. Here is a means of
adapting.
It is as to provide as the commercial advertisers will be
directed more and more towards the cyberspace
One can even wonder that if the newspapers are threatened, it
is less as regards readers (people will remain attached to the paper
impression), that side of the advertisers.
The with dimensions one of France, Western France46(*) French daily newspaper
launched its own sites of advertisements like automobile west France47(*) or western France real
estate48(*).
Western south did not let pass this opportunity by creating to
him also its own sites small advertisements.
There are 5 sites of small advertisements for
south-west :
- sudouest-immo.com
- sudouest-auto.com
- sudouest-emploi.com
- kitrouve.com
- reflex camera-immo.com
After having shown the principal means which Internet offered
to be financed, one can give a small current a report on the profitability of
the daily newspapers on line in the world on this date.
4.7 Current State of the profitability of the daily
newspapers on the fabric.
Indeed as one saw before so that a newspaper makes profitable
and makes benefit thanks to publicity, it needs a strong audience what is not
yet the case of Internet.
There is one or two years the daily newspapers thought that
their sites, thanks to the richness which the multi-media one offers, was going
to have a better audience. But the progression is not as strong as it did not
think it, which led the daily newspapers to turn to other measurements.
First large measurement is to make pay part of their contents
but also to lay off employees whom they had taken in the euphoria of a rise to
power of the Internet.
At that time, the audience of the sites did not cease
growing, they had the appearances of gooses that lays the golden eggs. So much
so that the investors who entered in 2000 the capital of Release49(*), like the funds of British
venture capital, were especially enticed by its electronic publishings.
The end of the year 2001 was terrible. Liberation.fr,
created in 1995, lost two thirds of its manpower: there remain 11 paid out of
32. The site of Release collected only 0,5 million advertizing euros
of receipts against the 2,3 million envisaged with the budget. Blow it lost 1,5
million euros... A small result which it is necessary to relativize because of
edition paper which lost, it, more than 7,6 million.
Elsewhere, it is not better: the site of
Parisian50(*)
separated from 10 of its 23 employees. That of the Echoes51(*), ten on 50. As for the site of
the Barber52(*),
decapitated, it preserved only 3 people out of 30.
The other sites resisted a little better, but much of them,
including that of the New Observer, re-examined their budgets and
their ambitions with the fall. Even the tribune.fr53(*), which released from
(small) the profits for the first time in 2001, tightens the belt while waiting
for the recovery. «One was careful. There is a strategic plan and one must
return account every month to our shareholder LVMH54(*)», known as Emmanuel
Cacheux, multi-media director of the economic daily newspaper. Thanks to the
support of its associate, the group Lagardere, the site of the World,
leader of the sector, continues in a good way, with a team of 55 people.
But environment is not any more with serenity. «Two years
ago, it was almost a promotion to go to work on the Web, tells a journalist of
the interactive World. Today one feels threatened55(*) ».
It should be specified that the last results published, at the
moment of the number of subscriptions, reveals 13.000 subscriptions what is far
with the top from the objective envisaged and which makes it possible to
consider an improvement of environment.
The problem does not come only from the audience but also in
the way very disputed of the sale of advertizing spaces while basing itself at
the rate of click on the stringcourses. It is not very carrying.
Thus, in 2000, the Express train carried out 230.000
euros of advertizing receipts on its site against 53 million euros for the
version paper.
The problem also is the exemption from payment and it is also
on that that the editors are reacting.
«After the slap of 2001, the challenge is to find a model
economic. One cannot any more hope to draw 80% from the incomes of
publicity»56(*)
explains Benoît Lucciani, general manager of
Parisien.com57(*),
which develops sponsoring. With each one its receipt: the
Observer58(*)
launched out in the electronic trade with its shop « The object of
the month ». The Express train put on the small
advertisements. The site of the Platform59(*) has escaped with stagnation because a third of its
annual incomes, which largely exceeded the 5 million francs, comes from the
sale from contents to companies, primarily from the banks and insurances.
Already all the sites, or almost, make pay the
consultation of their files. A not very gainful employment, even for «the
World» which asserts 700 in 1.000 sold articles each day.
It is very dangerous for a daily newspaper to pass from the
free whole to the paying whole, it is almost assured collapse.
The World him like other A henceforth part of free
information and another part with paying added value. This part is with five
euros the month what appears reasonable.
The World has just published its results and it
records 13.000 subscriptions. This result is with the top of the discounted
objectives.
The echoes propose a paying part and a subscription
with 299 euros per annum which includes/understands :
· All the Daily newspaper Echoes on line as of 3
hours of the morning
(Paris time).
· The access in 100 articles per month with the choices
extracted the files.
· 10 last editions of the daily newspaper.
While globalisant a little, the International Innovation
group Media carried out last March a new survey on behalf of World
Association off Newspaper. This world study, carried out starting from the
information provided by 429 newspapers, considers the strategy and the
viability of developments Internet in the press. A still fragile viability,
since only 17 % of the questioned newspapers indicate to approach the year
2002 while having a profitable activity Internet. They were 15 % in 2000.
This level of profitability varies according to the geographical
establishment : 39 % of the North-American newspapers indicate today
to be profitable on the Web. This proportion falls to 7% in Europe and 5 %
in South America.
|
The profitability of activities Internet of the press
in 2002
(Innovation source International Media)
|
|
World
|
Europe
|
North America
|
|
Loss
|
58 %
|
71 %
|
35 %
|
|
Balance
|
25 %
|
22 %
|
26 %
|
|
Advantageous
|
17 %
|
7 %
|
39
|
Remain that among the questioned titles, 2002 seem one year
hinge since 25 % of the newspapers at the world level intend to reach
balance on Internet on the current year. This prospect is supported by the rise
in load for the paying services : 46 % of the newspapers admit like
«very probable» or «probable» the launching of premiums
offers from here 2003. According to the study, the margin of progression on the
matter appears high, 84 % of the titles present on the Net drawing their
incomes only from publicity.
|
Types of paying services suggested on Internet sites
newspapers
(Innovation source International Media, 2002)
|
|
.
|
World
|
Europe
|
North America
|
|
Subscriptions
|
20 %
|
19 %
|
20 %
|
|
Services with the chart
|
70 %
|
67 %
|
75 %
|
|
Both
|
10 %
|
14 %
|
5 %
|
In the field of the activity, 48 % of the questioned
newspapers have two sites and more. These levels of audience do not seem
affected by the arrival of services premiums : 68 % of the newspapers
which launched paying offers noted any erosion of their traffic and 14 % a
fall lower than 10 %.
4.8 Analyze assumption
This assumption does not seem to be checked by theoretical
research.
At least in the current state and the close state to come, the
electronic version of the daily newspapers seems, for the majority, to have
evil not to make a loss and the benefit are done very rare.
The problem comes primarily from a lack of audience and
principle of the exemption from payment but one saw that this new media made it
possible good to become profitable if the audience had suddenly climbed
strongly.
It appears clear that the near future is likely to be
difficult for the electronic daily newspapers but in a future a little more
remote !!!
5. Statute of the press on Internet
This sixth and last assumption state that the statute and the
legal rules applicable to the clipboard are similar to those of the press on
Internet.
The advent of this press Web is not long in questioning the
lawyer. Indeed, this new press which uses a support of diffusion new and
complex always easily does not let integrate within the already old framework
of the traditional press.
It is appropriate in this respect very briefly recalling, that
the French press was very early seen framing by the legislator, even if, in
many texts, it is recalled that the press is free in France.
5.1 History of the right of the press
Indeed the press is free in France thanks to the principle of
the freedom of expression which was posed by article 11 of the declaration of
the rights of man and of the citizen of 1789.
It states that « The free communication of the
thoughts and the opinions is one of the most invaluable rights of the man, any
citizen can thus speak, write, print freely safe to answer of the abuse this
freedom in the cases determined by the law ».
Principle stated at the beginning of each law constitutive of
the French Right of the communication and especially of the law of July 29 1881
which marks to it true birth of and the sanction freedom of the press of its
abuses.
The right of the press will evolve/move at the rate/rhythm of
technologies of the communication, and if in 1881, it is question only of
newspaper industry, the law was applied during the century with all the new
inventions such as photography or the radio.
The appearance of television nevertheless will cause the
intervention of the legislator to juridically frame this mode of communication
of mass.
The law of 1982 proclaims that « the
audio-visual communication is free » and puts an end to the monopoly
of the state on television.
Actually, the audio-visual press, while being subject to
certain specific legal rules, reiterated on its account the main part of the
rules of the newspaper industry and the same applies to the press on
Internet.
5.2 The statute of the press on line.
The company of press definite nor is not governed by a
particular statute. No particular obligation is provided as for the legal form
that must cover a company publishing a publication of press, whether it is
published in form paper or electronic form.
With the particular case of the constitution of a limited
liability company, the article L 491 of the code of the companies provides that
the limited liability companies publishing a publication within the meaning of
the article first of the law of August 1 1986 are authorized to limit their
authorized capital to 2000 F. the definition of «mode writes diffusion of
the thought placed at the disposal of the public and appearing with regular
intervals» is not circumscribed with the only publications published on
paper and can extend to the publications published on electronic medium since
they meet these characteristics.
The services of information disseminated on Internet
constitute services of audio-visual communication within the meaning of the law
of September 30, 1986 modified by the law of August 1, 2000, and within those
of the services of communication on line. The communication on line is defined
as a subset of the audio-visual communication which is characterized by the
fact that it is transmitted on individual request.
In order to affirm the principle of freedom prevailing on
the Internet, the law of August 1, 2000 carried out the suppression of the
declaratory formality for the services of communication on line.
On the other hand, the editor of Internet sites must place at
the disposal of the public, his name and his address if it is about an
individual, her denomination and its registered office if it is about a legal
entity, as well as the name of the director of the publication, or if
necessary, that of the person in charge for the drafting within the meaning of
article 93-2 of the law of July 29, 1982 on the audio-visual communication. The
editor must also indicate the corporate name and the address of the person
receiving benefits who is by contract dependant with him for the setting on
line of his Web pages. This last case designates in theory the shelterer.
By exception, the persons or entities, publishing on a purely
nonprofessional basis, can preserve their anonymity by indicating only the
name, the denomination and the address of their shelterer provided this one
received beforehand the identification of the person in charge for the
edition.
Consequently, the shelterer who would be unable or who
would not like to provide the information relating to the editor would be
probably regarded as person in charge if the site were legally reprehensible.
Also the mode of declaration envisaged by the law of July 29
1881 is it reserved with the clipboard. It is the same for the formalities of
deposits (administrative and legal deposit, registration of copyright near the
national Library).
The infringements of press and the particular procedural mode
which sticks to it apply whatever the mode of communication used. These various
infringements aiming at instituting a balance between the freedom of expression
and the protection of the people are likely to be characterized whatever the
support and the means of expression (written, word or image on the public
highway, presses, television...) since there is publication. It is the same for
the penal provisions aiming at the acts of publication and returning to the
particular mode of responsibility in the event of infringements for press
(publication of messages in pornographic matter or violent one (article 227-24
of the penal code), reached with the intimacy of the private life).
All this finds application in the law of July 29, 1881 but one
can henceforth add a rule which poses problem with the arrival of Internet.
This rule is the regulation of the infringements of press.
Indeed, the most particular rule of the violations of the
press laws is, without question, regulation the three months. It is considered
that information is prejudicial only during a very short time.
Thus in a lawsuit of press, the magistrates must seek the date
of the first act of publication, because the infringements of press are
offenses known as instantaneous. It is necessary to know the moment from which
the public had access to the litigious document, moment which gives the
starting point of the three months regulation.
So for the audio-visual emissions, it is the day of the first
diffusion, for monthly magazines and editions of book, the effective day of the
provision of the public.
The problem which was posed for the sites of press on Internet
is to know if the articles are regarded as continuous publications when they
remain available to the public on the site.
Indeed a newspaper is a perishable and furtive matter whereas
Internet, of share its design features, leaves the possibility more easily to
the Net surfer of reading the article a long time after the first
publication.
The violation of the press laws can be regarded as a
continuous publication since the author decided to maintain it on his site and
that the provision with the public remains continuous. The three months
regulation would thus not be applicable to the press on the Net.
It is in any case what declared the decision of the Court of
Appeal of Paris of December 15, 1999 in the Costes business which seemed to
slice the debate. The Court concludes there that the publication on Internet is
a continuous act. Therefore, the term of limitation starts again to run each
day.
This measurement is likely to be a danger to the setting in
memory of the articles on Internet. Indeed if one regards the articles as
continuous publications, a site can constantly be attacked dice the moment that
it keeps in files of the articles !!
Nevertheless, in a recent decision (Cass.crim., January 30,
2001, Annie Rousseau C/A. Benssalem), the Supreme court of appeal confirmed the
application of the term of limitation three months before the date of the
quotation. According to this decision putting an end to the jurisprudential
hesitations, the time starts to run at the day of the first act of publication
and not of that of knowledge by the civil part of the defamatory
remarks.
As, the reasoning of the Supreme court of appeal makes it
possible to conclude as the publication on Internet is not a continuous act.
It is necessary all the same to wonder about a possible
interpretation, under the terms of which the act of publication would be
renewed with each modification or actualization of a site, and would constitute
a new starting point of the regulation, the editor choosing to maintain or not
contents.
Let us see another point now that the press on line from its
new support of diffusion raises. It relates to the assistances with the press
given by the state to facilitate the edition.
This help with the edition must make it possible to help the
diffusion and to preserve the financial independence of the companies of press.
This must help the reader indirectly has to have access to a better diffusion.
Under the assistances to the diffusion appear: preferential
postage rates, assistance with the form of the French press abroad, assistance
with the bearing.
Under them assistances intended to protect financial
independence appear: a reduced rate of VAT of 2,1% on the sales, a special
mode of provisions for investments (article 39 (a) of the General Tax Code),
the exemption of the professional tax, the funds of direct assistances to the
daily newspapers of political and general information, the bottom of
modernization of the daily and comparable press.
Majority of the assistances, direct and indirect, which melt
the economic mode of the press are not applicable to the multi-media press.
The postal assistances and of imposition must be approved to
be applicable by the Joint Committee of the publications and agencies of press
answering the criteria of the articles D 18 and following of the code of the
stations and telecommunications and 72 and 73 of appendix III with the General
Tax Code : to be of general interest as for the diffusion of the thought,
to be marked legal, to appear regularly at least once per quarter, to devote
less two thirds of their surface to publicity, to be the subject of an
effective sale.
In an opinion on 23 June 1959 delivered about a publication of
press diffused by way of telefax, the Council of State specified that it was
advisable to limit the benefit of the economic mode of the press to the
«printed publications, allowing by immediate reading the diffusion of the
thought and not requiring a special equipment». This interpretation was
confirmed by the high jurisdiction in a stop of 23 November 1987 refusing the
extension of the assistance to the telematic press.
Moreover since it
does not obey same the particular constraints of manufacture and distribution,
the press on line is not likely to be given the same aids as the clipboard. The
benefit of the economic mode of the press is justified by the supported
material constraints (manufacture, impression and distribution of the specimens
paper) not supported by the press on line. The absence of loads related to the
production paper (impression, pulling) reduced expenses of realization of the
newspaper with approximately 50% of the costs, to limit those only to the only
costs of collection and drafting of information.
The VAT with 2.1% is not applicable one any more to the sale
of the numerical newspapers as it is it for the sale on paper medium.
The proposals for a tax relief for the newspapers on line
or various products multimedia were not retained in the finance law for
2002.
The deputy RPR Patrice Martin-Lalande did not make a success
of his blow of inch. He had proposed to reduce the taxation for the press in
line with 2.1%.
Definitively adopted by the French National Assembly on
December 19, the budget 2002 does not contain this provision.
The reason of this refusal always remains that the electronic
press is not subjected to same the expenses as the newspaper industry.
The sale of a numerical newspaper thus remains to 20.6%.
Apart from that, the numerical press all the same will be
given certain aids.
Under them assistances of which can profit the electronic
press, must be mentioned the bottom of assistance presses and multi-media.
Several titles also could profit from the bottom of
modernization of the press to contribute to projects of diversification and
numerical development.
5.3 Royalty
The question of the
royalties is not new, insofar as the plundering of works of the spirit did not
await Internet to start. However the network is likely to give a worrying
broadth to him.
Juridically, the royalty is defined as «the prerogative
allotted to the author of a work of the spirit». This prerogative
comprises a right pécunier which is the right to benefit from the work,
and a moral right which is the royalty of a work literary, artistic, or
scientist to reveal it, to fix the conditions of operating of them and to
defend the integrity of it. The respect of the moral right gives to the
journalist a possibility of control, inalienable on the use which is made of
its work. Any use of the latter cannot be made without its prior agreement.
The presence of a work on Internet implies beforehand its
digitalization. However, such an act corresponds not only to one reproduction
of work, but also to its adaptation, because of transformation of analogical
data into binary data. In this respect, the Green Book of the European
Commission on the royalties and the close rights (July 1995) establish that the
digitalization of a work must fall under the empire from the reproduction
right, just as the loading of this one on the main memory of a computer.
The digitalization of a work must thus be authorized
beforehand by the holder of the rights.
The question which interests us primarily is to know if a
journalist who works for the daily newspaper of a newspaper industry will be
able to take advantage of his royalty when the article is transposed on the
numerical support.
Indeed, the editors of press pour readily the contents of
their traditional publications on the Fabric. But when nobody asks for the
agreement of the journalists, lawsuits and negotiations follow one another.
The first lawsuit which was the symbol of the position of
French jurisprudence is the lawsuit of the Last News of Alsace60(*) (DNA).
February 1998, it is a first in the French press: the Court of
Bankruptcy of Strasbourg gives reason to the journalists of the Alsatian daily
newspaper in the conflict which opposed them to their direction on the
remuneration of the articles diffused on Internet61(*).
The daily newspaper of Strasbourg had then diffused free for
two years a Web version of its newspaper paper. For the trade unions which
carried the business in front of justice, the question is to know if the
journalists have rights on their production. Beside a tiny remuneration, they
especially claim to be associated the diffused product. In light: to have a
right of glance.
For the direction, the Web constitutes a mode of diffusion and
not another publication. The returned ordinance will oblige it to re-examine
its copy and to open negotiations. The court judged indeed that
it « journalist limits the transfer of his royalty to a first
publication, and that the reproduction of the work of a professional journalist
in another periodical is subjected to authorization « .
April 9, 1998, the journalists and the direction end up
falling from agreement. The journalists will perceive 8% of the receipts
generated by the paying products and 10% of the clear margin of the free
products with a minimum of 200 F for the permanent ones and 30 F for the
freelance journalists.
This solution will be confirmed in one second business
implying the trust company of the Barber Magazine.
The editor had carried out the telematic publication of his
files and proposed the sending of copies of articles by fax or e-mail...
without the agreement of his journalists. In front of the court, defense again
tried to make admit that « the telematic edition is only one
prolongation of the diffusion of the newspaper «, not requiring
a new agreement of the journalists.
But, April 14, 1999, the Court of Bankruptcy of Paris
concludes in a general way that any reproduction, « on a new
support resulting from recent technology «, namely the Minitel,
Internet, and about CD-ROM, requires not only one new remuneration of the
journalists but, especially, the assent express train of having the
right62(*).
Teaching already bore its fruits since the direction of
the Echoes agreed to negotiate the fate of the articles of its
journalists.
The agreement authorizes the free use of the articles for the
electronic publishing of the day. On the other hand, the journalists will
receive a remuneration for any consultation of the articles fallen into the
paying files. A reasonable solution: it does not compromise the setting on line
of the traditional press.
The World also made to him from the agreements with
its journalists in order to authorize a reproduction of the articles on the
numerical one. These agreements seem to show that the journalists are obviously
not hostile with the publication of their articles on the network but refuse to
be completely put has the variation.
5.4 Chart of journalist
The chart is delivered by the Commission of the indentity card
of the professional journalists (CCIJP)63(*).
This commission is made up with parity of representatives of
the editors of newspapers and trade unionists elected by the journalists, this
commission is charged by the law with delivering a professional chart with the
journalists who can claim there. Because this law, adopted without debate
unanimously of the Parliament in March 1935, gives for the first time a
professional statute to the journalists who were deprived by it.
To deliver the chart, the commission will analyze each file of
the whole of the requests to decide to allot or not the statute of
journalist.
It will be based on a definition which characterizes the
function of journalist.
«The professional journalist is that which has as a
principal, regular and remunerated occupation, the exercise of its profession
in a daily or periodic publication published in France or in a French agency of
information and which draws the main thing from it from the resources necessary
to its existence».
It should be known that one can to have an activity of
journalist without having the chart but the national collective agreement of
prohibited work of the journalists to employ during more than three months of
the professional and comparable journalists who would not be titular or for
which this chart would not have been required.
Since May 22, 1936, date on which joined together the
commission on the first time, the journalists of the newspaper industry can
have by this chart a statute of journalist.
Later, the appearance of the journalists on radio or
television did not prevent the commission from delivering charts to them but
what for the journalists of the multi-media one happenhappens ?
Vis-a-vis the trade and technological developments, the higher
commission of the professional indentity card of the journalists does not
exclude the recognition from an activity of journalist within a multi-media
company of information, although it is not a framework of activity expressly
recognized by the fair labor standards act.
Consequently, the journalists carrying on their activity
within such a company can present a request for delivery of professional chart
attached to the commission. They must then be able to bring the proof of the
principal and regular character of their activity of data
processing.
Indeed, the commission carries out a strict examination of the
journalistic character of the activity of the applicant within sight of a
precise description of the tasks, a list of the covered subjects and services
on which they are offered to the public. It requires moreover that the
applicant be attached to the national collective agreement of work of the
journalists and to the one of his qualifications.
The social status afférant with the quality of
journalist (the allowance for expenses of employment of the journalists and
reduced rates of contributions of social security which had by the companies of
press for employment) finds application.
In short a journalist on Internet can have the chart of press
if it answers has three principal criteria :
1. To work as journalist in an independent structure.
2.
To have for principal mission, that to inform the public.
3. To raise of the
collective agreement of the journalists and to be remunerated like tel.
5.5 Analyze assumption
This assumption was not really checked owing to the fact that
the press on Internet was seen granted some specific legal rules to its
statute.
Indeed, it belongs to a subset of the field of the
audio-visual communication.
The rules, which direct the press on Internet, in general will
find application in the old law of the press of 1881 but it also will have its
own rules which come from its new design features.
It will not have, for example, of preliminary declaration to
make as it will not have either access to assistances which are planned for the
newspaper industry and which will not apply to the electronic press.
It remains it should be noted that there is no fundamental
change between the rules which apply to the newspaper industry and the rules
which apply to Internet.
CONCLUSION SECOND PART
The theoretical checking of these assumptions showed us in a
first point that the electronic version of the daily newspapers was going to
come complémentariser the version paper.
Indeed it makes it many possible to that Ci to develop by
these new media.
Like made the radio and television, Internet is new media
which go complémentariser with the others.
The theoretical checking of these assumptions also proposed
this activity as being a new profession with new professionals and a particular
statute.
With regard to his state in the economic market, one feels
although the electronic press suffers from a lack of audience.
Internet is a media still little used compared to the others
and when it is used is not primarily to go on the sites of press.
The profitability of this electronic press does not cause in
general at present profit.
INTRODUCTION THIRD PART
This part will be primarily devoted to practical research.
There is indeed the report/ratio of a maintenance carried out
near Mr Frederic Saler, journalist multi-media with the electronic daily
newspaper Sudouest.com. 64(*)
With also carried out an investigation near the population of
the South Basin with a sample of 150 people.
This research had several aims.
The first was to present the Western Southern group and its
Sudouest.com. daily newspaper.
In the second place, this research will analyze the behavior
and the attitudes of the population of the South Basin to reach their regional
information.
Lastly, they aim to support our theoretical research in order
to check our assumptions.
III. The regional daily press on Internet.
1. Group South-western
1.1 Presentation of the daily newspaper
Western south was created on August 29, 1944 per
Jacques Lemoine.
That thus made more than one half century that it is
with the service of regional information.
Western south became a powerful group accepting
responsibility for several editions and several media.
More closely let us see certain figures which shows us
the range of this daily newspaper :
second daily newspaper regional (paid
diffusion 2000)65(*)
|
West France
|
767 469
|
Western south
|
336 771
|
|
The Voice of North
|
321 317
|
|
Nice Morning
|
281 284
|
|
Progress
|
267 932
|
|
The Dauphine one Released
|
256 376
|
|
NRCO
|
247 791
|
|
Is Republican
|
210 230
|
|
The Mountain
|
208 170
|
|
The Dispatch of the South
|
206 143
|
|
DNA
|
202 030
|
|
Provence
|
167 689
|
|
The Lorraine Republican
|
167 383
|
|
Free midday
|
160 168
|
1.528.500 confirmed regular readers66(*)
This are the figures of the year 2000 but into 200267(*) the figures did not change
much since the diffusion is with 336.602 specimens and there are 1.031.800
regular readers.
Manpower is of 1136 people including 280 journalists.
It there A 22 editions out of 8 departments and 3 areas, there
are also 31 agencies and offices (including one with bets).
Moreover Southern West is a strong group of press but
S `does not stop there.
Indeed, he is a also editor of books with more than 350 works
published in ten years by the Western Southern editions.
He is also in the middle of the regional advertizing market,
by ensuring the advertizing control of the five daily newspapers of the group,
for sales turnovers of 459.5 MF in 2000.
He is an actor in the audio-visual and electronic media with
radio operator Atlantel which ensures unhooking buildings of Europe 2 out of
eleven cities.
Atlantel image ensures to him the regional correspondences of
TF1 and LCI without forgetting that Southern West has 49% of the shares of TV7
Bordeaux.
Finally and what interests us at most, Atlantel
Multimédia develops and lodges on the Web of the products of editions
(information, services, small advertisements, urban guides) and of the
solutions of electronic trade
Indeed the site sudouest.com68(*) is, as for him, to some extent independent, although
it belongs to the same group.
Let us see the sites that the Western Southern group created
on the Net by having all various objectives.
Sites of the Group:
The Group can be based on an advertizing control dedicated to
Internet (GSO Web Governed).
Apart from the sites of local information, the other sites
have a vocation which is more at commercial purpose.
The system of the small advertisements was treated higher in
this memory.
An important site is the creation of the site viapolis.com in
response to a competition on the local information which was set up on
Internet, them « cityguides ».
The stake, this time, they are information services, the data
bases, the classified advertisements, in short, one of principal goodwill of
the PQR (regional daily press).
« This know-how, other operators can control
them « , notices Denis Ruellan, director of the department
information communication with the IUT of Lannion and lecturer at the
university Rennes 1.
Indeed he says69(*) « It is not difficult to recover the
schedules and the programs of cinema, it is domain public. Any operator who
creates a cityguide will find this information by a collecting system or a
partnership with the advertisers of the corner. »
Young companies quickly included/understood it and it is like
that that Web city was created in 1998 by a twenty year old Lyonese, Alexandre
Dreyfus and who extended his network on several cities of which obviously
Bordeaux.
The PQR reacted thus and launched it also of the cityguides.
It is initially West-France70(*) which set up at the end of 1999
maville.com71(*) with the
principal towns of its zone of influence.
It is then the Telegram of Brest72(*) which joins the
Lorraine republican73(*) to create vivalaville.com. 74(*)
Thus Southern west as created its cityguide to him as it named
viapolis.com. 75(*)
Viapolis.com is already in competition with several cityguides
with knowing :
In all the cases, these sites have a vocation more commercial
than the sites of information such as Sudouest.com the purpose of
which is truly to prolong the daily newspaper on paper medium.
For better including/understanding how Sudouest.com
functions, was carried out a maintenance deprived with Frederic Saler,
multi-media journalist full-time with Sudouest.com.
1.2 Discussion with Frederic To salt
How much people work for the electronic
drafting ?
« There are four people who work for the electronic
drafting :
there are Hubert Barat, journalist, and person in charge for
the electronic publishings of the Western Southern Group.
There are me, Frederic Saler, journalist in TDCI with
SudOuest.com and There are also two other freelance
journalists. »
How and when information must be brought up to date on
the newspaper ?
« From 5h30, all information of the daily newspaper
of the newspaper industry is put has our provision.
It remains us of 5h30 with 9h00 to put them under the format
of the newspaper on Internet. It is also in our duty to bring up to date the
headings which are not present on
version paper.
It is necessary that with 9h00, the site of the newspaper is
ready. »
What arrives you it if information such as the brutal
death of Alain Juppe occurs ? It is possible to rock it of continuation on
the site ?
« Without going until there, it is possible at the
time of a sudden news to immediately found it on the site and therefore
somebody remains all the day in order to follow the news of AFP. »
Is there more information on the printed newspaper or
that of Internet ?
« On the topicality, there is less of information on
the electronic version than on the version paper but one finds other
information on the electronic version thanks to the headings which are designed
exclusively to diversify information.
The objective of the drafting of Western South is of
complémentariser the written support.
One should not in general find on Internet more details on the
articles which are on paper but one must find there a summary and the
possibility of processing other data which are not quoted on the version
paper.
It is not necessary that the numerical version encroaches on
the version paper. »
The electronic version is not likely T it not in the
future to compete with the version paper ?
« Not, because the will of the drafting is well to
implement a complementarity of the two supports.
Moreover the assistantship is sometimes different and it is
thought that there are people, who lived on Bordeaux and who moved, which comes
on our site, because it is easier access for them.
Is what you know the number of visits that there is on
your site and the difference with that of the paper medium ?
« Yes, there are 100.000 visitors per month and one
can say that the most attended hours are between 9 and 10h00 Monday at Friday.
The number of readers for the newspaper industry is marked on the site and
accounts for 1.031.800 000. »
That is it interactivity with your
readers ?
« One answers approximately 40 malls per days that
one receives our readers »
You sometimes happens T it to put audio and video
elements in your site ?
« Yes that arrives to us, but I must say that it is
rather rare. »
Have in your contract a special remuneration for your
royalties ?
« Yes. There is a lump sum as well as a percentage
on the sales of the files but I must say that the sale of these files is not
very lucrative because of a very weak rate of sale. »
What happenhappens profitability of the site of
press ?
« I am not well-informed very, but in any case it is
sure that this site is not made to earn money but primarily to spend about it
the least possible.
It is used as product of call and of complementarisation to
the version paper and is not for the moment in a policy of money
profit. »
1.3 Analyze maintenance in connection with the
assumptions
This maintenance proceeded very well and Mr Saler was very
co-operative.
He comes out from it from this maintenance an adequacy with
the theory evoked previously to check our assumptions.
It is clear that the numerical version of Western South seems
to come complémentariser the version paper.
The fact also, to have with its responsibility of create new
information which is not in the version paper, also makes him a multi-media
journalist with clean creations. On the other hand the aspect of the
classification of the data of the printed newspaper of the day seems to occupy
an important place.
When with profitability, one feels well that the audience is
not yet enough high to speak about large benefit but South-western rather tends
towards a philosophy to lose some the least possible.
The group preferred miser on other sites, which are more with
commercial vocation and to preserve Sudouest.com in order to represent the
image of the daily newspaper.
In spite of the other sites, the Multimédia part does
not seem to be very carrying.
It is already enough to see it by graphics Ci below of the
proportion of the sales turnover even if it is in 2000 and that the multi-media
one evolves/moves quickly. 76(*)
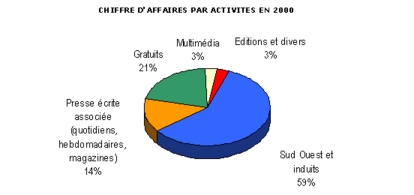
The multi-media category does not include/understand only
Southern Ouest.com but also the whole of the sites of the Western Southern
group.
2. Inquire into the regional daily press
2.1 Methodology of the investigation
The purpose of this investigation is to analyze the behaviors
and the attitudes of the population of the South Basin to go to seek their
regional information.
The questions treat primarily Internet and newspaper industry
like media of regional information.
The purpose of it is also to sit or contradict the theories
which one saw before while transposing it of the state of the general press to
a practical analysis of the regional press.
We took a sample of 150 people to treat this investigation.
These people were questioned in a random way in three communes
to know Gujan-Mestras, Tests it of Buch and Arcachon.
After having designed the questionnaire, I made a test near ten
employees of the town hall of Arcachon without their asking me even the
questions.
The return of this investigation did not appear a success to
me.
Indeed, the press on Internet is not very known and people seemed
not really not to include/understand the put questions and not to answer
objectively.
This questionnaire was thereafter this slightly modified test but
especially the decision to manage this questionnaire in direct relation seemed
to me obligatory.
By managing this questionnaire by direct relation, it was
possible to return it more clearly when it was felt that the interlocutor
butted.
It was managed in a completely random way with share makes it
take care not not to too much question people living of other areas.
2.2 Result
1. Have by an unspecified means access to
Internet?

This first analysis gives us what to reflect.
Indeed according to official figures' presented at the
beginning of this memory which shows us a weak rate of access to Internet, one
sees in these results that 60.6% of the questioned people state by an
unspecified means to have access to Internet.
It is true that this figure shows only the possibility of
access and not the practice of Internet.
To have access to these media included not inevitably regular
practice of that Ci.
Moreover, the possibility of accesses does not include that it
is in the residence as shows it the answers of the following question.
2. At which place do have you access to
Internet?

The residence is the first place which makes it possible to
have access to Internet but one can note all the same that the place of work is
answered has 30.67%.
When with the answer « others » which is
quoted all the same to 7%, it is observed that a certain number of people have
the possibility of going to knowledge to them to connect itself if need be.
3. Is Internet it a means for you of reaching regional
information?

31.3% of the population observed declares that Internet is a
tool for them to reach regional Information.
That is equivalent saying that approximately half of the
people who have access to Internet is used for about it to have regional
information.
There is also the other half for which it is not an access to
regional information.
Let us see which are the reasons thanks to the question
four77(*) :
|
Reasons
|
Nb.cit.
|
Fréq.
|
|
Internet is useful only for research personnel or work.
|
12
|
27.5%
|
|
State not to be to interest has to seek information
regional
|
10
|
25%
|
|
State to rather find it by other media.
|
6
|
15%
|
|
State not of it to think when it is connected.
|
5
|
12.5%
|
|
State not to have time
|
2
|
5%
|
|
Declare that Internet is not easy access
|
2
|
5%
|
|
Total obs.
|
40
|
|
It was gathered in six topics the observations of the
population observed.
The reason first, quoted by the population which declares that
Internet is not an access to regional information, comes from a use for
personal or professional research.
In the second place they state not to be interested by the
search for this information.
There are also those, which say to pass by other media to have
this information, and others which say not to think of going to seek it when
they are connected.
One does not feel in these observations that it is a technical
problem which slows down them but quite simply a will not to want to go to seek
it.
Let us see now by which sites those pass which declare that
Internet gives access to them regional information.
5. By which sites do pass you to reach this regional
information?

One can notice a strong quotation of the observation
« others » with 18%.
In this concept of « others » comprised
primarily the information provided by the gates of the suppliers of access,
such as wanadoo, which is used as regional information provider.
Indeed a Net surfer with the possibility of having this
information on his page of starting of Internet thus it will have more easily
access.
Thereafter with 11.33%, the site more declared is that of a
regional daily newspaper of the traditional newspaper industry.
It strongly dissociates daily newspaper only designed for the
Net or of the cityguides.
Let us change a little direction to make a comparison of the
various media which offer regional information.
6. Preferably classify by order these media of
regional information

There are thus here 69,33% of the population observed, which
did not answer has this question owing to the fact that they do not use
Internet to have access to regional information.
Then, 15,33% on the 30.67% remainders declare that television
is their favorite media to reach regional information.
9.33% for the traditional press and 5.33% for the radio.
There is not that 0.67% are only one person who declares that
Internet is its favorite media to have access to regional information.
This reinforces although the newspaper industry still has
beautiful days in front of it.
7. Which are the advantages for you which offers the
regional daily press on Internet?

The advantage which was quoted the most seems to be the
possibility of sailing between several sites of information.
The second advantage is to have more information, this
advantage is more or less dependant with the first and shows by these
observations that the wealth of information on Internet is a considerable asset
with the eyes of the population.
To also note the exemption from payment which reaches 10%.
8. Disadvantages?

The first quoted disadvantage is the slowness of the opening
of the Web pages.
This disadvantage is likely in the future to grow blurred,
thanks to the high flow which is settling more and more in all our cities.
The second disadvantage is that Internet would not be
comfortable, it is true that the reading with the screen is more tiring than
that of a newspaper.
9. Summers you subscribed (E) or would be you suitable
for subscribe you with a regional daily press on Internet?

On 31.3% of the population observed which answered has this
question, there are 24.6% of them which states not to be suitable for
subscribe.
We thus have just observed the part of the population
which has access to Internet and which reaches by this media regional
Information.
Now let us see those which do not have access to Internet.
10. Do you have for project to equip you in order to
have access to Internet?

Quantify striking, there is 18% out of 39.33% of the
population observed, not having access to Internet, which does not have at all
a project in the future to reach it.
This figure comes on the one hand from those which are against
this tool but also of a large part of the old population which feels exceeded
by this tool.
There is all the same approximately 13% which has a
medium-term project.
11. For which reasons wish to have access to Internet
to you?
|
Reasons
|
Nb.cit.
|
Freq.
|
|
To seek information when the need arises.
|
12
|
35.2%
|
|
To communicate by the instantaneous transport and limp them
E-mail.
|
8
|
23.5%
|
|
Others.
|
6
|
17.6%
|
|
To find topicality on the sites of press.
|
4
|
11.76%
|
|
To download files, vidéos, musics.
|
2
|
5.88%
|
|
For electronic trade.
|
2
|
5.88%
|
|
Total obs.
|
34
|
|
The reason to find topicality on the sites of press reaches
the 11.76%.
It is a percentage which is not negligible and which is placed
at the top of that of the electronic trade.
Now let us see the behavior of the population vis-a-vis the
traditional regional newspaper industry.
12. Regularly read a regional or local daily press
written?

The population observed was almost divided into three.
One could almost say that a third of the population reads the
every day a daily newspaper, another third 2 to 4 times per week and the last
third does not read a daily newspaper at all.
13. Does this information seem to you you it to be
complete?

42% of the population which reads a daily newspaper find it
complete.
On the other hand, 24.6% do not find it complete and it is
thus this part of the population which can be potentially reader of press on
Internet.
The answers of the question 1478(*) answer two
questions :
In a first place, they question the reasons of the population
which does not read a written daily newspaper and the reasons of those which
think that it is not complete.
Let us see initially the reasons of those which do not read
the daily newspapers.
It thus was gathered in seven topics the quoted answers.
|
Reasons
|
Nb.cit.
|
Freq.
|
|
State not to be interested.
|
20
|
30.3%
|
|
Preference for television.
|
18
|
27.2%
|
|
Not time.
|
11
|
16.6%
|
|
Another press.
|
7
|
10.6%
|
|
The price is too expensive.
|
6
|
9.09%
|
|
Preference for the radio.
|
3
|
4.5%
|
|
Preference for Internet.
|
1
|
1.5%
|
|
Total obs.
|
66
|
|
Reason first D `nona reading of the regional newspaper
industry comes according to declarations' from a lack from interest for that
Ci.
In second position the possibility appears of finding this
information by the media of television.
One can note that television is a media which is quoted to
27.2%, the radio with 4.5% whereas Internet is not quoted that at 1.5% is a
person.
Now let us see the reasons which declare that the regional
press is not complete.
The answers were gathered in five topics.
|
Reasons
|
Obs.cit.
|
Freq.
|
|
Not exhaustive
|
19
|
52.7%
|
|
Not objective
|
12
|
33.3%
|
|
New formula of South-west not clear
|
3
|
8.3%
|
|
Too much fixed
|
1
|
2.7%
|
|
Not clearly
|
1
|
2.7%
|
|
Total obs.
|
36
|
|
It thus appears clearly that the first reason is a lack of
contents.
This can be an advantage in favor of the press on Internet in
order to complémentariser as one saw before.
It should be also noted that 33.3% of the population which
declares that the regional press is not complete think that the newspapers are
not objective.
It is a worrying figure for L `image of the press.
The continuation of the results on questions
15,16,17,18,19 are analyzed in appendix79(*) because they are used primarily as data to find
correlations between the answers.
One thus now will try to analyze the correlations of the
answers thanks to the system of the cross sorting.
First of all, we will try to analyze if this investigation
reinforces the theory which the media of Internet are primarily used by a
rather young population.

Between 10 and 25 years, there are 15 people out of 16 who
have access to Internet.
Between 26 and 35 years, there are 38 people out of 55 who
have access to Internet.
In these age brackets, one observes that there are more people
who have access to Internet compared to those which do not have access
there.
Afterwards in sections 36-45 and 46-60, one observes that
there are as many people who have access there than people who do not have
access there.
On the other hand in the section 61 et+, one observes that
there are only 6 people out of 17 who have access to Internet.
There is thus more access to Internet when the population is
young.
The more the age increases and the less it with the
possibility of access to Internet.
After having compared the age compared to the access, we will
compare the socio-professional category with the possibility of access.

There is no difference in proportion of access to Internet
between the category « employee » and that of
« tally ».
Indeed there are 46 employees out of 73 who have access to
Internet either 63% and 19 frameworks out of 31 or 61%.
On the other hand the category which is outstanding is that of
the students to knowing that there is in this population observed 11 students
out of 11 is 100% which have access to Internet.
We now will try to see whether there is a bond between the
people, who think that information is not complete on the written regional
daily press, and those, whom have access to regional information on Internet

One can thus observe that there are 9 people who declare that
information on the press is not complete and who have access to regional
information by Internet.
In lower part there are 11 people who declare that information
is not complete and who do not have access to regional information on
Internet.
One cannot, according to this analysis, statement which the
people, who find the regional press incomplete, have tendency to go to seek it
on Internet.
Another correlation possible to analyze. The purpose of it is
to analyze the age according to the people who go on the sites of a daily
newspaper of the traditional newspaper industry.

One can thus realize in this analysis that category 26-35
years has much more tendency that the other categories of age to going on the
sites of a regional daily newspaper of the traditional newspaper industry.
There are indeed 11 people out of 17 who go on a site of
regional press which has between 26 and 35 years.
That confirms well that the assistantship is younger on
Internet than for the traditional newspaper industry.
2.3 Analyze investigation in connection with the
assumptions
Like it was known as before in this memory, the purpose of
this investigation is to give an outline of the behaviors and attitudes of a
population to reach its regional information.
Nevertheless, the purpose of it was also to look at if this
investigation practices were in adequacy with our theoretical research to check
these assumptions.
- With regard to the assumption where it was seen that
the press on Internet was complementary to that on paper medium and
noncompeting :
It was seen by certain figures, at the beginning of memory,
that the population had a weak rate of access to Internet.
By this investigation, it was analyzed, with surprise, that
there was all the same approximately 60% of the population observed which said
to have access to Internet.
It is necessary all the same to relativize by the fact that to
have access does not include a regular practice.
It is also necessary to learn has to relativize the results of
an investigation which can have a probability of error on the
representativeness.
It was also seen in our theoretical part that the press on
Internet had the possibility of complémentariser information on paper
medium while bringing other elements there on Internet.
Two points to be underlined in this investigation :
A first point which shows that 19 people out of 98 readers of
regional press written think that this information is not exhaustive what can
be in favor with this possible complementarity.
A second point which shows that the population observed
thinking that information on the written daily newspapers is not complete (by
including all the reasons) does not tend to have more access to regional
information on Internet.
In this theory was explained, thereafter, which the press on
Internet could touch an assistantship younger than it cannot by the paper
medium.
One saw in this investigation that a strong majority of the
people which looked at sites of regional press was indeed in a young
section.
- With regard to the assumption or profitability seemed
difficult for the press on Internet :
The study shows us that 17 questioned people out of 150 pass
by a site of press on Internet to go to seek regional information.
It is a honourable figure but which remains an audience weak
and thus not easily carrying profitability.
In the same order, there is only one person who states
Internet like the ideal media to reach regional information.
It is shown in the theoretical part that the press on Internet
tends to go towards contents which will be of with dimensions free and from
another with dimensions paying.
Our investigation shows us that 37 people out of 47 are not
suitable for subscribe with a regional press.
It is thus not a total refusal but the figures are strongly in
favor for nonthe payment on Internet of the press.
- With regard to the assumption on the credibility of
journalism on Internet.
It is shown indeed that information on Internet dimensioned
which goes the décrédibiliser and others which will enable him to
make it credible.
The investigation puts just ahead which the stake is serious
because there are 33.3% of the population declaring that the press is not
complete which thinks that it is owing to the fact that it is not objective.
- With regard to cyber-journalism like a new
trade.
The fact that the investigation shows us that meadows of 23%
of the population observed find that one of the assets of the regional press on
Internet is to be able to sail between several sites of information tends
towards a new writing or the organization of the bonds must clear and be well
ordered.
There is a point important to underline in this investigation,
that it is on the level of the administration of this investigation or these
results, one feels well that a majority of the population observed did not
really integrate Internet in its process of information retrieval and in these
regular activities.
Internet is not yet really integrated in our company in spite
of the social pressure which surrounds it.
This point is to be put in parallel with the theoretical
results of our assumption on Internet and its possible revolution.
CONCLUSION THIRD PART
These studies practice primarily well represented the
theoretical research carried out in the two preceding parts.
They showed well by the discussion with Frederic Saler, the
concept of complementarity of the electronic press.
This maintenance as made it possible to see as Sudouest.com
does not escape the lack from profitability of the press on Internet.
The investigation achieved the role to give us an outline of
the behaviors and attitudes of the population of the South Basin and one
withdraws some that the press on Internet is the media less used to go to seek
this information.
It also by the analysis of the behaviors of a population,
succeeded in on certain points illustrating theoretical research carried out
beforehand.
Other tracks to be explored :
It is difficult to precisely evaluate the nearest evolution of
Internet.
At all events and from the propaganda and the social pressure
which turn around this tool, one can affirm that its use will progress in the
next years.
There are also new techniques which are gradually setting up
itself and which is likely to facilitate and to return more functional
Internet.
One saw in our investigation that the slowness of the opening
of the Web pages is a major disadvantage quoted by the population observed.
It is well also smelled that the newspapers do not place too
much of video in their topicality since the time of remote loading of a video
is a brake with that Ci.
Currently a new technique is set up which will decrease
considerably the slowness of opening of the Web pages.
This technique is called « high flow »
which is carried out that is to say by a system « of ADSL »
is by a cabled network.
This technology installation in the large cities and certain
average cities will multiply by ten the speed of Internet.
It is a system which can help to develop Internet and to make
more pleasant navigation on the Net.
From this fact, it will help the electronic press indirectly,
by partly removing the disadvantage of the slowness of the opening of the Web
pages.
It was also seen that the reading with the screen of computer
did not seem very comfortable and slower.
It was also question in this memory of a weak rate of
equipment out of computer in the hearths compared with the equipment of the
television sets.
It would seem that a new technique is setting up itself and
who would give access Internet from his television set.
The user would be provided with an infra-red keyboard and
could from his television set reach the mother of all networks.
One does not know too where is the evolution of this
technique, that not made a few years that one speaks about it, but nothing is
marketed for the moment, there is thus a problem whose reason is unknown.
Nevertheless, if this product had suddenly developed, one
could wonder about the impact which it would have in the use of Internet by the
population.
There would not need more a computer to connect itself and the
population is already equipped to approximately 90% with television sets.
Comfort will certainly not be that of a printed newspaper but
the population is already accustomed to frequently looking at this screen.
Moreover one television screen is generally larger and returns
less luminosity.
This tool assimilated with the high flow can enable us to
wonder about the future.
Another point, one saw in our theory and in the investigation
which the media of Internet touched a rather young population and which more
the age increased and more the use decreased.
The old people often smell themselves forsaken by this tool,
they say being too old for that and which they will not be able to
include/understand the use even if they tested.
They put only the with dimensions one and say that it is a
tool for the young people.
How much little children left to seek the information for
which need had their large parents who are victims of the i-electronism.
In all the cases, a good part of our new generation learns,
it, to use Internet. Thus although it ages, it is possible, knowing to make use
of it, that it perdure this use.
To with dimensions rising generation will follow and learn.
One could then be in a population where the technophobie old people would have
decreased considerably.
This point can be an asset for the number of users of Internet
and the electronic press.
There is also a completely different point which would be
interesting to treat concerning the characteristics of the press on
Internet.
Internet is a media which makes it possible to give
information to a world scale gold , one realizes that each country has its
own rules concerning the freedom of the press.
The press on Internet is likely to make pass from information
which would be prohibited to be revealed in certain countries.
How the law applies you it in these cases ?
If French gives information in a site conceived in France on
the intrigues of the American government.
Which law will apply ? This is that of France on the
freedom of the press ? or that of the United States, which seems a little
more to censure ?
Internet is for that a formidable asset of freedom of
expression which can traverse the world and deviate certain laws of the
information of each country.
That can also be a danger if there is an abuse this capacity
of expression which characterizes the mother of all networks.
GENERAL CONCLUSION
The problems of this memory are :
E-press : Press in danger or further information ?
Internet offers, indeed from its characteristics and its
assets, of the considerable means to the press to diversify.
Only, that does not do all and presses it on Internet
currently suffers from a considerable problem of audience which harms its
profitability and thus indirectly its development.
If the audience and the interest of the population had
suddenly developed then one would attend a beautiful complementarity between
the two supports.
Currently the other media such as the radio, television and
the newspaper industry are very well inserted in the population to give
journalistic topicality. In spite of the richness which Internet offers, it
remains, all the same, a new media with a weak use.
the slowness of the opening of the Web pages, the tiring
reading has the screen, the difficulties of access to Internet are considerable
obstacles in spite of the assets and the principle of exemption from payment of
this new media.
It is difficult to envisage the evolution which Internet in
the future will have. It is not known too much if it will evolve/move more and
more quickly or then to have a constant evolution.
In all the cases, the richness of this media and the
propaganda which follows it, will still involve an evolution and once the
access will be increasingly available and that the systems of high flows will
be common, then the interest of the population goes can be in majority to turn
to this new media without of course erasing the others.
The day when it will be the case, it appears probable that
electronic journalistic information with strong added value will not be
available any more free.
From this point of view, the press on Internet will have truly
the means of developing and then it will become a further information even
richer for our population.
BIBLIOGRAPHY
Works :
- Breton Philippe ; « The worship of the
Internet », Editions the discovery ; 2000.
- Domenica Wolton ; « Internet and
afterwards ? » ; Flammarion editions ; 2001.
- Charles Laubier ; « The press on
Internet » Editions Which I know ? ; 2000.
- Serge Guerin ;
« Cyberpress » ; Hermès editions, 1996
- Books of journalism
n°5 ; « Journalism and new
technologies » ; 1998.
- « Local newspaper and data-processing
networks » ; Denis Ruellan and Daniel Thierry ; 1998
Memory :
- Bruno Risgallah ; « The legal statute of the
press on Internet » ; D.E.S.S. Author's copyright and artistic
right of communication to the University Bordeaux 4.
Numerical works :
- Charles Laubier ; « The press online in
Europe » ; 1999 ;
www.scd.univ-tours.fr/epress/sommaire.html.
File numerical :
- Laurent Geslin and Olivier Tillered ; « The
local press on Internet » ; IUT of journalism ;
2000 ; http://mapage.noos.fr/lgeslin/pqr/pg/index.htm
- Stephan Arteta ; « Foul weather for the
press on line » ; New observer ; 2002 ;
http://www.nouvelobs.com/articles/p1946/a11757.html.
- « Key figures and topicality
media » ; Newspaper of the Net ; 2002 ;
http://www.journaldunet.com
- « Cybermetry » ; key figures of
Internet by Mediametrie ; http://www.mediametrie.com
- « Key figures of Internet » ;
nielsen-netratings ; www.nielsen-netratings.com
- « Key figures of the media » ;
Media pocket ; 2001-2002 ; http://www.media-poche.com/home.htm
- « Kiosk of press on line » ;
Proxiland ; 2002 ;
http://www.proxiland.com/France/Media/presse/presse.asp.
- « Keys of the room, not
« Net » the press ? » ; Charles de
Laubier ; 2002 ; http://www.tocsin.net/dossier/3_local/index.htm.
- « Group South-western » ; Multi-media
Atlantel ; http://www.gso.enfrance.com/page1.html
- « Journalism and media » ;
Frenchlog ; 2002 ; http://www.frenchlog.org/.
- « Clipboard, press on line: which
statute? » ; Text prepared at the time of the 22nd summer school
of the Communication ; August 2001 ;
http://www.ddm.gouv.fr/presse_ecrite/dossiers_thematiques/pressecrlign.html.
- « Suppression of the declaration preliminary of the
Web sites to the public prosecutor » ; Legalnet ;
http://www.legalis.net/legalnet/.
- Master Thibault Verbiest ; « the
electronic press : which legal framework ? » ;
www.juriscom.net
- Marc Laimé ; « Newspapers vis-a-vis
the competition of Internet » ; The diplomatic world ;
1999 ; www.monde-diplomatique.fr.
- Francoise Quaire ; « The electronic press
with the daily newspaper » ; 2000 ; www.adbs.fr.
- John Kohut ; « Technology and
freedoms » ; Mail of UNESCO ; 2000 ; www.
unesco.org.fr.
- « Journalism and Internet : daily newspapers
with the challenge of journalism on line » ; Research tasks of
the Institute of political studies of Paris ; 1999 ; www.
multimania.com/elisecolette/accueil.htm.
- Pascal Fort ; « Which deontology for
information on line? » ; 2001 ;
http://www.minirezo.net/article506.html.
- Pascal Fort ; « Journalism on line with the
risk of the money » ; 2000 ;
http://www.minirezo.net/article193.html.
- A. Agostini ; « Journalism with the challenge
of Internet » ; The diplomatic World ; 1997 ;
http://www.mondediplomatique.fr/1997/10/AGOSTINI/9299.html.
- « Journalism and the press per hour of
Internet » ; Jlist (various studies on journalism on
Internet) ; http://www.jliste.net/.
- « The charter of electronic publishings « ;
Release ; http://www.liberation.fr/licence/charte.html.
- « Affaire Lang counters Voltaire »,
extracted the report/ratio of the public prosecutor of Paris on January 15,
2001 ; www.reseauvoltaire.net/actu/proces/appel-procureur.htm.
- Lionel Thoumyre ; « Legal tribulations of the
press on Internet » ; Juriscom.net ; 2000 ;
http://www.juriscom.net/int/dpt/dpt21.htm.
- « Schedule business DNA » ;
Juriscom.net ; 1998 ;
http://www.juriscom.net/txt/jurisfr/da/tgistrasbourg19980204.htm.
- « Judgment of the company
Barber » ; juriscom.net ; 1999 ;
http://www.juriscom.net/txt/jurisfr/da/tgiparis19990414.htm.
- «Law n°86-1067 of September 30, 1986 on the law
relating to the freedom of communication » ;
légifrance ;
http://www.legifrance.gouv.fr/texteconsolide/PCEAJ.htm.
- « Conditions of attributions of the chart of
journalist by the Commission of the indentity card of the professional
journalists »; www.ccijp.org
Sites of local daily
newspapers :
http://www.sudouest.com/;
http://www.charente.com/;
http://www.france-ouest.com/;
http://www.alsapresse.com/;
http://www.bretagne-online.com/;
http://www.corsematin.com/;
http://www.courrierdemantes.com/;
http://www.ledauphinelibere.com/;
http://www.ladepeche.com/;
http://www.dna.fr/;
http://www.estrepublicain.fr/;
http://www.le-journal-de-saone-et-loire.fr/;
http://www.lozere-nouvelle.com/;
http://www.midilibre.com/;
http://www.nrpyrenees.com/;
http://www.leprogres.fr/;
http://www.laprovence-presse.fr/;
http://www.republicain-lorrain.fr/;
http://www.lavoixdunord.fr/;
Sites of daily newspapers general
practitioners :
http://www.lefigaro.fr/;
http://www.liberation.fr/;
http://www.lemonde.fr/;
http://www.leparisien.fr/;
http://www.humanite.presse.fr/journal/jour.html;
Economic sites of daily
newspapers :
http://www.lesechos.fr/;
http://www.latribune.fr/;
http://www.agefi.fr/;
http://www.journaldesfinances.com/;



15.Quelle area do you live?
|
Area
|
Obs.cit.
|
Freq.
|
|
Aquitaine
|
133
|
88.6%
|
|
Others
|
17
|
11.3%
|
|
Total obs.
|
150
|
|
As wished, a very strong majority of the population lives in
Aquitaine.
16. Always lived this area ?
|
Area of origin
|
Obs.cit.
|
Freq.
|
|
Always state to have lived this area.
|
91
|
60.6%
|
|
State not not to have always lived this area.
|
59
|
39.3%
|
|
Total obs.
|
150
|
|
60.6% always states to have lived this area against 39.3%.
17. In which age bracket are located you?

The most questioned people have between 26 and 35 years.
18. You are sex?

A questioned majority is against male sex with 60% 40% of
female.
19. Of which socio-professional category are
you?

A majority of employees was questioned.
* 1 Domenica Wolton ;
Internet and afterwards ; ED. Flammarion ; 2000
* 2 Domenica Wolton ;
Internet and afterwards ; ED. Flammarion ; 2000
* 3 Breton Philippe ; The
worship of the Internet ; ED. The discovery ; 2000
* 4 Bill Gates ; The road
of the future ; ED. Robert Laffont ; 1995
* 5 Pierre Levy ; World
philosophy
* 6 Yves Studies ; The
World ; April 28 ; p16-17
* 7 Pascal Bubble ;
Release ; February 25, 2000
* 8 Domenica Wolton ;
Internet and afterwards ; ED. Flammarion ; 2000
* 9 Breton Philippe ; The
worship of the Internet ; ED. The discovery ; 2000
* 10 Jean Paul Fitoussi ;
The new age of the inequalities ; Threshold ; 1996
* 11 This report/ratio is
composed of five different documents, of which that written by Ducan Campbell,
the Scottish journalist who revealed the existence of the system Echelon dice
1998.
* 12 www.cnil.fr
* 13 City in Social sciences
n° 108 ; August-September 2000
* 14
http://www.liberation.fr/
* 15 http://www.benchmark.fr;
Expertise Internet with the service of the companies
* 16 Charles de Laubier ;
« The press on Internet » ; ED. What I know
?; 2000 ; Pages 6
* 17
http://www.mediametrie.com
2 http://www.mediametrie.com
* 18Association of the
Suppliers of Access to Services on line and the Internet
* 19
http://www.mediametrie.com
* 20
http://www.media-poche.com/home.htm
* 21 http://www.lesechos.fr/
* 22 Charles de Laubier ;
« The press on Internet » ; ED. What I know
?; 2000 ; Pages 14
* 23
http://interactive.wsj.com/home.html
* 24 www.bva.fr
* 25 Domenica Wolton ;
Internet and afterwards ; ED. Flammarion ; 2000
* 26This exenple is quoted in
the work of Charles de Laubier ; The press one line in Europe ;
http://www.scd.univ-tours.fr/Epress/sommaire.html; Chapter 3
* 27
http://www.latribune.fr/
* 28 Agence France Presses
* 29
http://www.drudgereport.com/
* 30
http://www.washingtonpost.com/
* 31
http://www.latribune.fr/
* 32 http://www.lesechos.fr/
* 33
http://interactive.wsj.com/home.html
* 34 http://www.lemonde.fr/
* 35 www.sudouest.com
* 36 Author of «
Désigning Web usability : The practice off simplicity
» ; New riders publishing ; 1999; One can see his site with
www.useit.com
* 37
http://www.mediasource.com/
*
38http://www.france-ouest.com/
* 39 European online
advertizing ; by Jupiter communications ; 1998
* 40 Charles de Laubier ;
The press one line in Europe ;
http://www.scd.univ-tours.fr/Epress/sommaire.html; Chapter 9
* 41 Charles de Laubier
; « The press on Internet » ; ED. What I know
?; 2000 ; Pages 92
* 42
http://www.doubleclick.com
* 43
http://interactive.wsj.com/home.html
* 44 http://www.lemonde.fr/
* 45 Charles de Laubier ;
« The press on Internet » ; ED. What I know
?; 2000 ; Pages 96
* 46
http://www.france-ouest.com/
* 47
http://www.ouestfrance-automobile.com
* 48
http://www.ouestfrance-immobilier.com
* 49
http://www.liberation.fr/
* 50
http://www.leparisien.fr/
* 51 http://www.lesechos.fr/
* 52 http://www.lefigaro.fr/
* 53
http://www.latribune.fr/
* 54 speeches quoted by
stephane Arteta ; « Foul weather for the press on
line » ; New observer ; 2002 ;
http://www.nouvelobs.com/articles/p1946/a11757.html.
* 55 Idem with note 1
* 56 Idem with note 1
* 57
http://www.leparisien.fr/
* 58
http://www.nouvelobs.com/
* 59
http://www.latribune.fr/
* 60 http://www.dna.fr/
* 61 « Schedule
business DNA » ; Juriscom.net ; 1998 ;
http://www.juriscom.net/txt/jurisfr/da/tgistrasbourg19980204.htm
* 162 « Judgment
of the company Barber » ; juriscom.net ; 1999 ;
http://www.juriscom.net/txt/jurisfr/da/tgiparis19990414.htm.
* 63 http://www.ccijp.org/
* 64
http://www.sudouest.com/
* 65
http://www.gso.enfrance.com/page1.html; site carried out by multi-media
Atlantel which presents the Western Southern group
* 66
http://www.gso.enfrance.com/page1.html; site carried out by multi-media
Atlantel which presents the Western Southern group
* 67
http://www.sudouest.com/210902/decouvrir.asp
* 68
http://www.sudouest.com/
* 69 Cities in Laurent
Geslin and Olivier Tillered ; « The local press on
Internet » ; IUT of journalism ; 2000.
http://mapage.noos.fr/lgeslin/pqr/pg/index.htm
* 70
http://www.france-ouest.com/
* 71 http://www.maville.com/
* 72
http://www.bretagne-online.com/telegram/index.html
* 73
http://www.republicain-lorrain.fr/
* 74
http://www.vivalaville.com/
* 75 http://www.viapolis.com
* 76
http://www.gso.enfrance.com/; site carried out by multi-media Atlantel which
presents the Western Southern group.
* 77 Even questionnaire in
Appendix 1
* 78 See questionnaire in
Appendix 1
* 79 Even appendix 2
| 


